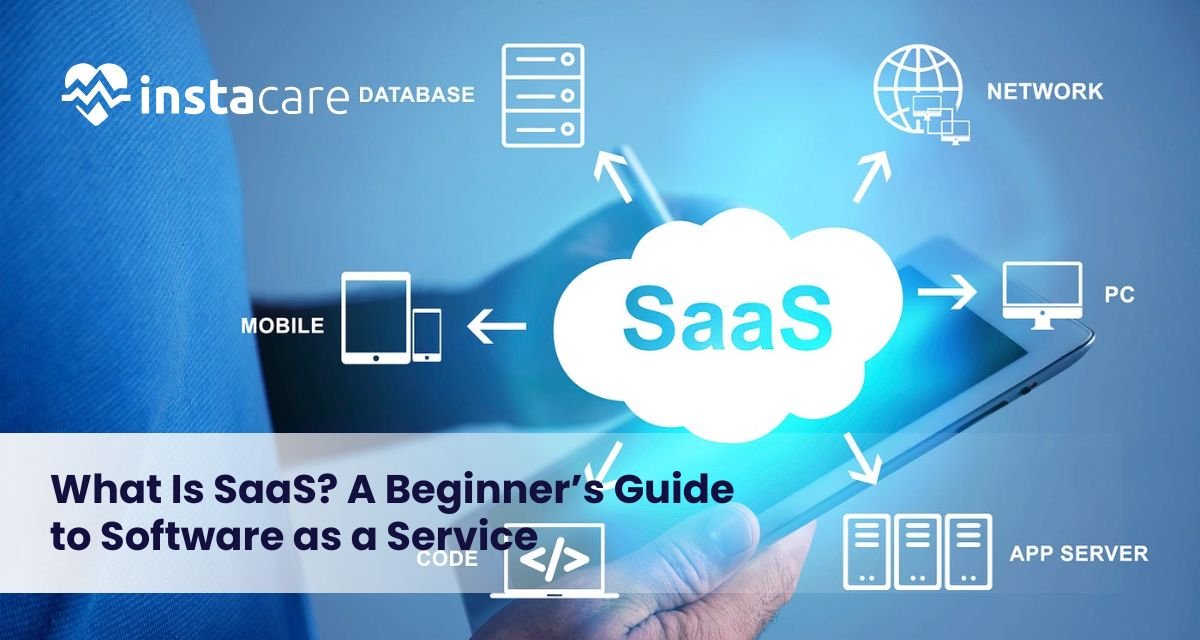
What Is SaaS? A Beginner’s Guide to Software as a Service Ever since the beginning of the age of computers and digital technology, companies and individuals have depended increasingly on software to carry out day-to-day tasks, communicate with each other, keep information stored, and perform processes automatically. Some of the most significant advances in history have been the invention of cloud-based software, that is, Software as a Service (SaaS). Precisely what is SaaS, anyway? How are folks using it, and why is it so globally popular among so many different types of industries? This beginner’s guide contains everything you ever wanted to learn about SaaS from the way it works to its advantages, examples, and problems prior to implementation. What Is SaaS? SaaS meaning is “Software as a Service,” which is an on-demand delivery model for software where a third-party company owns the software and hosts it on the internet to customers. Rather than installing and maintaining software on individual computers or internal servers, customers can access web browser-based SaaS applications on a pay-per-use basis. The SaaS definition can be employed to articulate a wide variety of software solutions, from productivity suites like Google Workspace to customer relationship management (CRM) solutions like Salesforce. Unlike traditional software, which has to be installed physically and updated periodically, SaaS provides perpetual access, ongoing updates, and minimal setup. History of SaaS traces back to the 1960s when mainframe computing rendered sharing of software on use inevitable. The modern SaaS model which started gaining momentum in the course of the late 90s was pioneered by Salesforce through offering web-based software. SaaS has since become a ubiquitous application structure of business establishments of any size implementing software. How Does SaaS Work? To learn about SaaS, consider renting software instead of purchasing it. SaaS applications are stored on the provider’s servers. The provider does all the work: hardware, software updates, security, and infrastructure. Users just log in over the web to access the software. The SaaS model is usually accompanied by recurring fees, annual or monthly. Both the user and producer benefit from the model. Producers get stable revenue, while users avoid front-end expenses and pay when they use. One of the advantages of SaaS includes: Multi-tenancy: Various users share one infrastructure but maintain their data segregated. Automatic updates: Features and fixes are provided without involving users. Accessibility: Individuals can utilize software from anywhere they are accessing the internet. Scalability: Simple to scale up or down usage depending on the requirement. Advantages of SaaS Advantages of SaaS are many and have made it present in nearly every sector. Below are the main advantages: Cost-Efficiency: No hardware or software acquisition cost. There is a subscription fee, which spreads the cost over time. Ease of Use: The majority of SaaS solutions are easy to use and don’t demand technical expertise to become operational. Availability: Clients can access software through any device that is networked, which allows working remotely and communicating. Scalability: The companies are easily able to scale up and down with no concern for infrastructure. Security: The best security features are readily available, including encryption, backup, and compliance certification of the SaaS vendors. Automatic Updates: The security patch and updates are automatically applied. Integration: SaaS applications will typically integrate with other company software to enable process streamlining. There are SaaS pros and cons, but even with those pros. Some of the cons include the absence of control over customization, reliance on internet connections, and vulnerability to data security breaches if left unattended. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Common Use Cases of SaaS SaaS applications today touch nearly all personal and business operations. Below are some of the most utilized SaaS businesses and software: ● Collaboration & Communication Remote work necessities include tools such as Slack, Zoom, and Microsoft Teams. ● Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM are programs that manage company sales pipelines and customer relationships, similar to how Clinic Management Software helps healthcare providers streamline patient interactions, appointments, and administrative workflows. ● Accounting & Finance Easy-to-use bookkeeping software is offered by cloud-based solutions for small and medium-sized businesses, such as QuickBooks or Xero. ● Project Management Asana, Trello, and Monday.com make task management and collaboration with a team extremely simple. ● Marketing Automation ActiveCampaign and Mailchimp make email marketing, email segmentation, and lead nurturing easy. ● E-Commerce Both Shopify and BigCommerce allow businesses to create storefronts online without being experts in web development. ● Human Resources BambooHR and Gusto help in automating Human Resources services, such as onboarding, payroll, and benefits services. ● File Storage & Sharing Google Drive and Dropbox enable one to save business and personal files in the cloud. SaaS in healthcare is fast developing in the niche markets with electronic health record (EHR) systems, telemedicine software, and patient scheduling applications Key Considerations Before Choosing a SaaS Product There are numerous benefits of SaaS, but choosing an appropriate one requires vigilant consideration. The following are key things to consider: Data Security and Privacy: Consider how the SaaS provider approaches data backup, data security, and regulatory compliance (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA.). Pricing Model: Find out how much it will cost in total: subscription fee, fee per extra user, license to watch. Integration Capabilities: Ensure that the SaaS product fits into your existing equipment and infrastructure by not causing too much of a wrench in your operations. Service Level Agreements (SLAs): SLAs have guarantees of uptimes, support response, and support that is important to the mission-critical applications. Scalability: Go with a platform that scales along with your business and has scalable pricing plans. SaaS vs PaaS vs IaaS SaaS is one of the three basic models of the long list of cloud computing. The other three models are PaaS and IaaS models. SaaS (Software as a Service): pre-installed software over the web (e.g., Gmail, Dropbox). PaaS (Platform
Digital Transformation in Healthcare: Opportunities, Technology, and Emerging Trends Healthcare is transforming at light speed by adopting digital technology. Digital transformation of healthcare can be stated as the integration of digital means into medical procedures such that services are offered more efficiently, outcomes are enhanced, and efficiency is optimized. From telemedicine adoption and electronic health records (EHRs) to remote patient monitoring and artificial intelligence diagnosis, the trend is revolutionizing the way healthcare is accessed and delivered. For the vendors of technology, payers, and medical care providers, the transition represents a gigantic opportunity for health tech innovation, save, and enhance care in general. Understanding Digital Transformation in Healthcare Healthcare digital transformation refers to the intelligent application of technology to facilitate all the components of health care service. It is beyond automation of some functions but changing the manner in which health care is rendered in a digitally enabled era. It varies from health tech apps to advanced cloud-based hospital information systems. Some of the most important features of healthcare digitalization are: Healthcare Digitalization: The replacement of paper-based systems with electronic records. Telemedicine Usage: Assisting patients in consulting doctors remotely using either a video or a mobile application. Remote Patient Monitoring: Demonstration of mobile monitoring and wearable sensors to monitor the vital signs of a patient out of the hospital. Healthcare Software Solutions: Implementation of appointment scheduling