SaaS Logistics: Smart Supply Chain Management to Cloud Solutions Technology is revolutionizing business company usage of supply chain management, and logistics are being remapped. The software used for managing logistics has evolved a great deal from old-school on-premises models to agile, cloud-based models. The transformation allows companies to achieve ultimate efficiency, simplicity, and control over operations. SaaS supply chain management allows inexpensive and adaptive solutions to be utilized by organizations of all sizes. Cloud logistics solutions allow organizations to relish real-time data, automate operations, and improve the delivery process without major IT investment. What is SaaS Logistics? SaaS logistics refers to cloud-based software utilized to handle logistics and supply chain functions. In contrast to conventional systems, the software is web-hosted and subscription-based. Among them are transport management system (TMS) software, warehouse management SaaS software, and fleet management SaaS software. These are cloud-based software which enable firms to manage everything from inventory control to delivery without laying out money for costly hardware or software licenses. SaaS logistics and shipping guarantees harmonious integration of supply chain procedures, focusing on efficiency and ongoing monitoring. Logistics tracking software provides real-time monitoring of shipments by companies, resulting in better decision-making and customer satisfaction. SaaS Logistics Software Key Advantages Cloud logistics software enjoys the following benefits compared to traditional systems: Cost Savings: No infrastructure cost for capital and assurance of subscription fees. Scalability: Cloud logistics software expands with your expanding business. Accessibility: Perform control operations wherever, whenever you want cloud connectivity. Real-Time Information: Your real-time logistics tracking software provides real-time delivery and stock details. Integration: Tight integration with other company systems, enabling data transfer between platforms smoothly. These are the features that make SaaS for supply chain management the correct choice for companies wishing to streamline operations and lower overheads. Key Features of SaaS Logistics Platforms Solution-specific solutions by emerging logistics SaaS solution vendors address unique needs. Most critical capabilities are: Transport Management System (TMS): Combines planning, execution, and tracking of loads to accomplish optimal route delivery and cost savings. Warehouse Management SaaS: Offers order processing, storage administration, and inventory management functionality. Fleet Management SaaS: Monitors vehicle usage, upkeep, and driver performance to accomplish maximum delivery efficiency. Last Mile Delivery Software: Designed for last-mile delivery optimization to enable on-time order fulfillment. Order Fulfillment Software: Order processing, packaging, and shipping are automated to automate supply chain processes. They are cloud-based, analytics-AI-powered solutions. Advantages of SaaS in Supply Chain Management Supply chain management implementation by SaaS builds operational advantages: Enhanced Visibility: Cloud logistics software allows a single point of access to data and enhances supply chain activities. Enhanced Efficiency: Automated logistics elements of logistics automation platform solutions minimize human error and intervention. Enhanced Decision-Making: Real-time information through real-time logistics tracking software allows managers to make more informed decisions. Less Cost: Pay-as-you-go models guarantee efficient budgets. Businesses that use SaaS to ship and logistically operate become more competitive by offering better customer service and automated transactions. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Application of SaaS in Logistics Logistics platforms based on SaaS provide support for different segments of the supply chain: E-commerce: Order fulfillment software and last-mile delivery software are used by business firms to ship on time and monitor customer orders. Freight Companies: SaaS freight management solutions enable them to route plan and load optimize. Retail Chains: They use SaaS to control the optimal levels of inventory and avoid shrinkage. Distribution Centers: Take advantage of warehouse management SaaS, which controls automated picking, packing, and storage operations. Fleet Operators: Take advantage of fleet management SaaS, which controls vehicle performance and driver behavior. Below are some of the avenues through which various industries benefit from SaaS in supply chain optimization. Challenges and Considerations Despite being beneficial, SaaS logistics also has challenges: Data Security: Use of cloud services comes with concerns about sensitive information. Difficulty in Integration: Incorporating logistics management software into current business systems is challenging. Vendor Reliability: Not every company that offers SaaS logistics offers the same service or uptime guarantee. Limitations of Customization: Certain cloud-based logistics software has little room to customize compared to on-premise systems. These are things one must learn well in advance before deciding on a platform to automate logistics for your enterprise. Selecting the Proper SaaS Logistics Platform When selecting a SaaS platform, follow these: Features & Functionality: Make sure the platform has the type of transport management system (TMS), warehouse management SaaS, and order fulfillment software relevant for your business. Scalability: Make sure cloud logistics solutions scale up to support your organization’s requirements. Integration: The platform should integrate well with your current ERP or CRM platforms. Vendor Reputation: Check customer reviews, uptime record, and service quality of logistics SaaS providers. AI & Automation Features: Logistics SaaS solutions with AI capabilities provide predictive analysis and automation of decision-making. Smart choice will get your shipping and logistics SaaS investment yielding returns in the long term. SaaS Logistics Future The future of SaaS logistics is favorable with recent advancements such as AI, IoT, and blockchain. AI in Logistics SaaS: Artificial Intelligence will further transform demand forecasting, route optimization, and risk management. Logistics Automation Platform: Automation will make supply chain operations smooth, from tracking stocks to automated delivery systems. Real-Time Logistics Tracking Software: IoT will enable companies with even better tracking and predictive
SaaS Accounting: The Comprehensive Guide to Revenue, Billing & Compliance SaaS businesses have unique business and financial models that require unique accounting methods. Business Schools need to cover this: SaaS businesses versus product businesses. When compared with product businesses, issues related to recurring revenues, long-term customer relationships, and complex compliance issues are uniquely relevant to SaaS businesses. The answer to the question What is SaaS accounting? is particularly important for accounting and finance teams that need to run operations, maintain compliance, and make decisions based on facts. This guide covers everything from the unique accounting for SaaS companies to revenue recognition, billing types, financial statements, metrics, and more automated compliance and forecasting tools. What is SaaS? SaaS accounting refers to the contribution of the financial administration and bookkeeping of the Software as a Service (SaaS) organizations. SaaS companies have recurring revenue which comes in form of subscriptions unlike in traditional businesses meaning it has special revenue recognitions, tracking of deferred income as well as specialized metrics which include Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). SaaS accounting estimates within tolerance in order to provide good forecasts, reporting to investors, and strategy. It usually employs cloud-based accounting systems that mainly support subscription billing, CRMs and payment gateway services and the software makes the process of financial reporting for SaaS business automated and scalable. Unique Challenges in SaaS Accounting Accounting challenges in SaaS are due to the subscription model. In contrast to retail, the revenue cannot be recognized upfront. Rather, it must be recognized throughout a customer’s subscription. Accrual accounting is required for SaaS. Accounting challenges of importance in SaaS include: Servicing multi-period contracts Accrued revenue management in SaaS Compliance with SaaS rules under ASC 606 Recurring revenue monthly (MRR) and annually (ARR) calculation Convergence of subscription billing accounting systems In addition, SaaS companies must address issues like the management of cash flow SaaS where advance payments skew near-term liquidity. Principles of Substantive SaaS Accounting SaaS accounting is founded on principles that ensure financial reporting is accurate and regulatory compliant. They are: 1. Accrual Accounting Accrual accounting for saas retains revenue and expense on the books whenever earned or incurred but not when cash is paid. This method of accounting provides a better picture of the real financial position of a company. 2. Revenue Deferral Deferred revenue for SaaS means payment made in advance of services completion. In a customer paying annual plan upfront, one-twelfth of the revenue is recorded each month. 3. Revenue Recognition Compliance With ASC 606 SaaS compliance, businesses must recognize revenue at satisfaction of performance obligations and not when cash is received. Adhering to the standard helps align finances with economic activity. These foundations lie at the center of accounting integrity for SaaS businesses and promote transparency for stakeholders and regulators. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Revenue Recognition in SaaS SaaS revenue recognition is based on ASC 606, an internationally accepted standard manual. ASC 606 requires SaaS companies: Identify a customer contract Define performance obligations Determine the transaction price Allocate price to obligations Recognize revenue on fulfillment of obligation This is especially crucial for tiered-pricing or multi-service businesses. For example, if a SaaS business offers onboarding support along with the software license, it must break and defer the revenue accordingly. Good SaaS revenue recognition keeps companies in compliance and to make sound financial choices. Some automate it using saas accounting software. SaaS Billing Models Subscription accounting billing adds one more complexity to SaaS operations. Common billing cases are: Flat-rate billing: One flat rate for all usage. Tiered pricing: Multiple plans based on features or levels of usage. Usage-based billing: Charge on actual usage (e.g., per API call). Hybrid billing: Combination of fixed fees and usage-based fees. Every model impacts revenue forecasting SaaS, customer turnover, and revenue accounting. Usage models, for instance, will require estimates and patches on every billing cycle. Business-built billing systems not only bring revenue precision but also improve cash flow management SaaS, especially for high-growth companies. SaaS Financial Reporting & Metrics Financial reporting for SaaS businesses is more than balance sheets and income statements. SaaS companies use performance measures almost solely in terms of operating metrics. Saas financial metrics of interest include: Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): Measures recurring revenue earned in a month. Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR): Annualized version of MRR. Churn Rate: Number of customers or revenue lost over some time. Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) Monitoring churn rate and revenue impact is especially crucial. Inordinate churn can cripple expansion regardless of whether acquisition is robust. Monitoring these saas financial metrics allows companies to act pre-emptively and decide to optimize price or product strategy. Reporting also allows revenue projecting SaaS, allowing leaders to prepare for hiring, growth, or fundraises. SaaS Accounting Tools & Software With the sophistication of subscription billing and compliance, companies make wide use of master saas accounting software. These solutions aid: Subscription billing accounting ASC 606 SaaS compliance Deferred revenue schedules Consolidated financial reporting MRR/ARR dashboards A few of the popular solutions are: QuickBooks with SaaS add-ons Xero with subscription plug-ins Chargebee and Recurly for automated billing NetSuite for enterprise-level reporting Precise saas accounting software can automate processes, reduce errors, and enable your staff to spend more time on strategic goals rather than manual data entry. Best Practices for
SaaS Marketing: Strategies, Funnels, and Tools to Grow In the rapidly accelerated Software as a Service (SaaS) pace of business in today’s world, just being that cool with your product isn’t going to be enough. Competing successfully and changing buyer behavior require an intelligent, data-based SaaS marketing plan to fall back on for customer acquisition and ultimate success. The equation? Get to know your people, create a SaaS marketing funnel, and employ the right tactics and tools to turn curiosity into fandom. This book offers incredible SaaS performance marketing funnels, software, and growth hacking techniques to differentiate and build your company. What is SaaS? SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a software delivery model in which software runs on the cloud and is delivered via the web. It is generally paid per subscription by the user, and there is no installation or infrastructure. Those above-mentioned SaaS solutions are highly successful SaaS solutions. B2B SaaS marketing is different from other marketing since it’s recurring-revenue, long-term-value, and customer-retention driven rather than that initial buy. Learning the SaaS Customer Journey A successful SaaS marketing plan indicates learning the customer journey from awareness to advocacy. 1. Awareness The customer is surfing and venturing out to search for solutions. That is where SaaS inbound marketing (blog, social, SEO) comes into play. 2. Consideration Customers are weighing products today. SaaS product marketing is transparent, with case studies, demos, and differentiators. 3. Decision The user selects a provider. SaaS email marketing campaigns, trials, onboarding, and SaaS email marketing campaigns dominate this stage. 4. Retention Retention is the objective once users are onboarded. Customer support, new product feature release, and gated content fuel retention. 5. Advocacy Activated customers are your solution’s advocates. They’re then utilized with user-generated content and word of mouth to drive SaaS customer acquisition. Seeing the process in this straightforward way puts power in the hands of marketers to segment touchpoints and content by funnel stage. SaaS Marketing Strategies That Work A successful SaaS marketing strategy is multi-channel and user-focused. The greatest SaaS content marketing practices are the following: 1. SaaS Content Marketing Onboarding new users and educating them to use guides, blog posts, eBooks, and webinars. Solution to problems, use cases, and flaunting expertise should be the content of the discussion. 2. SEO and Organic Traffic Quality leads are gained with solid search results. Use fine industry keywords and long-tail search keywords in the feature or pain points. 3. SaaS Email Marketing Drip campaigns, onboarding, and feature rollouts turn behavior, turning leads. Email remains one of the best conversion and retention tools. 4. Product-Led Growth (PLG) Let the product speak for itself. Free trials or freemium levels allow users to experience your value proposition for themselves. 5. Paid Performance Marketing Scale reach with Google Ads, LinkedIn Ads, and retargeting. Keep SaaS marketing metrics in balance at all times, attempting to measure ROI. 6. Review and Referral Programs Ask happy customers to review on G2 or Capterra and incentivize them with discounts or credits as referrals. Building a SaaS Marketing Funnel A SaaS marketing funnel is a paying customer and a little bit more. Here’s how to create one: Top of Funnel (TOFU) – Awareness Tactics: SEO, blog, social, PPC ads Objective: Traffic and brand awareness Middle of Funnel (MOFU) – Consideration Tactics: Case studies, webinars, gated content Objective: Convert visitors to leads and educate them Bottom of Funnel (BOFU) – Decision Tactics: Free trials, demos, price pages, comparison sheets Objective: Convert leads into paying customers Retention Funnel Tactics: Support, onboarding, newsletters, in-app messages Objective: Churn prevention and loyalty building Tracking how the users are engaging with the funnel keeps the marketer aligned with where the users are dropping off and optimizing at every stage. Tools Used for SaaS Marketing The right SaaS marketing tools can automate, scale, and optimize for you. Must-haves are: 1. CRM & Automation Tools: HubSpot, ActiveCampaign, Salesforce Usage: Follow up leads, automate email sequences, score leads 2. Analytics Tools: Google Analytics, Mixpanel, Amplitude Use: Track user behavior, conversion funnels, campaign ROIFunctions: 3. SEO & Content Tools: Ahrefs, SEMrush, Clearscope Use: Keyword research, backlink checkup, content optimization 4. Social & Ads Management Tools: Buffer, Hootsuite, Google Ads, LinkedIn Campaign Manager Usage: Scheduled posts, start paid campaigns 5. Email Marketing Tools: Mailchimp, Drip, ConvertKit Use: Use to onboard, for drip campaigns, customer retention emails These are the foundation blocks of a successful SaaS digital marketing agency stack that encourages in-house teams or third-party partners to scale. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation SaaS Growth Hacking Strategies SaaS growth hacking is high-urgency growth hacking to find scalable growth hacking strategies. These are safe bets to try: 1. Viral Loops Share per share by referral, in-app invitation, or shareable attribute, e.g., Dropbox’s “get extra space” referrer campaign. 2. Freemium to Premium Upsell Offer limited features for free, and upsell interested customers to paid plans through value-based invites. 3. Behavioral Triggers Trigger behavior-led upgrade or engagement emails, like periodic feature utilization. 4. A/B Testing Test price pages, email subject lines, CTAs, and feature highlights to ensure the highest conversions. 5. Partner Integrations Boost visibility and adoption by natively integrating into apps your target user base already uses (e.g., Slack, Zapier). The greater hacking, the greater creativity, velocity, and instantaneous failure are the covert ingredients to some SaaS marketing hack. SaaS Marketing Errors to Avoid Even old-school teams screw up preventably. These are SaaS product marketing mistakes that occur often: Forget onboarding: Murky starts cause churn. Keep it easy with tooltips, tutorials, and guided setup. Missing selling to existing customers: Don’t miss-sell to your existing customers, you already have. They are less expensive than new ones. Vanity metric abuse: Page views and likes aren’t covering the mortgage. Use actual SaaS marketing metrics like CAC, LTV, churn, and MRR. No positioning: Customers need to understand what pain you are alleviating in 10 seconds, or the messaging is horrible.
