EDI in Healthcare: Meaning, Benefits, and How It Works To a great extent, the healthcare sector relies on data that is delivered correctly, at the right time, and in a safe manner among providers, payers, clearing houses, and regulatory authorities. With the increasing volume of patients and administrative needs, manual organization of data has proven to be ineffective and inaccurate. This is where healthcare EDI becomes very important. The EDI system has redefined the way healthcare institutions deal with billing, claims, eligibility, and compliance. Electronic data interchange healthcare systems enhance efficiency, cost reduction, and regulatory compliances by substituting paper-based operations with standardized electronic communications. EDI has become an essential part of the new healthcare management and revenue cycle. What Is EDI In Healthcare? EDI in healthcare is a term used to refer to the formal fallout of administrative and financial data between healthcare organizations through electronic interchange. Data transmission between parties is done in standardized digital formats which can be processed automatically by computer systems instead of sending paper forms, emails, or faxes. Healthcare EDI is mostly applied in the insurance claims, eligibility checks, payment remittances and prior authorizations transactions. These transactions are formatted to strict rules that are accurate, consistent and interoperable across systems. EDI healthcare systems assist companies to facilitate the smooth running of operations, decrease errors and have quick communications among the stakeholders in the organizations. How EDI Works In Healthcare? The EDI procedure in the healthcare is generalized into a systematic workflow that guarantees data accuracy and compliance. Every step will ensure information between systems is validated, translated and sent in a secured manner. A conventional EDI procedure consists of: Healthcare information development in a billing or EHR system of a provider. Transformation of data to standardized EDIs. Transmission via an EDI clearinghouse or through direct connection. Error checking and validation. Payment to the payer-receiving party. Response generation and processing. A clearinghouse that handles EDI is usually an intermediary, setting the data to payer-specifications before submitting. This process will minimize rejections and fast-track the reimbursement processes. Common EDI Transactions In Healthcare Healthcare organizations also depend on a very extensive variety of EDI transactions to facilitate their daily administrative and financial functioning. All the types of transactions in the revenue cycle have their purpose. Typical EDI transactions in healthcare are: The EDI claims processing (837) is used to present insurance claims. EDI to check patient coverage (270/271) To monitor claim progress, claims status inquiries (276/277) are claimed. Remittance advice (835) of payment and adjustment information. Previous authorization forms (278) The enrollment and disenrollment (834) Such transactions allow communication between providers and payers to proceed faster and curtail administrative work. EDI Standards Used In Healthcare Healthcare EDI depends on standardized formats to be used in order to achieve consistency and interoperability. These standards describe the arrangement and transfer of data. The most popular healthcare EDI standards are: The major standard of the healthcare administrative transactions is ANSI X12. The HIPAA EDI transactions also require certain format to be used by the covered entities. Pharmacy-related transactions are usually handled using NCPDP standards. The standards of healthcare EDI help to guarantee effective communication between various systems irrespective of the software vendor and the size of the organization. Benefits Of EDI In Healthcare EDI has considerable operational and financial benefits to healthcare organizations. EDI enhances efficiency at the revenue cycle by automating administrative processes. Key benefits include: Fewer paperworks and manual data entries. Quicker claims filing and refunding. Better quality of data and a reduced number of errors. Reduced administration and operation expenses. Improved scalability to expand companies. Enhanced patient satisfaction by speedy billing. The use of EDI billing software in medical billing has a significant part in the maximization of these advantages through incorporating EDI processes into the healthcare finance platforms. Challenges Of EDI Implementation Even with its benefits, the introduction of healthcare EDI may be a challenging task, especially when applying it to a smaller organization or a company switching to old systems. Common challenges include: Initial set up and integration costs are high. Multifacetedness of payer-specific regulations. Continued upkeep and modification. Problems of data mapping and compatibility of format. Training and change management of the staff. These issues can be resolved by means of proper structuring, supporting the vendor, and constant monitoring of the system. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation EDI And Healthcare Compliance A very important factor in healthcare data exchange is compliance. The EDI systems will be required to meet stringent regulatory aspects in order to safeguard patient data and provide legal responsibility. Such areas of key compliance are: Compliance with HIPAA EDI transactions guidelines. Protected information transfer and encryption. Audit trails and tracking of the transaction. Effective access laws and identification. Not adhering to the EDI rules may lead to rejection of claims, the fines, and the rupture of reputation. EDI product lines that are compliance-oriented assist the organization to remain in line with regulations. Best Practices For Implementing EDI In Healthcare The implementation of EDI must be done strategically and in a structured manner. Best practices in organizations will increase chances of attaining efficient and scalable results in the long run. Best practices would be recommended as: Choosing good EDI billing software and partners. With an established EDI clearinghouse. Normalization of internal data. The regular testing and validation. EDI Workflow and compliance training. Tracking performance and error rates of transactions. These measures can be used to guarantee a seamless integration and long term operational dividends. Future Of EDI In Healthcare The future of healthcare EDI is closely associated with the use of digital transformation and interoperability efforts. With the development of healthcare systems, EDI is still improving to meet new technologies and regulatory needs. Emerging trends include: Connection with cloud-based systems. Artificial intelligence in terms of increased automation. Increased interoperability to EHR systems. Increase of real-time eligibility and authorization tools. Greater emphasis on analytics and reporting of data. Although newer technologies like APIs are becoming a topic of focus, EDI is still part
MVP in Healthcare: Building Smarter Digital Health Solutions Digital innovation is essential in the rapidly changing healthcare sector to address patient needs, automate clinical processes, and be in line with the industry standards. An MVP in healthcare is one of the most effective methods to implement a digital health concept into practice. A minimum viable product in healthcare enables an organization or a start up to test the main features of the product, see feedback with the users, and prove the business idea prior to spending large amounts of money on a complete solution. With an emphasis on fundamental functionalities, healthcare MVP reduces the risks, spares resources, and shortens the time-to-market. What is MVP in Healthcare? A Healthcare MVP is a streamlined digital health solution that has only the essential features that can show value to the users. It is designed to: Confirm assumptions using actual patients, physicians or medical personnel. Gather practical feedback on product enhancement. Minimize the financial risk of full scale development. Make sure that healthcare regulations are met in time. In comparison to consumer applications, healthcare MVPs have to be highly privacy, data security, and clinical reliable. Challenges in Healthcare Product Development Producing digital products in healthcare is associated with some distinct challenges, which include: Hurdles to regulations: HIPAA and other local compliance measures. Data privacy issues: How to secure sensitive patient health data. Complexity of integration: Making sure that it is compatible with the current electronic health record software. Clinical accuracy: Prevention of mistakes in high-stakes processes in healthcare. User adoption: Facilitating adoption by the medical and patient community. With a digital health MVP, teams can solve these issues during the initial stages and minimize the mistakes that are expensive to fix in the future. What Makes a Healthcare MVP Different? The nature of healthcare MVPs is different compared to conventional technology products due to the stakes involved. Major differences will be: Demand in HIPAA compliant MVP healthcare solutions. Putting an emphasis on patient safety and clinical effectiveness. Tough requirements of validations and testing. Concentrate on the interoperability with the current healthcare IT systems. Healthcare MVPs should focus on trust and