systems, diagnostics, billing, and so on. Digital Health Technologies: The pillars in constructing smart healthcare ecosystems are AI in healthcare, blockchain, big data analytics, and IoT. The other issues that digital transformation has dealt with are interoperability to allow health data to move freely among systems and security to allow the law to be followed say HIPAA. Benefits of Digital Health Transformation The digital revolution benefits all the players in the healthcare ecosystem. The benefits of digital transformation in healthcare range from operational effectiveness to patient care. Better Clinical Outcomes Accessibility of real-time medical records allows faster and better-informed decisions. Artificial intelligence diagnosis identifies diseases at an earlier stage with better treatment success rates. Predictive analytics facilitates early treatment with fewer hospital admissions. Better Operational Effectiveness Healthcare Automation Tools eliminate manual errors and administrative paperwork. Computerized processes allow for improved staff scheduling, appointment scheduling, and inventory management. Automated systems release healthcare practitioners from paperwork rather than patient care. Enhanced Patient Engagement Patient engagement solutions provide members with access to health records, health information, and communications tools. Mobile health applications provide medication reminders, appointment reminders, and wellness tracking. Engaged patients become empowered consumers of their health care. Reduced Costs There are simplified revenue cycles through electronic billing systems and insurance verification. Remote diagnostics reduce the number of in-office visits, saving resources and time. Preventive care regimens help to reduce the treatment expenses in the long run. Data-Driven Decisions Population health strategies are informed by data analysis tools, which identify patterns in the data about patients. One way predictive analytics can be utilized is to predict the risk of patient decline or readmission. Data analytics help in resource planning and optimization. Accessibility and Reach Use of telemedicine enhances care access to the rural and underserved population. Attractive multi-language, mobile-friendly patient engagement software reduces the language and mobility barriers. Online consultation becomes a solution because it eradicates geographical and logistical barriers in healthcare. Regulatory Compliance and Transparency Electronic Health Records (EHRs) provide accurate, secure, and audit-compliant records. Automated notifications can alert personnel to regulatory violations or protocol deviations. Audit trails and electronic consent promote trust and accountability. Flexibility and Scalability Cloud computing in healthcare enables speed to deploy and scale systems. Healthcare organizations can scale up to varying volumes of patients. New services and applications can be rolled out with minimal disruption. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Key Digital Transformation Technologies Emerging and new technologies are leading the digital transformation of healthcare. Electronic Health Records (EHR) Decentralized electronic health records containing patient history, medications, test results, and imaging. Enhance provider coordination and prevent redundant tests. EHR systems also enable improved management of chronic illness. Telemedicine Platforms Enable real-time consultations, e-prescription, and distant diagnosis. Beneficial in public health crises as well as in the management of chronic illness. Streamlines it and minimizes patient waiting times. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) Smart devices can track the following parameters: heart rate, blood glucose level, and Oxygen saturation. Enhances chronic-condition care and post-operative care. Due to this, it permits prior interventions before actual emergencies can occur. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Healthcare AI supports image analysis, clinical decision making, and a virtual nursing assistant. When performing such daily administrative tasks as billing, transcription, and the processing of claims, automates them. Certain trends in big data can also be discovered by the use of AI, introducing new findings in the medical field. Cloud Computing Offers access to applications and data from any device or location. Lowers infrastructure expense and disaster recovery readiness. Enable collaborative care by sharing data in real time. Blockchain Technology Aids secure, tamper-evident third-party partner and hospital data sharing. Increases trust and transparency for billing and medical records. Lessens clinical trial and pharmaceutical supply chain fraud. Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Medical appliance network with internet capabilities, sharing patient data in real time. Enables early detection of abnormalities and individualized treatment. Enhances quality of care
The Importance of Patient Education in Modern Healthcare Patient education has emerged as an essential component of quality care in the current evidence-based, patient-focused healthcare system. As healthcare systems progress toward value-based indicators of success, patient education has never been more significant. Knowledgeable, well-informed patients intimately familiar with their condition, treatment, and Preventive care through education will most likely be active patients, adhere to physicians’ recommendations, and enjoy better health outcomes. Patient education is also a critical component of enhanced patient-physician communication. It creates trust, enables Informed decision-making in healthcare, and encourages long-term compliance with care plans. To health organizations, it translates to lower rates of hospital readmission, lower operating costs, and higher patient satisfaction scores. What Is Patient Education? Patient education is the process of teaching and informing the patient regarding his disease, treatment, drugs, disease prevention, and life alteration. It is conveyed in a way which can be easily understood, remembered, and implemented by the patient so that he is able to take proper decisions on his own account. Patient education is not merely the distribution of pamphlets. It is an ongoing, interactive process in which health practitioners, nurses, pharmacists, care coordinators, and websites work together to improve health literacy and involve patients. Why Patient Education Matters in the Modern Health Care Setting Increased chronic disease, aging populations, and more complicated treatments pose health care systems worldwide the challenge of providing effective and efficient therapy. At the center of this revolution is patient education. Patient Empowerment in Healthcare: Educated patients become more active and assertive concerning their care. Patient empowerment in healthcare is likely to adhere to treatment regimens and lifestyle changes that are in their best interest to heal. Health Literacy: Limited health literacy is a barrier to enhanced outcomes. Education in simple terms and patient-specific education fills that gap and instills trust. Informed Decision-Making: Patient education enables patients to be informed participants in their own health care decisions, increasing satisfaction and reducing legal liability for the provider. Key Benefits of Good Patient Education 1. Enhanced Health Outcomes Knowledgeable patients are more apt to follow treatment, adhere to medication as directed, and recognize early warning signals of complications. This translates into better disease control and more rapid recovery. 2. Improved Patient Compliance Patient compliance improvement is greatly done when patients know why a treatment is necessary and what steps to take. This is particularly important with chronic disease education. 3. Reduced Readmission Rates Hospitals with effectively established patient education programs have reduced readmission, especially in cardiac rehabilitation, diabetes, and recovery after surgery. 4. Improved Doctor-Patient Communication Patient education improves communication. Patients are listened to and heard, hence improving Communication between doctor and patient as being more personal. 