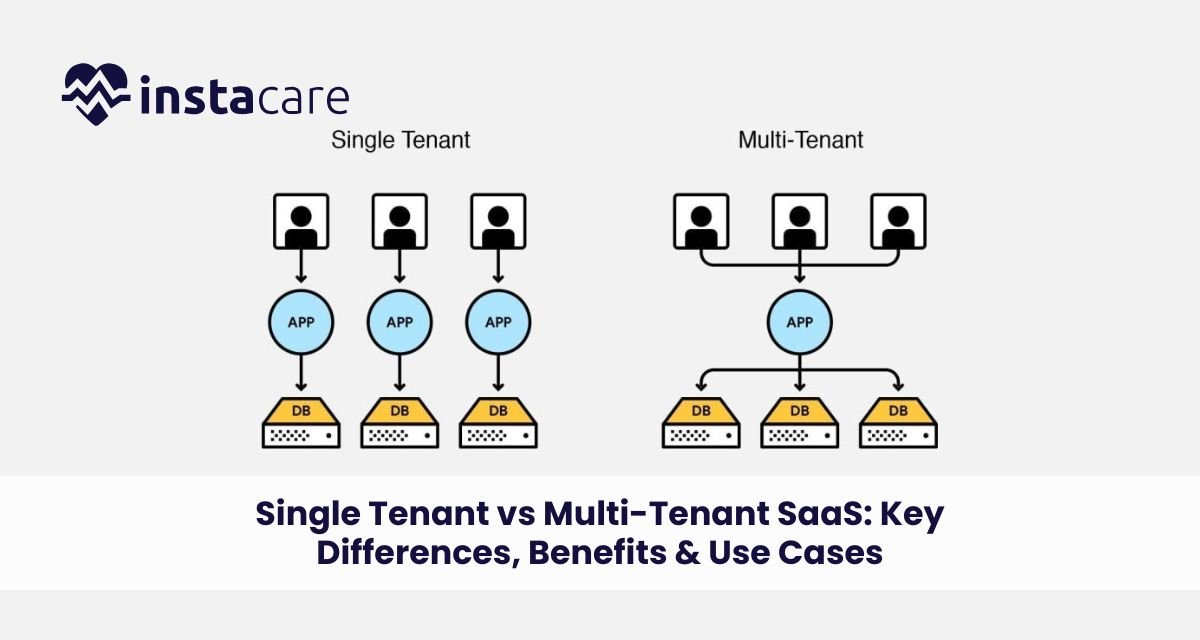
Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant SaaS: Key Differences, Benefits & Use Cases For cloud apps, SaaS (Software as a Service) is the dominant model of software delivery at scale. Perhaps the most important design choice for SaaS vendors, and their customers, is to use either a single-tenant or multi-tenant SaaS solution. Each has different advantages, trade-offs, and operational concerns. For IT leaders, product managers, and CTOs, it is worth knowing what is single tenant, what is multi tenant, and single tenant vs. multi tenant. It directly affects performance, security, cost-saving, scalability, and long-term success. What Is SaaS Tenancy? SaaS tenancy is the way the tenants, users or organizations are segregating or sharing software resources within a SaaS application. Here, a “tenant” refers to one customer or group of customers using the software. What is Multi Tenant? Multiple customers are sharing a single instance of an application and database, and data segregation at the application level in a multi-tenant SaaS model. What is Single Tenant? In a single-tenant SaaS, one customer has his or her own dedicated software environment, complete database isolation from all other customers. Multi tenancy in cloud computing is important because it impacts product design, deployment strategy, and operational overhead. What is a Single-Tenant SaaS Model? The solo tenant SaaS definition is in the sole resource dedication: every customer has his or her own isolated software environment. It involves separate databases, application tiers, and infrastructure. That isolation also provides complete customization, greater control over updates, and greater security. This is incredibly reassuring in compliance-heavy industries such as healthcare or finance. Use cases for single tenant saas through Isolation of the tenants is also one of the largest benefits to the model and enables compliance requirements per tenant to some standards and per-tenant performance optimizations. Though it offers independence and flexibility, the cost of single tenant vs multi-tenant tends to be higher because of replicated resources and intricate maintenance. What Is a Multi-Tenant SaaS Model? Multi tenant SaaS model is a method of hosting multiple companies or users within one instance of software. Each tenant has his or her data logically isolated even though they are on the same infrastructure. This style maximizes the use cases for multi tenant saas, its resources, accelerates rollouts, and maintains affordability. It’s the norm for the majority of contemporary SaaS platforms. Organizations that appreciate velocity, scalability, and efficiency in operation like this architecture. However, tenant isolation depends so much on safe application logic that security in single tenant vs multi tenant becomes an issue of utmost priority concern, particularly for organizations dealing with sensitive information. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Main Differences: Single-Tenant vs Multi-Tenant Let’s analyze the difference between single tenant and multi tenant along major technical and business considerations: Isolation: Complete tenant isolation in saas is available in single-tenant; multi-tenant provides logical isolation. Customization: Simpler in single-tenant because of isolated environments. Cost: Multi-tenant less expensive with shared resources. Upgrades: Simpler to handle in multi-tenant with global upgrades; single-tenant can have specific rollouts. Scalability: Multi-tenant supports high growth, consistent with scalability in SaaS architectural objectives. Performance: Comparison of single-tenant and multi-tenant performance leans in favor of single-tenant when dealing with high workloads, although current multi-tenant systems are very tunable. The differences facilitate groups in matching infrastructure with strategic goals. Advantages of Single-Tenant SaaS Establishing the pros and cons of single tenant begins with its greatest advantages: Increased Security: As every customer is on its silo, it is not open to security breaches by other tenants. On a plus with workload-intensive companies with high compliance needs, security in multiple tenant vs single tenant is a big plus to the latter. Performance Thresholdlessness: There is no noisy neighbor issue. It has consistent performance and is unaffected by other customers, and this is desirable with high-throughput workloads. Customization and Control: Customers may order specific features, integrations, or settings that won’t affect others. This is particularly appropriate in specialized enterprise spaces. Compliance-Friendly: Most regulatory systems (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) are simpler to comply with in single-tenant systems because of increased audit trails and control. All these characteristics explain why most applications for single tenant SaaS cover sectors such as healthcare, banking, legal technology, and government. Advantages of Multi-Tenant SaaS The pros and cons of multi tenant replicate its excellent efficiency and scalability benefits: Low Cost: Shared infrastructure reduces operational expenses, such that the model is optimal for mid-market and startup SaaS products. Easy Scaling: Centralized administration of resources makes it easy to add new tenants or users, priceless in high-growth situations. This is perfectly in harmony with today’s scalability in SaaS architecture principles. Faster Updates: Centrally pushed updates, patches, and fixes are applied, cutting technical debt and allowing for fast iteration. Simplified DevOps: DevOps is easier to keep simple when working with a single infrastructure and codebase setup. Similarly, typical applications for multi tenant SaaS include eCommerce websites, CRM systems, team collaboration tools, and other high-traffic applications. Challenges of Each Model While both tenancy models have advantages, they each come with trade-offs: Single-Tenant Challenges Higher Cost: More admin, more infrastructure. Complexity of Updates: Multiple instances to update is a time-consuming activity. Reduced Operational Efficiency: Hard to automate and standardize processes across customers. Issues of Multi-Tenanting Security Risks: If not well architected, a weakness in one tenant seeps into others. Customization Limitations: Shared environments limit customized deployment. Performance Instability: Resource-intensive tenants cause system performance instability in general. Organisations must balance these in the single tenant vs multi tenant cost dilemma. New Emerging Trends: Hybrid & Flexible Architectures To accommodate
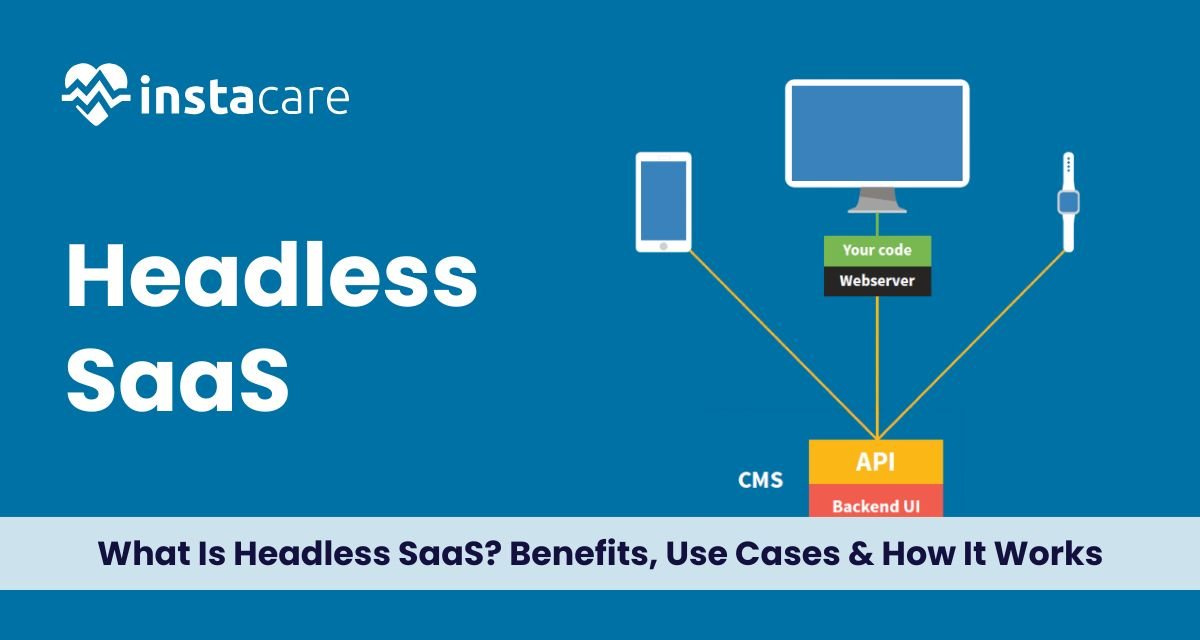