security, as well as compliance with regulations but also should not forget to provide practical user value. Key Components of a Healthcare MVP Creating a healthcare MVP requires the addition of features that will indicate real-world clinical and administrative requirements. Components often include: Basic capacity to undertake the primary healthcare issue. Patient data storage and access security. Convenient access to health information by health care providers and patients. Monitoring outcome analytics dashboard. Notifications or telehealth integration are tools of communication. An effective Healthcare app MVP is a balanced functional, compliance, and use app. Benefits of MVP in Healthcare MVP has a number of strategic benefits: Quick time-to-market: Pilot the product to the users. Economy: Do not invest on features that might not be necessary. The user-cantered design: Add actual feedback to enhance functionality. Compliance: Be sure that they comply at an early stage. Risk mitigation: Assume validation prior to full scale launching. MVPs are particularly useful to healthcare start-ups who can prove their value to investors and enhance their patient care. Common Healthcare MVP Use Cases Healthcare MVPs may be used in a number of purposes, which include: Telemedicine Software: Testing, secure video consultation. Digital health applications: Symptom tracking or scheduling an appointment (early-stage). Healthcare SaaS MVP: hospital/clinic cloud-based tools. Patient engagement solutions: Medicine adherence reminders. Remote surveillance systems: Wearable vitals monitoring. The use cases assist in establishing the feasibility, adoption possibility as well as the clinical impact of the solution. Steps to Build an MVP in Healthcare To develop a successful MVP, a process must be involved. Key steps include: Diagnose the problem: Figure out patient or provider pain points. Identify target audience: Determine who to use the product. Priority: Add only the necessary features. Prototyping: Design a prototype (a wireframe or clickable prototype). Create MVP: Develop the basic solution containing secure and compliant infrastructure. User testing: Gather user feedback on healthcare professionals and patients. Test and optimize: Optimize features with real-world data. This is to provide a functional, validated and user-friendly product. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Regulatory and Compliance Considerations The issue of compliance is a crucial point in healthcare MVP development. Key considerations include: Assuring MVP healthcare standards of data protection that are HIPAA compliant. Implementing the use of encryption and patient encrypted authentication. Maintaining clinical decision and patient interaction audit trails. Staffing in line with FDA digital health solutions. Reporting on all the development processes to be reviewed by the regulatory authorities. Compliance with laws is not a voluntary exercise but it guarantees confidence and mitigates the legal risk. Measuring Success of a Healthcare MVP To define the success of an MVP, medical teams are supposed to monitor the following indicators: Rates of adoption and engagement amongst users. Clinician and patient feedback. Clinical data error-free and reliable. Decreasing workflow inefficiencies. Healthcare organization benefit or profit on investment. These lessons are used to guide the subsequent product development and to scale the solution. Scaling from MVP to Full Product Once a healthcare MVP has been validated,
Data Analytics in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care and Decision-Making Technology is causing a significant shift in the healthcare industry and one of the most influential changes is the introduction of healthcare data analytics. Data analytics is transforming the decision-making and care delivery processes of healthcare organizations, whether it is the desire to improve patient outcomes or to streamline hospital operations. Due to the increasing amount of medical records, diagnostic reports, wearable device data, and administrative information, healthcare systems cannot be dependent on intuition-based analysis anymore. Analytics helps in making accurate diagnoses, effective treatments and improved long-term planning by transforming raw data into valuable information. Consequently, clinical data analytics has emerged to be part of the fabric of the modern, data-driven healthcare decision making. What Is Data Analytics in Healthcare? Analytics in hospital management is a process that involves the systemic gathering, processing and analysis of health related information with the aim of enhancing clinical and operational results. It is the study of huge amounts of data concerning