5. Lowered Cost Informed patients use fewer emergency services and are less likely to be readmitted. This reduces the financial strain on healthcare systems and payers. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Methods of Delivering Patient Education Education of Handouts Patient education can take numerous diverse forms, dependent on population, locale, and available resources. Some of the following effective ones, including the Role of doctors in patient education, are: 1. One-on-One Counseling Direct interaction between the provider and the patient is the norm. Individualized counseling, immediate clarification, and reassurance are offered. 2. Group Classes and Workshops Applicable to chronic diseases like diabetes, groups offer a peer-to-peer learning opportunity and interaction with each other. 3. Printed Materials Pamphlets, brochures, and teaching sheets are effective, presented in plain format and supplemented with visual aids. 4. Patient Education with Digital Tools Modern Technology in patient education has transformed Patient engagement strategies. Mobile applications, patient portals, teaching videos, and interactive questionnaires help deliver Personalized health education on demand. 5. Visual Aids and Models Anatomical diagrams, infographics, and models offer simplified definitions of complex medical terms. Challenges of Patient Education Patient education is not free from several challenges despite its benefits: 1. Low Health Literacy The majority of patients are unable to comprehend medical terminology, directions, or even basic health information. Misinterpretation or neglect of directions can be the result. 2. Cultural and Language Barriers Language and cultural variations might interfere with comprehension and education. Materials and approaches must be multilingual and culturally attuned. 3. Inadequate Time for Providers Doctors and nurses are generally under tremendous stress, and therefore, no time can be wasted on proper patient education during consultations. 4. Resistance to Change Patients will deny new facts or resist routine change if medical advice has already changed before. 5. Technological Accessibility Though technology is a great gadget, not all patients are owners of technology or technology-oriented, especially the disadvantaged or elderly patients. Strategies for Effective Patient Education To meet these challenges and deliver good results, healthcare organizations must adopt targeted strategies: 1. Customize the Education Adjust materials and messages to suit the patient’s age, literacy level, ethnicity, and condition. Customized health education is much more effective than delivering generic information. 2. Plain Language Avoid the use of jargon. Use clear, unambiguous language and define terms with illustrative examples. 3. Multimedia Tools Photographs, videos, and interactive resources support learning and make it more enjoyable, especially among low-literacy patients. 4. Involve Healthcare Teams Healthcare workers should be trained in communication and provided with resources that are easier to use. Physicians’ involvement in patient education is paramount, but the entire team needs to be involved. 5. Invite Patient Feedback Ask the patient what they already know, what is confusing them, and what they would like to learn more about. This individualizes the education strategy and establishes trust. 6. Facilitate Learning Repeat and reinforce. Educational messages must be reinforced on more than one visit or through more than one communication channel. 7. Use Technology for Patient Education Use telemedicine platforms, chatbots, and apps to take education outside the clinic. They can give real-time reminders and guidance. Conclusion Patient Management Software plays a crucial role in modern patient education—it’s no longer a luxury in healthcare, but
Know About Marketing Automation in Healthcare Healthcare is evolving at light speed, and patient expectations are rising, with more competition and a need for effective, scalable solutions. Patients today want more personalization, where messages from their healthcare organization happen more in the moment, and the age-old method of handling things manually simply won’t do anymore. This is where healthcare marketing automation comes in handy. This technology of digital innovation allows the automation of marketing activities, simplifies communication, and distributes controlled, focused messages to channels. In this guide, we’ll explore what marketing Automation in Healthcare is, why healthcare providers need it, the key benefits, how to select the right platform, and what the future holds. What is Marketing Automation? Marketing automation refers to using software to manage and automate marketing processes such as email campaigns, Healthcare lead nurturing, social media posting, and customer segmentation. In the field of health care, it goes beyond the conventional marketing, it sustains Automated patient engagement, allows clinics to stay connected with patients by sending out automatic appointment reminders, and offers smooth healthcare CRM automation, and assists long-term patient connections through Patient retention strategies. Here is a real-life experience of health care marketing automation below: Sending specific Personalized healthcare campaigns to patients through SMS or email Creating Marketing workflows in healthcare for defined segments of patients Follow-up no-show or post-consultation by Automated appointment reminders EMR integration with marketing to offer personalized health news and information SMS marketing in the healthcare industry for the campaign of the new service or health program Automation is what provides accuracy and consistency, something handbook effort can never provide on any size that really matters. Why Healthcare Can’t Afford to Ignore Marketing Automation? Here’s why healthcare marketing automation is now a necessity: 1. Patient Expectations are Increasing Patients expect healthcare providers to give them convenient, digital-first experiences. They expect appointment reminders, medication reminders, and health tips to be delivered to their phones or inboxes. Automation enables you to deliver this daily. 2. Operational Efficiency It is reminding every patient individually or by sending out newsletters, taking time, and prone to human mistakes. Automation is releasing your staff from performing such tasks so that they can worry about more important matters like patient care, as technology manages the drudgery. 3. Competitive Differentiation In a busy health care environment, receiving timely and tailored communication puts you ahead of the crowd. Healthcare digital marketing software puts you ahead of the pack, yet employing archaic methods of communication. 4. Lead Nurturing and Retention Most of them visit only once and never appear again, not because of poor care, but simply because they were not followed up on. Health care lead nurturing processes ensure that potential patients are routed to scheduling, and prior patients are followed up on. 5. Compliance and Data Management Health care marketing platforms feature HIPAA-compliant marketing automation capabilities, protecting patient data and providing communications security. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Principal Benefits of Healthcare Marketing Automation 1. Convenient Appointment Scheduling Scheduled appointments by automated reminders cut down on no-shows. The patient is confirmed, rescheduled, and reminded without administrative intervention. 2. Patient-Specific Patient Paths Patient-specific messages automatically sent based on the status, behavior, or preference of the patient are achievable. Reminder for a mammogram or automatically sent newsletter for diabetic patients, maximum satisfaction is achieved from Patient journey automation. 3. Greater Marketing Efficiency With clinic marketing automation, doctors can develop a campaign once and message all media, such as email, SMS, and social media, hence conserving time and enjoying messaging consistency. 