What Is Headless SaaS? Benefits, Use Cases & How It Works The modern digital age demands flexibility, agility, and user-oriented personalization. Enter Headless SaaS as a game-changer. Unlike traditional software-as-a-service solutions, Headless SaaS decouples the frontend presentation layer from backend functionality, providing businesses with unmatched control over user experience. With API-first SaaS, headless architecture, and composable SaaS platforms now available, companies can now tailor digital interfaces to unique needs without being restricted by inflexible templates. Whether an expanding eCommerce business or to handle multi-channel content strategy, Headless SaaS delivers flexibility that traditional platforms can’t provide. What Is Headless SaaS? Headless SaaS is a software-as-a-service that distinguishes frontend and backend. It means developers can use whatever tech they want to create the user interface, and yet the backend services remain intact through APIs. It is a name that is taken from headless CMS, content management systems that are used to store and deliver content without a hardcoded frontend. Headless SaaS platforms, in the same way, are designed to serve SaaS backend decoupling to enable brands to construct experiences on web, mobile, IoT, or even voice platforms. This frontend-agnostic SaaS strategy enables users to create a consistent backend logic and tailor the frontend according to branding, UX, and device-specific requirements. This enables organizations to create faster, more dynamic digital solutions that are easy to scale in the long run. How Headless SaaS Works? At the center of headless software development is the decoupling principle. Decoupling occurs between the frontend and the backend, where the central business logic, data, and APIs reside. Headless API integration is what developers employ to link the two levels together. This pattern flourishes on APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), which serve as bridges between the user interface and the backend services. In a microservices in SaaS architecture, individual components such as content delivery, payment, authentication, or user management can be separated and deployed separately. Let’s consider headless eCommerce platforms for example. The product catalog, the checkout process, and the inventory are all backend elements that are not touched, and the customer-facing UI can be fully custom-built or customized without impacting core functionalities. Key Benefits of Headless SaaS 1. Full Customization With frontend-agnostic SaaS, developers can have total control over what their application looks and feels. This works best for stunningly well-designed brands or those with multi-platform businesses. 2. Agility and Speed Independent rollout of frontend changes minimizes downtime while allowing for rapid experimentation. This modularity is at the heart of composable SaaS platforms, allowing businesses to create best-of-breed solutions. 3. Future-Proofing By being API-first SaaS, your tech stack is up to date. New platforms (e.g., voice assistants or smartwatches) can be integrated without full system refactoring. 4. Better Performance Because the headless software development pattern allows for streamlined frontends with only what’s required, applications load quicker and respond better. 5. Scalability Microservices in SaaS architecture make each service component scalable in isolation as per demand, which leads to system performance and reliability improvement. All of these headless SaaS advantages combined provide the top-notch agility, which is not possible for traditional platforms. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Typical Use Cases of Headless SaaS Headless SaaS is more than just a buzzword and is driving innovation in different industries. Some of the headless SaaS use cases where its promise shines through are listed below: 1. eCommerce Headless eCommerce sites enable online stores to provide blazing-fast, interactive shopping experiences. Merchants can utilize various frontends for mobile apps, web stores, or kiosks with a single backend for operations. 2. Content Management Tools Headless CMS software is becoming popular among publishers and marketers requiring multichannel delivery. Content can be reused by websites, applications, and digital signs with centralized APIs. 3. No-Code & Low-Code Applications With headless SaaS no-code frontend, even non-technical people can develop frontend interfaces because developers keep complex backend logics in isolated. This enables marketing and product teams to work with velocity. 4. SaaS Platforms That Require Flexibility If your solution is for enterprise customers requiring white-labeled or very customized interfaces, customizable SaaS solutions with a headless backend provide the optimal setup. These headless SaaS applications demonstrate why this trend is becoming the norm for companies needing agility and innovation at scale. Headless SaaS vs. Traditional SaaS Headless SaaS disconnects the frontend from the backend, giving users more flexibility and customizability. Between headless SaaS vs monolithic SaaS, Traditional SaaS employs a static, monolithic architecture with limited flexibility in design. Headless SaaS enables companies to serve content to infinite platforms through APIs, making it more appropriate for omnichannel experiences. Headless SaaS is easier to implement but restrictive as the needs increase. You use Headless SaaS if you require speedy, tailored, and scalable solutions; for simple requirements, Traditional SaaS can still function. Is Headless SaaS for You? Before you spend money on headless SaaS, think about what you currently need and what you might need in the future. Do you require omnichannel delivery? Does frontend customization become important? Are you looking for internationalization or personalization? Is your development team API-aware or headless API-focused? If you said “yes” to most of these, then the headless SaaS advantages of flexibility and scalability will be ideal for you. However, if you want a shoe-box solution with minimum customization, an orthodox approach will remain appropriate. Companies that embark on SaaS backend decoupling typically reap long-term paybacks, especially in innovation cycles, user experience, and performance. Issues to Consider While the headless SaaS benefits are significant, headless SaaS does come with its own set of challenges: 1. Higher Development Effort Custom frontends need skilled teams. You’ll also need developers experienced with headless software development and microservices in SaaS environments. 2. Increased Complexity Managing decoupled systems involves handling multiple moving parts, APIs, security layers, and integration pipelines. 3. Upfront Costs Although scalable in the long run, initial setup with customizable SaaS solutions may be costlier than plug-and-play platforms. But for businesses prepared to pay
B2B SaaS vs B2C SaaS: Key Differences, Strategies & Business Models Software as a Service or SaaS transformed the consumption of software for the better. Nobody downloads software onto a local machine anymore or purchases single-off licenses anymore. People and companies use software and applications from the cloud on a subscription basis today. SaaS operates anywhere, selling productivity software to organizations or a one-person language tool. Not every SaaS company is the same. The market is divided into two general categories: B2B SaaS (Business-to-Business) and B2C SaaS (Business-to-Consumer). You need to know how B2B and B2C SaaS differ from each other since product creation all the way to marketing and selling is affected by whether you sell to a business or end-customer. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental differences between B2B and B2C SaaS, showcase examples, dive into business models, and highlight top SaaS go-to-market strategies, including how to drive growth, revenue, and retention in each category. What is SaaS? SaaS is a software application computer software that is offered and used through the Internet. Instead of manually installing software, users can access the service from any computer. Software is typically pay-per-use and, in some cases, includes ongoing updates, cloud storage, and technical support. There are two broad categories: Examples of B2B SaaS: Salesforce, HubSpot, Asana, business, professional-, and team-developed applications to achieve efficiency and collaboration. Examples of B2C SaaS: include Netflix, Duolingo, Spotify, and software products intended for end-users for self-enhancement, education, or entertainment. All SaaS products, audience or not, are based on good SaaS business models with recurring revenue, scalability, and an emphasis on long-term user stickiness. B2B SaaS vs B2C SaaS: Key Differences While both B2B and B2C SaaS products deliver value as cloud software, customer acquisition, customer retention in SaaS, and customer finding for them are different. Let us explore the difference between B2B and B2C SaaS in a little more detail. 