several sources to determine patterns, trends, and correlations that can be used in decision making. Key aspects include: Clinical and administrative data collection. Manipulation and storage of multifaceted data. Determining patient outcomes trends and patterns. Promoting clinical decision-making. This is based on the use of healthcare analytics software to convert all complex data into a simple, actionable information. Types of Healthcare Data The healthcare systems produce tremendous data on a daily basis. To analyze it successfully, it is necessary to understand what kind of data is involved. The typical examples of healthcare data are: Medical histories, lab findings, imaging reports and physician notes Clinical data. Administrative and billing documentation. Wearable and mobile health-related data provided by patients. Population health and demographics. Clinical trial data and research. Good health care data management will see that this data is accurate, secure and useful. Types of Data Analytics Used in Healthcare Various tools of analysis are used depending on the purpose and complexity of data. The main types include: Descriptive analytics to make sense of the events in the past. Causal and relationship diagnostic analytics. Predictive analytics in healthcare and risk and outcome forecasting. Prescriptive analytics to prescribe based on insights. Combined, these strategies make it possible to provide proactive and preventive health care. Key Applications of Data Analytics in Healthcare AI and data analytics in healthcare is important in various health care operations. Key applications include: Analytics of clinical data to make the correct diagnosis and custom-designed treatment. Trend and chronic condition population health analytics. Hospital management analytics to enhance staffing and scheduling and resource utilization. Treatment success and outcomes of patients. Assisting in the planning and policy decisions in the health of the population. These applications improve the quality of care and system efficiency of a patient. Benefits of Data Analytics in Healthcare Patients, providers, and organizations have numerous benefits associated with healthcare analytics. Major benefits include: Better diagnostics and treatment planning. Improved quality of care and patient safety. Less operation costs and wastage of resources. Improved healthcare business intelligence use in performance tracking. Quick and better-informed decisions. Altogether, analytics make the healthcare system more efficient and patient-driven. Role of AI and Machine Learning in Healthcare Analytics The embarkation of AI and data analytics in the healthcare system has increased the levels of analytics tremendously. Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Large and complex data analysis using automation. Pattern recognition of early disease detection. Risk assessment of patients by a predictive model. Clinical decision support systems in real-time. These technologies keep on enhancing precision with the availability of more data. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Challenges in Healthcare Data Analytics Healthcare analytics has multiple challenges, even though it has its benefits. Common challenges include: Weak data or incomplete documentation. Problem with assimilation of information across systems. Lack of experienced data and analytics experts. Expensive cost of implementation and maintenance. Opposition to the adoption of data-driven practices. These are the essential challenges to overcome in order to adopt analytics successfully. Data Security, Privacy, and Compliance HIPAA security is a highly important healthcare analytics issue. Key considerations include: Enhancing adherence to healthcare data rules. Securing information against cyber attacks and information intrusions. Applying encryption and authorization. Undertaking frequent security audits. Effective healthcare data management contributes to the preservation of trust and law. Future Trends in Healthcare Data Analytics New technologies keep changing healthcare analytics. Key future trends include: More real-time healthcare analytics used in making immediate decisions. Growth in the big data in healthcare through genomics, wearables and IoT devices. Increased use of AI-based predictive and prescriptive analytics. Expansion of personalized and precision medicine. The trends will also improve the quality and efficiency of care. Implementing Data Analytics in Healthcare Organizations A practical implementation of analytics should be well planned and executed. Essential steps include: Setting clear operational and clinical objectives. Investing in quality healthcare analytics software. Educating employees on