4. Data-Driven Decision Making There are click-through analytics, opening, conversion, etc. This enables the real-time adjustments to be achieved, increases engagement, and reflects ROI. 5. Enhanced Integration with Healthcare Systems Most software available today includes marketing systems integration with EMR. It keeps marketing processes in touch with patient records and history, allowing very targeted outreach. 6. Improved Retention Tactics From well wishes on birthdays to reminders for wellness checkups, patient retention tactics keep your hospital or clinic top of mind. Automation prevents any patient from falling through the cracks. 7. Multi-Channel Outreach No matter what health care Email automation for clinics or SMS health care marketing you are using, consistency between the channels is made possible through automation to find your patients wherever they are most engaged. 8. Scalable Growth As your health care business expands, automation also expands. You can reach hundreds or thousands of patients without needing more employees or swamping your existing team. How to Choose the Right Marketing Automation Platform 1. Seek Healthcare-Specific Capabilities Capabilities offered must include appointment reminders and patient education, EMR synchronization, and campaign tracking as an automated capability offered by the solution. 2. HIPAA Compliance You require it. Make sure that the vendor provides encryption in addition to data protection controls, and provides HIPAA and other relevant healthcare regulatory compliance. 3. Compatibility with EMR and CRM Platforms Ensure that the platform will also be compatible with your healthcare CRM automation tool or electronic medical records. Having the same data in both locations makes it simpler to target and report. 4. User Experience Overhead The platform must be easy to operate by your workers to operate. A ridiculously complex interface is a learning curve that weighs down the outcomes and extends an invitation for frustration. Look for simple-to-use dashboards and drag-and-drop automation builders. 5. Support and Training Make sure that the supplier offers onboarding, technical support, and training material to enable your employees to get the most out of the platform. 6. Budget and Scalability Choose a solution that is affordable to your budget today but scalable enough to support growth as your hospital or clinic grows. Look at the pricing model, some platforms charge for contacts, emails sent, or users. Trends to Watch: Healthcare Marketing Automation Trends of the Future Technology advances, and healthcare automation follows. Keep an eye on these trends: 1.
How to Secure Patient Data from Ransomware? The advent of the era of technology in the healthcare sector has made it more vital now than ever to protect patient data from ransomware. Healthcare organizations are a key target for cyber attackers because they hold vast quantities of sensitive personal and health information. The impact of a ransomware attack can be financial loss, damage to reputation, HIPAA breaches, and most significantly, disruption of essential patient care. In this guide, we cover the nature of ransomware, why patient data is an attractive target, and how to have effective ransomware protection strategies in place to protect your systems and ensure healthcare cybersecurity. What Is Ransomware? Ransomware is malware that encrypts data and systems, holding the users at ransom until payment is received. Such attacks often begin with a phishing email, suspicious attachment, or exploit on old software. Ransomware in healthcare, minutes of downtime can result in loss of life, so organizations will pay. Types of Ransomware There are many different types of ransomware: Crypto Ransomware: It encrypts important data, making it unreadable unless a decryption key is generated. Locker Ransomware: It locks down the whole device , with the only exception being application and file access. Double Extortion Ransomware: It encrypts data and additionally exfiltrates it. Threat actors threaten to pay or publish stolen data, doubling the pressure on victims. Current Healthcare Ransomware Trends The healthcare industry remains under siege: Clinics and hospitals are being targeted with an overwhelming increase in targeted attacks, where most prefer to close emergency rooms. Phishing methods are becoming complex with AI usage. Remote desktop protocols (RDP) are being targeted heavily. Third-party vendors and their connected devices are currently the best attack surfaces. Why Patient Data Is So Valuable? High Market Value of Medical Records Medical records differ from credit card information since they hold fixed details: names, dates of birth, insurance policy numbers, and complex medical history. Due to this, they are worth a lot of money on the dark web, going for 10–20 times more money than other personal data. Exploitation of Stolen Information Cybercriminals use medical information in various ways: Insurance fraud: Filing incorrect claims based on stolen insurance information. Identity theft: Opening unauthorized accounts or seeking medical treatment based on data. Misuse of prescriptions: Acquiring drugs or controlled substances illegally. Consequences of a Violation of Healthcare Information Violation of healthcare information can have serious repercussions: HIPAA violation: Heavy penalties from regulating authorities. Legal proceeding: Class action lawsuits by harmed patients. Federal investigations: Leading to operational audits and loss of licenses. Impact on Clinical and Operations Ransomware cyberattacks induce system downtime that slows down diagnoses and treatments, with the risk of jeopardizing patient outcomes. Patients also lose confidence in healthcare organizations that fail to keep secure medical records. Top Tactics to Safeguard Patient Data Adopt a Cybersecurity Framework Formulate an overall plan incorporating: Risk assessments to define vulnerabilities. Well-articulated cybersecurity policies and governance. Cybersecurity guidance from consultants. Strengthen Access Control Mechanisms Adopt strong access control by: Adopting role-based access to limit unwanted exposure. Activated multi-factor authentication (MFA). Monitoring login activity and system use for anomalies. Keep Software Current Software updates minimize the risk of exploits: Patch serious software vulnerabilities in a timely fashion. Utilize up-to-date antivirus and endpoint protection software. Scan legacy systems for hardening or retirement. Implement a Zero Trust Policy Trust no system or user: Verify all access requests. Enforce least-privilege rules. Randomly monitor user activity on the network. Vendor Risk Management Vendors and third-party service providers share the same patient data security needs: Screen vendors based on cybersecurity best practices for clinics. Place cybersecurity terms in contracts. Audit their access to sensitive patient information. Book Free Demo Different Data Protection Techniques Encrypt Patient Information Encrypting patient data ensures that even if the data is stolen, it is not usable: Use an industry standard such as AES-256. Encrypt data in transit and at rest. Use encryption for backup, email, and portable devices. Backup and Disaster Recovery Good backup practice lessens the impact of attacks: Adopt 3-2-1 rule (three copies, two different types of storage, one offsite). Regularly test backup integrity. Maintain backups on offline or immutable storage platforms. Secure EMR Systems EMR data security is commonly targeted: Select EMR systems with inherent security features. Enable audit trails and access logging. Integrate EMRs into overall cybersecurity efforts. Cloud Security for Healthcare Cloud security for healthcare providers is frequently utilized for storage and operations: Partner with HIPAA-approved cloud vendors. Employ end-to-end encryption of data stored in the cloud. Audit access and configuration options regularly. Physical Security Controls Physical security is frequently neglected: Restrict data center access via biometric or keycard authentication. Perform surveillance and regular inspections. Lock down devices in patient areas and take unattended devices away. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) EDR tools assist in detecting and quarantining ransomware attacks: Automatically monitor behaviors and detect suspicious activity. Quarantine infected systems from the network.