1. Audience & Buying Decision B2B SaaS is marketed and sold to organizations’ groups, teams, or departments. It is rational, systematic, and often multi-decision-maker buying. To illustrate, a CRM like Salesforce will need to flow through marketing, sales, and finance approval before selling. It is reversed, however, in the case of B2C SaaS. The consumer is a person. The purchase experience is emotional and spontaneous. An application like Headspace is installed by a user after viewing an ad, a recommendation, or even trying to solve a personal issue. 2. Sales Cycle It’s a long, complex B2B SaaS sales funnel. It’s product demo, pricing negotiation, contract negotiation, and onboarding. It can be weeks or months long, depending on company size. B2C SaaS, though, has a very low sales cycle. It’s usually the instance of a new user discovering a product and signing up, especially when there is a freemium. 3. User Experience & Design One of the more fundamental B2B vs B2C SaaS UX design distinctions is likely functionality vs simplicity. B2B UX is marvelous features and customization. The sites are all about efficiency, integrations, and enterprise-scale reporting. B2C UX is simple and enjoyable. It has to be usable, desirable, and fast because people make instant usability judgments. 4. Customer Retention Customer retention is worth it in both models but executed differently. Retention is founded on high support, onboarding, and longer behaviors in B2B SaaS. Stakes are involved; it is hard to switch if a business is dependent on a tool. In the B2C SaaS customer journey, they churn more unless a product is creating near-immediate value. Businesses therefore use in-app reminders, gamification, and content refreshes to keep individuals around. Business Models in B2B and B2C SaaS Your revenue model has an enormous impact on your capacity for scaling and expanding your business. Let’s compare the B2B SaaS vs B2C SaaS revenue model and configurations. B2B SaaS Business Models Subscription Tiers: By user base, feature set availability, or usage. Annual Contracts: Longer term-based contracts with discount or support included. Usage-Based Pricing: Customers pay for consumed usage (e.g., API calls or stored usage). B2B SaaS lead generation pays off and typically includes webinars, whitepapers, demos, and outbound. B2B SaaS isn’t surprising to be shown with household names such as Zoom (business), Monday.com, or Notion for Teams. B2C SaaS Business Models Freemium: Cost-free, low-featured plan with the choice to upgrade. Monthly Subscriptions: Low-price, cancel-at-will plans are perfect for intermittent users. In-App Purchases: Most commonly applied in education and wellness apps. B2C SaaS user acquisition is primarily driven by paid media, viral marketing, app store visibility, and influencer marketing. A few popular B2C SaaS include YouTube Premium, Grammarly, and Calm. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Marketing & Growth Strategies for B2B and B2C SaaS Alright, so let’s find out here how marketing varies between both SaaS types, i.e., what are the most effective marketing strategies, channels, and go-to-market SaaS strategies? B2B SaaS Marketing Strategies Content Marketing: Educate your audience through blogs, guides, and case studies. Account-Based Marketing (ABM): Messaging by business or role. LinkedIn Ads & Outreach: Best to reach decision-makers and professionals. Email Nurturing: Most required when employed for a long B2B SaaS sales cycle. Operational pain points will most likely be solved by ROI, logic, value, and solution-based B2B SaaS marketing strategies. B2C SaaS Growth Hacks Viral Loops: Referral and social sharing programs (e.g., Dropbox’s notorious growth hack). Push Notifications: Scheduled automatic reminders bring users back to the app. Gamification: Streaks, badges, and leaderboards encourage activity. Influencer Marketing: Surf the wave of social influencers’ trust. B2C SaaS growth hacks rely
Open Source vs Proprietary SaaS: What are the differences, advantages & disadvantages? Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) has become the cornerstone of much modern-day business activity. From CRM software, project management software, to marketing suites, SaaS solutions are being used in nearly every sector. However, companies need to make a crucial decision: open source or proprietary SaaS? Information regarding the open source to closed source model is key when selecting the perfect investment. Both contain certain pros and cons that can affect customization, flexibility, support, cost, and long-term growth. This article provides an extensive SaaS software comparison to help you make the right choice. What Is Open Source SaaS? Open source SaaS is cloud software written using publicly available source code. Businesses can learn, modify, and host the application on their server. The procedure is popular among developers and technically savvy teams who need to have greater control. Transparency is the largest open source software benefit. Since the code is available, organizations can audit the code for security vulnerabilities, modify features as per their need, and contribute to future software development. The majority of SaaS open source platforms are open source and are licensed under MIT, GPL, or Apache. They are put under different SaaS licensing models that offer free or altered use depending on meeting their terms. What is Proprietary SaaS? Proprietary SaaS is software owned, hosted, and created by a vendor who retains full control of the code. The product is accessed by subscribers and is delivered in its entirety over the web. Neither do they have ownership of the source code nor low-level modifications. Proprietary SaaS applications can include pre-packaged functionality, an easy-to-use interface, and technical support connectivity. Maintenance, data security in proprietary SaaS, infrastructure, and software updates are vendor-responsible, offering a hassle-free one-stop solution. This is the optimal path for companies that want simplicity and stability, especially when in-house development skills are not immediately available. Key Differences Between Open Source and Proprietary SaaS There are some proprietary software limitations. The most significant difference is customization and control. Open source provides the complete freedom of the codebase, whereas proprietary software locks the users into a single product. In the matter of customization, the customization in SaaS is significantly stronger in open source systems since developers can customize the platform to precise specifications. Open source platforms are more technically demanding to install, administer, and grow. Private platforms don’t have to be used straight from the box, however, and are appealing to businesses that value simplicity over highly customized solutions. Also, pricing models are diverse. Proprietary SaaS features is sold on a subscription basis that may include support, hosting, and maintenance. Open source SaaS may be less expensive to start with, but may require ongoing support and external maintenance. Advantages and Disadvantages of Open Source SaaS Advantages One of the best open source SaaS advantages is that it gives control to you. You can deploy the platform on your hardware, personalize code to fit your business processes, and create custom features not found in mass-market offerings. The cost of SaaS platforms is generally lower with open source since you lack ongoing vendor licensing costs. This is