data insight interpretation and use. Promoting interdisciplinary teams, IT and leadership. Upon putting in place good policies on data governance. An organized strategy guarantees sustainability in the long run and value. Conclusion Healthcare is being transformed by data analytics into making more intelligent decisions, achieving better patient outcomes, and streamlining operations. With the help of sophisticated analysis tools, healthcare organizations can convert complicated data to valuable information that will underpin high-quality care. With the further development of AI, machine learning, and real-time analytics, the role of analytics in healthcare is going to grow. To create a robust, effective, and patient-centered health care system, it is critical to adopt data analytics. FAQs What does healthcare data analytics do? It seeks to process health data in order to optimize patient care, efficiency, and to facilitate informed decision-making. What is the benefit of predictive analytics to healthcare providers? It aids in predicting risks, patient outcomes and resource requirements in order to provide proactive care. Does the hospital management benefit from the help of data analytics? Yes, it enhances the efficiency of operation, minimizes expenditures, and maximizes resources.
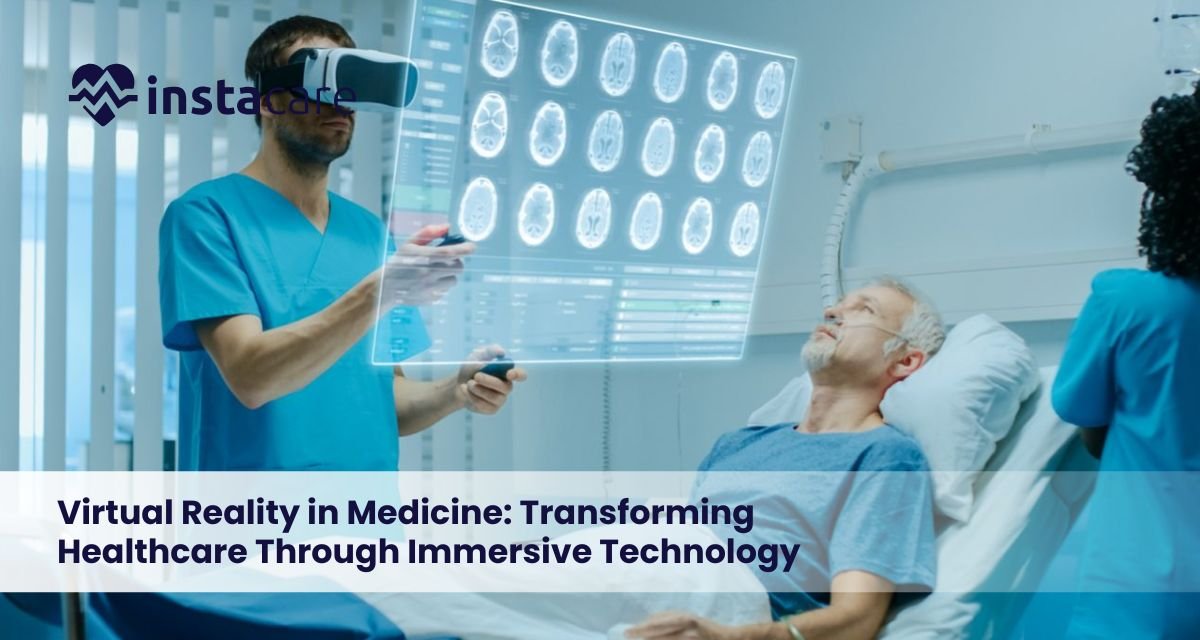
Virtual Reality in Medicine: Transforming Healthcare Through Immersive Technology The medical field is experiencing the digital revolution, and the idea of immersive technology in medicine is the focal point of the revolution. VR has not been restrained to entertainment anymore, but is currently being implemented in hospitals, medical schools, and therapy centers. VR is transforming healthcare delivery, whether it is creating more accurate surgery or making the procedure more comfortable. The use of modern medical virtual reality applications can provide healthcare workers with the opportunity to train in a safe manner, treat patients better, and increase clinical results thanks to real simulations. What Is Virtual Reality? Virtual reality refers to a three-dimensional environment and is a simulated environment created by computers and experienced by users through VR headsets and motion tracking devices. The major features of VR are: Complete involvement in an online world. Live communication with virtual objects. A great deal of visual and sensory stimulation. Augmented reality vs virtual reality in healthcare is a common comparison in healthcare-related discussions. Whereas AR is used to overlay digital objects on the physical one, VR is more preferable for training, therapy, and simulation-based care as it is fully immersive. How is Virtual Reality Used in Medicine? Virtual reality has clinical uses in many spheres of healthcare and has been used to benefit both the practitioners and the individuals receiving care. VR is commonly used for: VR in medical training and skill building. Treatment and therapy of patients. Virtual reality surgery simulation and planning. Physical recovery and rehabilitation. These applications indicate the way that VR for patient care enhances safety, accuracy, and involvement in the medical environment. VR in Medical Training and Education Medical training VR has altered the way medical workers understand complicated practices. Virtual reality medical education allows students to practice again and again without any risk in the real world. Perks to education include: Interactive 3D learning of anatomy. Simulation of emergency response. Procedural accuracy in a virtual reality simulation of surgery. Less use of cadavers and live patients. This simulative method enhances self-esteem, decision-making and technical ability. Virtual Reality in Patient Treatment The use of VR therapy in healthcare as a therapeutic tool is gaining more and more use. In the healthcare sector, VR therapy is used to control physical and mental health. Some typical uses of the therapy include: Virtual reality for pain management. Lessening anxiety and stress. Diversion therapy of chronic pain. Preoperative emotional preparation. The patients feel more comfortable, less dependent on medications, and their recovery is more successful. VR in Surgery and Clinical Practice VR promotes planning and execution in surgical settings. Virtual reality surgery simulation enables surgeons to practice complicated surgeries using patient-specific information. Clinical benefits include: Higher accuracy of surgery. Less risk of complications. Greater comprehension of the patients through graphic explanations. Improved cooperation between teams of medical workers. The developments enhance credibility and overall quality of care. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Virtual Reality in Medicine The benefits of virtual reality in the healthcare systems include: Increases learning experiences. Enhances the level of patient engagement and satisfaction. Embraces VR rehabilitation therapy. Reduces medical errors. Makes the process of treatment personalized. Increases medical education. VR is transforming the field of modern medicine through its ability to bring together innovation and empathy. Challenges and Limitations Although it has potential, VR adoption has a number of obstacles: Expensive initial costs of setup and maintenance. Training and technical complexity. Dizziness or eye strain to others. Data security and privacy issues. These limitations would have to be tackled in order to increase the use of medical virtual reality applications. Future of Virtual Reality in Healthcare The future of virtual reality in medicine is bright. VR will be combined with wearables, telemedicine platforms, and artificial intelligence with the advancement of technology. Possible future developments are: AI-based simulated personalized treatments. Remote VR-based medical training. High-level exposure to virtual reality therapy. More extensively used in mental and physical rehabilitation. Such innovations will turn VR into a commonplace feature of healthcare provision. Real-World Examples Virtual reality is already changing patient outcomes across the globe. Examples include: VR in PTSD and anxiety Phobia virtual reality exposure therapy. Stroke rehabilitation therapy using VR. Immersive distraction programs for pain management. These practical applications indicate the increased clinical effects of VR. When VR Is Most Effective in Medical Settings? VR would be best applied in a situation where simulation, visualization or emotional involvement is needed. It works best in: Healthcare education and training. Pain and anxiety management. Mental health therapy. Physical rehabilitation. Preoperative preparation and rehearsal. Immersive and controlled digital experiences are very useful in such environments. Conclusion VR is revolutionizing the medical field by contributing to better education, patient outcomes, and clinical efficiency. Immersive technology in medicine is transforming the medical field with VR in medicine training, therapy, and surgical uses. With an increasing number of issues addressed with virtual reality and increased accessibility, patient care, education, and clinical practice will remain redefined worldwide. FAQs What is the application of virtual reality in medicine? Medical training, surgery simulation, pain management, rehabilitation, and mental health treatment are some of the areas where medical virtual reality applications are applied. Does virtual reality work in the management of pain? Yes, virtual reality for pain management is useful in decreasing the perception of pain, which distracts the brain and decreases anxiety. What becomes of virtual reality in healthcare? The future of virtual reality in medicine involves AI-driven simulations, customized therapy, and broader application in everyday clinical use.
Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy: A Breakthrough in Mental Health Treatment There has been a rapid development in the field of mental health treatment through the incorporation of superior technologies. One of these new innovations has been the Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy (VRET), which has become a revolutionary way of treating anxiety-related and trauma-based conditions. VRET combines psychological principles with immersive digital worlds to provide clinicians with the ability to provide controlled, repeatable, and measurable therapeutic experiences. VRET is also transforming the models of delivering exposure-based interventions as part of greater Digital mental health therapies and is providing easier, more accurate, and personalized therapy. What Is Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy? Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy is a type of psychotherapy that involves the use of immersive and computer-generated environments to subject the patient to anxiety stimuli in a safe and controlled environment. It is a continuation of the old-fashioned exposure therapy based on cognitive-behavioral, and it is generally known as Exposure therapy using virtual reality. In contrast to the imagination-based or in-vivo exposure, VRET allows patients to undergo realistic simulations, which are very similar to real-world situations. This is especially useful in mental health because Virtual reality therapy in mental health allows people to create an image of situations they fear or find themselves in unprotected locations, making it a recognized form of