Ethics of AI in Healthcare Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the healthcare sector with advancements in diagnostics, treatment planning, predictive analysis, and administrative effectiveness. Right from AI-enabled radiology to virtual health assistants, applications of intelligent systems are enabling doctors to render faster, more precise, and more customized care. Yet, these advantages are paired with stern moral issues. AI algorithmic discrimination, patient self-determination, patient data privacy, AI accountability, and transparency are some of the direct concerns. Healthcare AI ethics is not an add-on; it is an urgent framework demanded to inform responsible innovation. This blog acknowledges the AI bias in medicine and highlights significant ethical standards and best practices required for ethical use and deployment. The Role of AI in Healthcare The uses of AI in the healthcare sector are far-reaching and continuously changing. Here are some of the main areas where AI is making its mark, with potential and moral issues. 1. Diagnostic Imaging AI algorithms analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans quickly than human radiologists. AI speeds up early disease diagnosis like cancer, stroke, and retinal diseases. This improves diagnostic accuracy and speed, yet bias in AI analysis is a problem if the training data are not representative and ends in misdiagnosis of minority populations. 2. Predictive Analytics Machine learning algorithms can predict patient decline, readmission to the hospital, or outbreak of epidemics. These systems enhance preventative treatment but can develop responsibility issues in AI systems when the prediction is wrong or induces unwarranted panic. 3. Personalized treatment AI can provide personalized treatment regimens based on patient history and international medical literature. These applications are excellent decision tools, but still require human supervision in AI-enhanced care. An entirely automated process risks dehumanizing care and reducing clinician autonomy. 4. Virtual Health Assistants Chatbots and virtual assistants enable activities such as scheduling appointments, symptom checking, and medication reminders. These are fashionable but raise ethical concerns in AI diagnostics and data security in AI healthcare tools. 5. Administrative Automation Paper is minimized to an absolute minimum, and billing, insurance processing, and record-keeping are accelerated through AI. Although it streamlines procedures, automated errors or biases can be disastrous, particularly for insurance claims and medical coding. Ethical AI Practice in Medicine Ethical AI practice in medicine relies on integrating novel technologies into fundamental values of medical ethics and artificial intelligence, beneficence, non-maleficence, justice, autonomy, and accountability in AI systems. 1. Beneficence and Non-Maleficence AI technologies must be designed to benefit patient health without harming them. Algorithms must be carefully examined for accuracy, safety, and representativeness. Failing to correct AI errors or admitting poorly trained models to practice contravenes this value. 2. Autonomy and Informed Consent Patients should be informed whenever AI is applied in their care and be capable of comprehending its use. Ethical AI must ensure informed consent and AI-informed care. This is achieved by providing transparent descriptions of how AI affects diagnoses or choices, possible harm, and information on what data is gathered. 3. Fairness and Justice There is fairness in healthcare AI algorithms in the sense of treating all patients equally, regardless of race, gender, or socioeconomic status. AI algorithms created from biased data may further aggravate existing biases. Algorithms have to be tested on heterogeneous populations by developers. 4. Transparency and Explainability One of the most controversial issues is the “black box” nature of AI. Clinicians and patients require transparency in medical AI so that they can trust its recommendations. Explainable AI (XAI) can enhance understanding and responsibility by demonstrating the mechanism by whereby conclusions were drawn. 5. Responsibility and Liability In medicine, if something goes wrong, there has to be clear delegation of responsibility. If a computer AI is giving a false diagnosis or advice, is the doctor, the hospital, or the programmer at fault? There has to be legal and ethical responsibility assigned to AI systems. 6. Privacy and Confidentiality Artificial intelligence systems need large quantities of health information, typically drawn from electronic health records (EHRs), imaging data, wearables, or mobile apps. Preserving data privacy in AI systems involves protecting consent, de-identifying data, and complying with policies such as HIPAA and GDPR. Greatest Challenges to Ethical Adoption of AI Despite the best efforts globally towards the ethical implications of AI in healthcare, some challenges are responsible for slowing it down: 1. Biased Training Data If AI models are trained mainly on information about specific geographic or demographic populations, what emerges won’t apply to others. This creates AI bias in healthcare, which exacerbates health disparities rather than enhancing results. 2. Flawed Regulation AI development is outpacing regulation. In many regions, there are no clear standards for clinical validation, deployment, or post-market surveillance of AI tools. As a result, developers may not be held accountable for flaws or misuse. 3. Lack of Explainability Deep learning models are often complex and difficult to interpret. If clinicians cannot understand or challenge an AI’s output, ethical problems arise, particularly in life-or-death scenarios where reasoning must be transparent. 4. Inconsistent Human-AI Collaboration AI must be employed to augment, not substitute for, healthcare professionals. But if not taught to engage with AI systems, clinicians will be likely to rely too heavily on buggy suggestions or ignore rich information. Managing human supervision of AI-driven care is crucial. Book Free Demo Best Practices for Ethical AI in Healthcare Software developers and healthcare providers should incorporate practices to maximize the application of AI for good and patient-oriented purposes. 1. Use Varied, Representative Data Training data must cover all ethnic backgrounds, ages, sexes, and histories to prevent AI diagnosis bias. Algorithmic bias can be identified and rectified over time through ongoing audits. 2. Use Explainable AI Use transparent and explainable models that offer justification for their suggestions to establish trust among healthcare providers and patients and enable AI decision-making in clinical settings based on informed information. 3. Design Oversight Mechanisms Hospitals and clinics should establish AI ethics committees that include a balance of ethicists, clinicians, patients, and data scientists as members. These committees can pre-screen tools before deployment
The Role of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) in Remote Patient Monitoring The digital revolution, in general, has transformed the majority of industries, and the healthcare sector is no exception. Intelligent technologies and connectivity have given rise to telemedicine or telecare, which has also gained momentum like never before. Pervasive use of the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is one of the most important developments that enable care to be patient-centric and effective. In particular, in remote patient monitoring (RPM), IoMT is bringing new possibilities of real-time diagnosis, disease management, and patient engagement, bridging gaps for conventional care and producing new value in the era of medicine. Understanding IoMT Internet of Medical Things, or IoMT, is a group of networked devices for gathering, processing, and transmitting medical information over the internet. Examples include wearable monitors and sensors, advanced diagnostic equipment, and health apps on mobile devices. With their cloud-based and AI, IoMT enables seamless data transfer between patients and healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care even if the patient is not physically near a clinic or hospital. This connected system of medical devices makes passive medical devices active participants in patient care. Advanced connected health technology enables clinicians to monitor patient patterns more intensively, personalize treatments, and reduce face-to-face contacts. The advantages are not just convenient but life-saving in cases of serious and chronic diseases. What is Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)? Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is the process for gathering patients’ health data outside of regular clinical settings and transferring it to medical professionals for observation and comment. It most appropriately applies to patients with chronic disease, post-operative care patients, or those needing extended therapy. RPM most often uses remote patient monitoring devices such as automated blood pressure, glucose metering, and pulse oximetry that automatically report in real-time. RPM increases the patient’s experience through home care and ongoing monitoring of conditions by doctors and intervening simultaneously if necessary. A prospective model of care such as this lowers hospitalization and emergency room visits, thereby enhancing overall health outcomes. How IoMT Enables Effective RPM? IoMT integration with RPM has revolutionized the way healthcare is delivered. IoMT devices collect patient information automatically with minimal human intervention to offer a high level of accuracy. Devices are usually sensor-enabled and Bluetooth- or Wi-Fi-supported and send data into cloud platforms from where healthcare providers can see and analyze data. For example, smart medical devices such as digital inhalers, network electrocardiogram monitors, and blood glucose monitors provide real-time feedback regarding a patient’s status. They not only aid in diagnosis but also in treatment tailored to the patient without requiring face-to-face consultations. Another important feature is real-time patient status monitoring, which will ensure that any patient status loss is recorded in real-time. Warning and message alerts offered by IoMT platforms enable taking prompt action, which, in the case of emergencies, can save lives. Additionally, as telehealth and IoMT come with a greater priority, these technologies no longer function in isolation. They collaborate and form a robust virtual care network to enable improved communication and responsiveness of clinicians and patients. Book Free Demo Benefits of IoMT in RPM Enabled and Active Patients: Seeing individual measurements vary daily inspires lifestyle modification and adherence. Targeted reminders by smart medical devices encourage activity, hydration, or medication, turning passive recipients into active stakeholders. Operational Benefits for Providers: Capacity experience may be tuned with automated monitoring. Artificial intelligence triage of normal data allows clinicians to focus on high-risk presentations, reaping benefits of remote monitoring, such as lowered readmission penalties and staffing plans that are smarter. Public Health and Population Insight: Shared dashboards enable community trends, which support resource planning and disease surveillance. Such pan‑view IoMT apps convert discrete points of data into population‑level insight. Preserving Privacy and Trust: IoMT data security, end-to-end encryption, zero-trust architecture, and HIPAA-style global regulation for vast datasets. Transparent policies assure patients that their data is safe. Future of IoMT in Remote Healthcare With advances in technology, the future for remote healthcare is very bright. The future enhancement of AI, machine learning, and 5G will further enhance the value proposition of IoMT for RPM. It will allow clinicians to forecast complications, and care plans will be personalized by machine learning algorithms learning from enormous amounts of health information. Miniaturization of equipment and increased battery life will also make wearable healthcare technology even more efficient and convenient. It will no longer be health monitors, but wearables will be able to help individuals interact with other household systems, living space being smart and integrated for health. Additionally, healthcare IoT devices growth will lead to more innovative and diversified solutions for common and chronic health conditions. They include smart beds, imaging systems with AI, and robotic surgical systems within an active, predictive, and personalized healthcare paradigm. The integration of policy reforms and innovation will serve to bring IoMT into mainstream public health systems. Health organizations and governments are increasingly finding it worthwhile to invest in RPM facilities and infrastructure that can support IoMT on a larger level. IoMT evolution will become a decisive factor in global healthcare equity. With proper infrastructure, even rural and underserved populations will have access to high-quality medical care through RPM. IoMT overcomes geographical distances and shatters conventional barriers in accessing timely healthcare. Conclusion The IoMT applications of remote patient monitoring through IoMT cannot be overstated. IoMT possesses immense possibilities to revolutionize patient care and provide it in, streamlined and agile manner. Whether chronic disease care or IoMT for elderly care population management, IoMT-based RPM is revolutionizing healthcare to unprecedented levels. Despite certain data security and integration issues, so far, there has been encouraging progress. As the healthcare environment continues to digitalize, the importance of IoMT in healthcare will only increase. It is not merely about staying technologically current but also viewing care from a different angle—wellness rather than illness, prevention rather than cure, and person rather than process. Tools like Clinic Management Software
ChatGPT vs Healthcare-Specific AI: Which Model Helps Medical Software More? AI is making a positive impact on healthcare by boosting the performance and accuracy of medical software. AI tools today can be classified into two categories: those designed for broad use, such as ChatGPT, and those for use in healthcare. Discussions around ChatGPT vs Healthcare-Specific AI point out some important factors, for example, adaptability, compliance, and expertise in healthcare. Medical institutions and developers must decide on the model that best meets their planned improvements in diagnostics, managing tasks, or patient communication. This article compares ChatGPT with custom healthcare AI systems, detailing the main differences, highlighted strong points, potential challenges and their applications in software used in healthcare. Understanding ChatGPT and Healthcare-Specific AI? ChatGPT ChatGPT is a language model that OpenAI has developed for general use. It can handle human-style communication and is often applied for creating content, helping with customer support, and responding to basic questions. One use of ChatGPT in medical software is to assist in making simpler patient notes, listing instructions for patients, and making it easier to communicate with them. AI Designed for Healthcare Alternatively, AI designed for healthcare is prepared using the rules and standards found in medical data. In most cases, these models are tied to EHRs, diagnostic tools, and how clinicians work in their specialty. While there are more ChatGPT medical applications, their overall design has some restrictions. Sometimes, they cannot access the proper knowledge for their field, manage difficult terms in medicine and find it tough to deal with sensitive data of patients. The Main Differences Between the Two ChatGPT This technology is a general-purpose language model. It can handle different topics in text, though not specifically designed for medical language, procedures, or industry processes. ChatGPT does not meet HIPAA standards on its own. Dealing with patient information in general requires considerable changes, encryption, and updated healthcare privacy technology. Because ChatGPT does not explain its reasoning, it may be difficult to rely on it in making medical decisions. Healthcare Specific AI AI technology used in healthcare is made with medical areas in mind. With the help of medical information and guidelines, models in this field gain accuracy and dependability. The Healthcare-specific AI tools made for healthcare are all created with compliance to both HIPAA and other regulations in the sector. They always ensure that your data is private and secure. Specific AI models for healthcare often help explain the process behind a recommendation or diagnosis. This