fantastic for startups or businesses walking a tightrope. Open source also gives you the maximum open source flexibility; you’re not locked into a vendor’s roadmap or ecosystem. You decide what to upgrade, when to upgrade, and how to take the platform forward. Disadvantages Despite open source software benefits, it requires in-house technical expertise. Installation, upgrades, and debugging are difficult to accomplish without a capable development team. Support typically occurs via web forums unless you shell out money for expert support. User interfaces can’t match proprietary ones, and documentation is a chance. Pros and Cons of Proprietary SaaS Advantages With proprietary SaaS, the app software company does everything, from hosting and updates to security and backups. The whole deal is attractive to firms that desire reliability without servers to maintain or developers to retain. Easy-to-use design, easy onboarding, and instant customer support access are standard on most platforms. Properly secured proprietary SaaS is a benefit as well because the vendors spend a lot of time protecting data, compliance, and threat blocking. These choices are perfect for those who need to go fast and do not have the technical burden of open source platforms. Disadvantages A major downside is lack of control. You can’t alter the way the software is behaving outside of what’s in the settings. Such restrictions on proprietary software constrain innovation, especially for organizations that need specific process specifications. Another problem is SaaS vendor lock-in. Your business is locked into a single vendor, who can raise price, change terms, or shut off features. Changing to another solution later on is expensive and labor-intensive. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Deciding Between Open Source and Proprietary SaaS You still get to pick the model that’s appropriate for your company. If your company wants control, customization, and innovation, then open source would be the appropriate selection. It supports extensive configuration, can handle special workflows, and avoids licensing danger. You also get to make the platform decisions according to your internal standards. If convenience, speed, and total vendor support are paramount, proprietary SaaS is probably the answer. It’s ideal for teams that need to “plug and play” without care about code-level changes or infrastructure. For companies with shallow technical depth, convenience and scalability of proprietary products are hard to beat. Scalability of open source SaaS will be heavily dependent on the quality of how it’s hosted and built. Installed properly, it can scale to SaaS for enterprises loads. But it does not happen automatically. Proprietary solutions, however, scale with you day one. Conclusion There is no one-size-fits-all approach for anyone in the open source vs closed source SaaS conversation. Instead, it’s just a matter of your business model, budget, internal capability, and road map forward. If you need something you can install, build on, and deploy wherever you wish, then open source offers uninhibited freedom. If your utopia
SaaS Churn: Mitigating Customer Turnover and Maximizing Retention Churn is perhaps the most important business metric for SaaS businesses. Customer loss to competitors or de-adoption can wipe out sustainable revenue growth in the long term. Incremental retention rate improvements can lead to phenomenal growth in recurring revenue, company value, and customer lifetime value. Having understood what is SaaS churn, monitor the right churn metrics, and take measures to minimize churn and maximize retention, you’ll build your subscription business on stronger grounds. In this, we’ll take a look at what exactly churn is, how to measure it, and effective steps to minimize it, and improve customer loyalty in SaaS and maximize retention at each step. What is SaaS Churn? Churn in SaaS is the percentage of clients who do SaaS subscription cancellations within some time frame, most commonly a month or year. It is also known as the customer churn rate and is either lost revenue or lost customers. It is so easy to calculate the monthly churn rate: sql CopyEdit churn rate formula (%) = (Customers Lost During Period ÷ Total Customers at Start of Period) × 100 For instance, if you began the month with 500 customers and 25 departed, your monthly churn would be 5%. Churn can also be measured as a percentage of revenue, or, as it is sometimes referred to, revenue churn or net revenue retention (NRR). NRR is recurring revenue retained that accounts for expansions or upsells, giving a fuller picture of retention performance. How to Measure Churn Effectively? Churn is not a metric. Segmentation and measurement of various types of customers at their lifecycle are required for proper user churn analysis. Some of the most important metrics include: Customer Churn Rate: Tracks the percentage of customers within a specific period. Revenue Churn Rate: Compiles recurring revenue lost as a percentage of first total revenue. Voluntary vs Involuntary Churn: Segments’ reason for churn. Monthly vs Annual Churn: Monitors trends over time to spot seasonal or subscription-duration effects. Net Revenue Retention (NRR): Accounts for upsells, cross-sells, and expansions minus lost revenue. By examining these metrics and analyzing which customer segments churn most, you’ll gain invaluable insights into customer lifecycle management and identify the most effective SaaS retention strategies. Strategies to Minimize Churn and Enhance Retention It’s not a matter of lowering churn, it’s a matter of showing value in each and every interaction point. Some effective ways of lowering SaaS churn are: 1. Enhance Onboarding Experiences New customers are most susceptible in their first days or weeks. Poor onboarding is the leading cause of early churn. Develop a seamless, frictionless onboarding process that guides new users to the “wow moment.” Product tours curated for every user, tutorial emails, and welcoming in-app tips will have customers discovering value in no time. 2. Prioritize Customer Success A single unified customer success team can track account health, observe usage, and react early to customers who appear to be disengaged. A successful customer lifecycle churn management tool puts the customer in the best possible position to get the right support, training, and check-ins, before they become cancellation drivers. 3. Personalize Customer Experience Customers love personalization. Use past behavior history and goals to personalize product experience and communication. Personalized recommendations, milestone reminders, and feature suggestions drive stronger loyalty and better retention. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation 4. Get Customer Feedback Gather customer feedback regularly, particularly at milestone lifecycle stages, and pay close attention to it. Actively incorporate it into your product plan so that your customers can hear themselves. By listening to what hurts them, you can address problems in the bud before they become churning causes. 5. Provide Flexible Plans Fixed pricing and contracts deter customers. Try flexible price plans, annual payment discounts, or “pause” terms to accommodate different budgets and lower cancellation. 6. Boost Engagement Regular value-added content engages customers. Product update announcements, expert webinars, training sessions, and success stories highlight additional features and enable customers to optimize subscription value. Regular engagement boosts retention and loyalty. 7. Offer Customer Support Customers tend to leave after open cases of support or a poor support experience. Provide multiple channels of support, live chat, help center, phone support, and monitor first-response and resolution rates very intensely. Supported happy customers stick around. 8. Enhance Product-Market Fit Customers occasionally leave because they weren’t a good match. Periodically review customer bases and make sure messaging is aligned with actual product strengths. Focus on acquiring and retaining the type of customer who requires what you’re best at. How to Minimize Involuntary Churn Whereas involuntary churn is usually the result of dissatisfaction or misfit, involuntary churn is the result of non-failed payments, i.e., expired credit cards or failed transactions. It can be prevented by proper measures: Automatic Payment Retries: Use dunning measures, which retry failed payments after a few days. Payment Reminders: Alert customers when their credit card is expiring. A gentle reminder avoids declined payments. Provide an Alternative Payment Method of Choice: Provide customers with an alternative payment method of choice, such as PayPal, Apple Pay, or direct debit, to increase success rates. Leverage Payment Dunning Software: Payment dunning software will send reminders to customers automatically after they fall behind on a transaction, so follow-up is convenient and the administrative cost is minimal. Conclusion Reducing SaaS churn is crucial to thrive in the long term with SaaS. Understanding what SaaS churn rate is, monitoring user churn behavior regularly, and applying tested retention and dunning tactics will minimize loss and facilitate sustainable growth. Proactiveness in the detection of at-risk customers enables you to catch them with the right communications and incentives before they go away. In addition, frictionless payment and renewal, with multiple payments
Future of Chatbots in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Engagement and Medical Services Healthcare industry is undergoing a shift towards digitalization where AI chatbots in healthcare are being established as a revolutionary solution to healthcare delivery. These is how these high end tools, driven by natural language processing in healthcare, are changing the ways patients interact with medical providers. Virtual health assistants are at the forefront of using care by making it easier for appointments to be scheduled, among other things. As the Healthcare technology trends continue to evolve, chatbots will most likely be part of the modern medical systems and assist in getting better outcomes, become more efficient, and enhance patient satisfaction. What are Chatbots? Chatbots are applications that pretend to imitate a human conversation with the use of AI and machine learning. They are able to interpret and answer user queries in real time using text or voice. In healthcare, conversational AI in healthcare is a term used for these intelligent bots intended to communicate with the patients, medical staff, and healthcare systems. These chatbots learn from huge medical datasets and are capable of doing anything from answering simple health questions to triaging patients. With AI in patient support, chatbots are no longer restricted to roles of Q&A interactions but are emerging as active players in the delivery of healthcare. Applications of Chatbots in Healthcare It has as a result of medical chatbot applications, it has been into various use cases in the medical field. These are some of the most exemplary cases for healthcare chatbot use: Appointment Scheduling and Reminders: Patients’ engagement tools such as chatbots may schedule, reschedule or cancel appointments automatically without involving human beings. They also send reminders thus reducing no-show rates and increasing efficiency of the clinic. Triage and Symptom Assessment: Chatbots for medical diagnosis can analyse symptoms based on structured questions and provide an adequate solution as a next step. These bots employ AI algorithms in directing the patients to emergency care, at-home remedies, or follow-ups. Mental Health Support: Chatbots for mental health provide round the clock support for those with anxiety, depression, or stress. These bots are used to give coping strategies, monitor the mood of users, and link users to mental health professionals whenever necessary. Telemedicine Integration: Telemedicine chatbots facilitate distance consultations by acquiring patient history, recommending specialists, and instructing users to establish video calls. They make telehealth services easier to be accessed and less scary. Medication Reminders and Management: By connecting with pharmacy systems, chatbots can prompt patients to use medications, warn them of the probability of side effects, and arrange the refill of the prescriptions. It enhances better compliance and health outcomes. Health Education: Virtual health assistants are very good at delivering evidence-based information about diseases and preventative measure as well as betterment of ways of living. They are trained to offer accurate and comprehensible health education. Administrative Assistance: Chatbots can be useful to Insurance companies and hospital billing departments because they can be used to answer FAQs and facilitate the processing of claims and insurance verification. It is a key catalyst of healthcare automation. Benefits of Chatbots in Medical Services The advantages of application of the AI Chatbots in healthcare are far-reaching as they extend to the patients, healthcare deliverers as well as the health care administrators. Some of the most potent Benefits of AI chatbots include the following: Enhanced Patient Engagement: The patients of today demand instant answers and smooth communication. Patient engagement tools such as chatbots provide real-time interaction and as such enhance satisfaction, promote proactive health management, and yield trust. Round-the-Clock Accessibility: Unlike human staff, chatbots work 24/7. This availability at all times will help patients to obtain care information and/or support whenever they need to, which is essential for chronic conditions or mental health cases. Reduced Operational Cost: Automation through chatbots ensures that their tasks in the healthcare field include automating repetitive duties such as answering questions, making appointments, or simply processing paperwork, thereby minimizing administrative costs and the loads borne by the staff. Improved Accuracy and Consistency: Virtual health assistants, unlike human agents, do not tire and get distracted. They provide reliable information each time hence eliminating the chances of miscommunicating or human error on each patient encounter. Scalability and Flexibility: Hospitals can implement chatbots to facilitate high volumes of queries without straining in human resource. Whether in the flu seasons or pandemics, bots can scale themselves without compromising their quality. Data Collection and Analytics: Chatbots collect well-defined information about the behavior, preferences and feedback of the patient. This data is priceless in enhancing service delivery, patients’ needs and health care plans reorientation. Empowerment of Healthcare Staff: Taking over the redundant, non-critical tasks, the chatbots release doctors, nurses and the admin staff to engage in high-value patient-centered activities. This leads to improved care quality and staff satisfaction. Book Free Demo Chatbots vs. Traditional Healthcare Communication Conventional healthcare communication is based on human contact, whereby phone calls, physical visits, and emails are used extensively. Although personal, this method is time-consuming and only available during business hours and is subject to delays. Patients have to wait for a long period, face inconsistent information, and experience administrative bottlenecks. Unlike AI chatbots in healthcare that are instant, 24/7, they offer answers, appointments scheduling, symptom assessment, and even mental health support. Empowered by natural language processing for healthcare, chatbots guarantee consistent and correct responses and can process thousands of queries at the same time – something that traditional systems are unable to do. Besides, chatbots enhance patient engagement tools as they provide individual attention and tips while relieving the staff members. They also gather and analyze data to improve decision-making and services. Although not a substitute for human feeling, virtual health assistants enhance medical teams as they simplify communication and access. When it comes to the Future of digital health, efficient and accessible, it is clear that chatbots are shaping it as healthcare automation