helps healthcare professionals trust each other and provide treatment based on research. Book Free Demo Use Cases In Medical Software While both types of approaches help, the results can depend on the chosen application. Here, we compare the use of different models in examples: AI Applications in Electronic Health Records: The purpose of using AI for electronic health records (EHR) is to lessen the amount of paperwork and improve the way data is accessed. Models used in healthcare often do data entry tasks, condense doctors’ notes, and discover errors in medical records with more reliability since their data is organized. Enhancing Healthcare with Natural Language Processing: Without NLP, interpreting doctors’ notes, radiology reports, or discharge summaries would not be practical. Although ChatGPT is effective in general NLP in healthcare, healthcare-specific NLP tools are more accurate at identifying elements in medical records and codes. Many times, these tools are included in decision tools and automated checking methods. Supporting Clinicians Through Decision Tools: With clinical decision support AI, physicians use patient information and get guidance based on evidence. An advantage of AI tools for healthcare is that they rely on methods and tools verified in real clinical settings. Forecasting Patient Outcomes: Predictive analytics in healthcare AI to predict a patient’s outcomes, the possible need for readmission, and the future stages of a disease. Custom AI models trained with hospital data are more accurate than others. Improving Telemedicine with AI in Patient Communication: It is becoming increasingly necessary to apply AI for patient communication in telemedicine and after leaving the hospital. ChatGPT can communicate with patients to respond to basic inquiries, remind people of their appointment,s or offer background information. Ensuring Patient Privacy: It is important to use HIPAA compliance and AI to ensure the privacy of patients is protected. The development of healthcare-related AI systems considers compliance issues and includes encryption, access control and audit logs. Automating Administrative Tasks in Healthcare with AI: It is helpful for healthcare to use AI to automate the repetitive duties of making appointments and issuing bills. But when it comes to AI integration in hospital software, using internal systems and rules for each patient, AI in healthcare does the work best. Comparing Medical Chatbots and Custom AI Solutions Unlike custom AI systems, AI chatbots in healthcare are simple to add and can handle a large workload, though they are less knowledgeable about medicine. Although it takes more time to build a custom AI system, the results are more accurate, conform better to rules, and keep patients more involved with their own health information and treatment plans. Role of OpenAI in Advancing Healthcare Technology OpenAI is being incorporated in healthcare by forming partnerships with healthcare technology firms and research teams, including its integration into Clinic Management Software to enhance administrative efficiency and decision-making. At the same time, there are still concerns related to protecting data, ensuring its accuracy, and maintaining regulatory compliance. To effectively use OpenAI in critical medical settings, additional safeguards and system enhancements are necessary. Conclusion Whether to use ChatGPT or a healthcare-specific AI depends on the organization’s plans, the amount of money available, and the rules they have to follow. While ChatGPT is convenient to use and covers many NLP tasks quickly, it may not meet clinical accuracy, compliance, or integration requirements. FAQs [sc_fs_multi_faq headline-0=”h3″ question-0=”Is there a difference between ChatGPT and healthcare-related AI?” answer-0=”While ChatGPT can be used for various applications, healthcare-specific AI is built
Is SaaS Safe for Storing Patient Data? With healthcare going digital, managing patients, using EHRs, conducting diagnostics, and offering telemedicine have come to rely on Software as a Service (SaaS) platforms. However, there are big concerns about the safety, privacy, and lawful handling of information when it is stored on a cloud platform. The key question arises: Are patients’ health records safe with SaaS software? This article discusses the effects of adopting SaaS healthcare compliance industry by exploring different SaaS risks in healthcare, legal issues, and best safety tips. What is SaaS in Healthcare? Software as a Service, or SaaS, makes it possible for users to run applications directly over the internet, without installing them on their own devices. SaaS is helping hospitals, clinics, and health tech startups to improve the way they function. This means providers can obtain and use medical software from anywhere, often paying a monthly fee. It is especially eye-catching due to its ability to grow, its low costs, and the simplicity of making updates. Some common SaaS applications in healthcare are appointment setup, patient portals, telehealth platforms, medical records software, and billing. The requirement for easy and instant access to information and integration of various applications is encouraging greater use of SaaS solutions by providers. Even so, saving patient records online raises issues about how safe the cloud is in healthcare and if these systems can meet strict information security regulations. Key Security and Privacy Risks With Saas Companies working with Protected Health Information (PHI) have to be aware of the special risks that come with SaaS adoption. Main problems include unauthorized users getting in, insecure APIs, not using encryption, and not requiring strong user authentication. Protecting patient data is a top priority, as Healthtech cybersecurity breaches or leaks can give rise to serious issues, for instance, legal issues and harm the company’s reputation. Because ransom ware and phishing are becoming more advanced, more healthcare data is being breached. As a rule, poorly configured Cloud security in healthcare and social engineering scams are often behind most data breaches. Besides, opening your system to third-party integrations can create security risks if they are not handled correctly. SaaS presents another problem in healthcare by not allowing full awareness of where or how medical data is managed, mainly in situations where many different customers share the same cloud infrastructure. If there are no strong security guidelines and accountability, important data could end up in the wrong hands. What Makes a SaaS Provider Secure for Healthcare? Not all SaaS vendors know how to keep healthcare data safe and secure. It is important for providers to check that vendors follow the laws such as HIPAA and GDPR. A Healthcare SaaS Solution should follow strict guidelines regarding encryption, activity logging, secure user access, and reliable data backup procedures. It’s essential to work with vendors who are willing to sign Business Associate Agreements (BAAs), ensuring accountability in handling PHI. Providers should also have clear conversations with SaaS companies about their data encryption methods, for both stored and transmitted data, to protect against unauthorized access. A safe provider will carry out routine security assessments and certify their actions by SOC 2 Type II, ISO 27001, or HITRUST. An audit of this type helps maintain privacy in the cloud and allows customers to trust that the provider will protect their data. When choosing a SaaS vendor, healthcare organizations also need to think about whether the SaaS services follow the GDPR compliance for SaaS healthcare rules if they are dealing with patients from the EU or process international data. GDPR also requires hospitals to meet certain standards on data access, consent, and reporting data breaches, along with HIPAA. Book Free Demo Best Practices for Healthcare Providers Using SaaS Healthcare providers need to implement multiple strategies, mixing technology and business processes, to protect themselves in SaaS. Following these steps helps lower the risk of threats and makes the company more compliant. Vendor Assessment: Make sure you fully check the compliance, certifications, and honesty of each SaaS vendor. Search for applications that are suitable for healthcare, with security and smooth Secure EMR software usage as priority. Encryption and Access Control: Ensure the SaaS data encryption systems in use are very reliable. Add multi-factor authentication, role-based access control, and make encryption standard throughout the systems. With these steps, PHI in Cloud-based EHR security is better protected from unauthorized people. Staff Training: A lot of Healthcare data breaches happen because of people making mistakes. Training regularly teaches staff why sharing patient data should be avoided and how to protect themselves from phishing and improper usage of sensitive data. Regular Audits and Monitoring: Regularly conduct inside evaluations and vulnerability scans to spot anything unexpected. Check system logs for unusual activities and choose vendors that carefully track and record every action done with patient data. Data Backup and Disaster Recovery: It’s important that your SaaS company automatically backs up its data and has a tested disaster recovery system in place. This is done to keep the system going if something like a fault or an attack occurs. Legal and Contractual Safeguards: Include in the agreement a description of who is responsible for the data, what the liabilities are, and how much time they have to report a breach. Being well structured, a Service Level Agreement (SLA) helps achieve accountability. Compare Deployment Models: Think about the differences in security when choosing between SaaS vs on-premise security options. Large organizations that have their own IT teams may find that on-premise models are a better fit for regaining more control. However, with the right provider, SaaS can be just as secure, if not more so—than on-premise alternatives. Data Residency and Local Laws: Look into whether the supplier stores your data in your region as required. In some countries, the rules say medical data must stay inside the nation’s borders, which affects how software-as-a-service companies can function. Conclusion Using SaaS platforms in healthcare, such as Clinic
Top Benefits of EHR Integration: Improving Care, Workflow & Data Sharing EHR integration is changing healthcare for the better by helping staff access info, smoothing out their routine tasks, and providing better care to patients. When different systems are linked, doctors can reach full information about patients and quickly make safe choices for their treatment. When EHRs are integrated, patient records are brought together, there are fewer administrative duties, and errors can be prevented with warnings and computerized documentation. Electronic health records make it easier for health experts and ensure that patients receive more customized and well-organized care. It is important for Patient data integration to exchange safely within a hospital’s internal network, and integration supports this function. Stronger EHR interoperability makes the healthcare system cheaper, quicker to respond, and puts the patient first. What is EHR? Electronic Health Records (EHR) copies the contents of the paper charts and puts them into a digital format. They consist of different data, such as the patient’s medical history, lab results, and what treatments are prescribed. EHRs are set up so that only authorized healthcare staff can access and edit them, giving a single, accurate picture of a patient’s health at any point. They are now the main part of healthcare infrastructure and have taken over the traditional method of keeping patient records in most hospitals and clinics. With the Advantages of EHR systems digital technologies, they ensure that vital records are easily accessed, well-coordinated, and can be stored over a long period of time. Importance of EHR Integration Although EHRs are useful separately, their biggest advantage is how well they speak to other tools and systems. With EHR interoperability, healthcare settings, groups, and specialists can easily share the necessary patient information. It ensures that healthcare providers can see the entire patient’s health information in one place. It makes it easier for healthcare workers to do their jobs, giving them more opportunity to help their patients. Because the health system is changing rapidly, making sure EHRs are incorporated with all our labs, pharmacies, imaging centers, and billing services is vital for coordinating care. Top Benefits of EHR Integration 1. Improved Patient Care and Coordination EHR systems help improve patient care by allowing staff to communicate more effectively. All medical information about a patient can be seen in one place by physicians, nurses, specialists, and technicians. Such Coordination of care helps to maintain consistent care, prevents using multiple medicines, and prevent unnecessary testing. Having a network connected to EHR allows doctors to offer better care, carry out follow-up patient care, and notice gaps in care. 2. Real-Time Access to Patient Information With EHR integration, providers have access to patient data at any time, regardless of the place of care. No matter where they practice, physicians are able to get reports, prescriptions, and past consultations immediately. Such quick access to patient’s information allows faster decision-making and quicker help in emergency cases. Doctors are able to access patient data faster than by waiting for it to be sent by fax or email. they quickly get access to the necessary information they need. 3. Reduction in Medical Errors EHRs are also important because they significantly reduce mistakes made in medical care. Common problems with paper-based systems include miscalculating a drug dose, neglecting to notice a patient’s allergy, or mistakenly reading medication plans. They make data consistent and depend on automation to address the most common human errors. If there is a chance for a drug interaction or allergy issue, or if lab results are unusual, the system will alert and remind clinicians. Such safeguards make sure that high care standards are maintained and mistakes that could be prevented do not happen. 4. Time-saving in clinics with EHR Workflows In older settings, it often takes a lot of time to write down documentation, retrieve charts, and collaborate between departments. EHR makes it quicker for clinics by keeping records up to date, allowing referrals to be sent electronically, and allowing instant access to the required information. Many projects can be done fast, but it once took hours. Healthcare staff can spend less time organizing documents and more time with the patients. The whole process from the first patient visit to the final paperwork gets faster, more efficient, and requires fewer errors. Book Free Demo 5. Enhanced Data Sharing Capabilities For people to receive collaborative care, health information should be able to be shared among those providing it. The use of secure sharing of information among different departments and specialists allows for quicker diagnoses and well-coordinated care. Using an integrated EHR system, patients’ data is kept safe and allows different healthcare teams to interact. Whenever a patient is transferred from one type of care to another, their information needs to move smoothly. Health data exchange has to be secure health data exchange so that there is compliance with HIPAA and the information is still accurate. 6. Cost Savings in Healthcare Practices Thanks to their single database and easy-to-use format, integrated EHR systems result in reduced business expenses. When all administrative tasks are managed using technology, smaller healthcare organizations have much Cost savings with EHR in this area. They can reduce expenses on storing files and paperwork, save time for their workers doing administrative tasks, and lower risks of financial loss due to claims and billing errors. These savings may be used to improve patient care or obtain more tools for diagnosis. 7. Support for Automated Clinical Documentation With EHR integration with lab systems, patients’ healthcare information is automatically put into the system and can be processed much faster and more correctly. These tools allow doctors and nurses to take notes about patients easily and quickly. Automation helps to detect any missing information or differences between records, making sure all documents are standardized. Automation helps medical professionals by reducing paperwork and saving time, while also making the documentation more comprehensive. Conclusion Access to electronic records is essential for top-quality and efficient healthcare today, rather than being just a dream for