The Future of API Integrations in Healthcare Technology is changing the landscape of health. In technological advancement today, API integration of EHR systems is cited as the most important and the biggest impact of technological advancement in creating new chances for delivering quality care and improving operations as well as service provision. APIs are application programming interfaces that connect various healthcare systems for easy communication among hospitals, clinics, pharmacies, and laboratories, and payers, making it simple for all of them to share data. Unison of communication extends from the interfacing across the different platforms, allowing healthcare professionals to access all patient information in real-time, which is likely to affect developing better-informed and better quality services. As healthcare data evolves, and becomes increasingly complex, the demand for Health tech APIs, which can manage and work with high volumes of patient data, is exploding. Specifically, FHIR healthcare APIs have arisen as a strong tool for making this process easier. FHIR ensures the easy sharing of all kinds of medical data between different healthcare systems by promulgating standardized formats of sharing medical data interchange. Understand the Current Landscape of API Usage in Healthcare APIs or application programming interfaces are the things which connect different software applications, which allows good communication and exchange of the data between those applications or pieces of software. APIs for health care allow different systems like electronic health records and lab information systems to connect to billing systems more easily, even with health systems in insurance. One of the most promising developments is the FHIR Healthcare API trends (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources), which are helping in the standardization of data formats and Interoperability in healthcare. FHIR is a health information exchange (HIE) framework designed to facilitate data exchange and understanding from system to system under the auspices of HL7. Furthermore, integration of third-party health applications has expanded the scope of healthcare systems and is considered to uplift patient engagement and personalized care. When incorporated through APIs, these apps can access and add to patient records and are capable of scheduling appointments, sending medication reminders, and tracking health. Some Benefits of API Integrations in Healthcare The optimization of healthcare systems through integrating APIs into them brings a multitude of benefits: Enhanced Data Exchange: APIs allow patient information to be shared in real time over several different healthcare platforms, thus allowing better coordination between the providers. This results in better and more timely decisions, hence, delay in care is reduced and better care outcomes are achieved. By making sure that all the healthcare workers involved will have the same current information at their disposal, API integration reduces the chances of misunderstanding. Improved Patient Engagement: Through patient data APIs, it is possible for a patient to get hold of health records, lab test results, prescriptions, and their treatment plans with ease. This flexibility allows patients to become agents in their health management and establish a partnership with their medical caregivers. It encourages them to stick more closely to treatment plans and has better long-term health outcomes. Operational Efficiency: By automating administrative procedures, e.g., appointment scheduling, verification of insurance, and handling the billing cycle, the burden of manual workload is reduced on healthcare staff. Not only does this reduce people’s errors, but it also increases the rate at which administrative procedures are carried out, subsequently, the healthcare organizations will spend fewer resources and can concentrate more on looking after patients. Innovation and Flexibility: APIs set the infrastructure on which continuous innovation in healthcare is based. They enable Healthcare organizations to rapidly develop and incorporate new applications/services which would respond to the emergent needs. Whether it’s a telemedicine platform or a new mobile health application, or an AI-enabled diagnostic equipment, APIs provide the ability to change according to the changing dynamics of the industry. Secure Data Handling: The patient-sensitive nature of healthcare data calls for strong protocols for the security of patient privacy. The use of secure API healthcare techniques would allow healthcare entities to guarantee that data is encrypted and safely transmitted according to industry standards such as HIPAA. This is useful in protecting the patient information from cyber-attacks, building a relationship of trust between the patient and his/her healthcare provider, as well as adherence to legal and regulatory requirements. Adding these benefits results in more productive healthcare operations and higher satisfaction ratings for the patient, along with easier application of innovative solutions aimed at addressing the ever-changing needs of the sector. Book Free Demo Emerging Trends Of API Integration in Healthcare Shaping the Future Multiple tendencies are forming the future of API integrations in healthcare: Real-Time Data Access: The escalating demand for real-time healthcare data enables providers to make quick, knowledge-based inferences in case of emergencies or normal care, thus enhancing patient outcomes. Personalized Medicine: Now, APIs are facilitating the integration of genomics data, biometric readings, and history of a patient to form highly customized treatment plans with advances in personalized medicine. Telehealth Expansion: With increased mainstreaming of telemedicine, APIs become important to link everything, make the EMR API integration smooth, and ensure data sharing is secure between doctors and patients. This continuity of care improves accessibility of care, especially for remote populations. Integration with Wearables: As smartwatches and fitness trackers become popular, health data exchange APIs are now capturing real-time information such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels, providing a wider perspective into patients’ health. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: APIs are making AI-powered tools be integrated into the healthcare system. This integration boosts the quality of predictive analytics, helps in early diagnosis, and also boosts the support of clinical decision-making. Systems can provide more accurate evaluations and tailored treatment suggestions by interfacing with algorithms in the form of APIs. Challenges Ahead Related to API Integration in Healthcare However, several obstacles keep APIs from being well-integrated in healthcare systems: Data Standardization: It is still a major barrier to getting uniform data formats on different systems, which affects the efficiency of the health