Virtual reality psychotherapy. How Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy Works? VRET is performed with the help of head-mounted displays and senses that make a patient experience virtual environments. In therapy, the clinicians progressively present fear-inducing stimuli as they take patients through coping mechanisms that include breathing, cognitive restructuring and emotional regulation. The treatment is usually made on a hierarchy-based exposure model. Patients begin with lightly wrongful situations and as they become more tolerant, they advance to more difficult situations. This method corresponds to Technology-assisted exposure therapy, which provides clinicians with fine control of the intensity, duration, and repetition of stimulus. Conditions Treated with VRET VRET has proved to be effective in a broad scope of psychological disorders especially in anxiety and disorders related to trauma. Some of the common uses are: VR therapy for anxiety disorders, including generalized and situational anxiety VR treatment for phobias, such as fear of heights or flying Virtual reality PTSD therapy for trauma survivors, including veterans and accident victims Simulated social interactions through VR therapy for social anxiety VR therapy for panic disorder, focusing on exposure to physical sensations and triggers Such applications illustrate the growing Clinical applications of virtual reality in psychology, particularly where avoidance behavior is prominent. The Science Behind VRET VRET is based on the neuropsychology and the theory of learning. Exposure therapy operates in the form of habituation, extinction learning and cognitive restructuring. The virtual settings stimulate the neuro-circuitry that is connected with the fear arousal in real life, allowing emotional processing and desensitization. According to studies of functional imaging, VRET affects brain areas that are a part of fear regulation, including the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. This neurobiological interaction justifies its application in psychotherapy in virtual reality where therapeutic learning is generalized into real life. Benefits of Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy VRET has many benefits compared to conventional exposure-based interventions: Great degree of control over therapeutic stimuli Secure and non-confidential treatment setting Closer interaction with patients via immersion Recurrent and personalized sessions Less logistical hindrance than in in-vivo exposure These strengths highlight the overall VR therapy benefits and effectiveness, particularly for patients who avoid or discontinue traditional therapy, and support discussions around VR therapy vs traditional exposure therapy. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Effectiveness and Research Findings The effectiveness of VRET in various disorders has always been supported by clinical research. The results of meta-analyses demonstrate similar or better results than those of traditional exposure therapy, especially in the field of phobias, PTSD, and social anxiety. Research has shown that VR therapy, compared to conventional exposure therapy, will more likely lead to increased patient acceptance and reduced drop-out rates. Also, the benefits of treatment are long-term, implying lasting therapeutic effects. The accumulation of evidence makes VRET an evidence-based and valid intervention. What a VRET Session Looks Like One of the standard VRET sessions is assessment and psychoeducation. The therapist illustrates the virtual world, goals and coping skills. Patients next put on a VR headset and are taken into a simulated scenario in accordance with his/her treatment objectives. In the process of exposure, therapists observe physiological reactions and emotions in real time. VR cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) techniques are frequently used in sessions and are a combination of exposure and cognitive reframing and behavioral skills training. Debriefing after the session supports learning and monitors progress. Challenges and Limitations The lack of access to VR tools and specialized software can be expensive, making it less available in specific clinical settings. A small group of patients may experience motion sickness, eye strain, or discomfort. Ethical concerns include the privacy of patient data within digital platforms. Informed consent is essential due to the immersive nature of exposure. Therapist training and technical competency are required. VRET may not be suitable for individuals with severe dissociation or neurological conditions. These factors must be addressed to ensure the safe and ethical use of Immersive therapy for anxiety. Future of Virtual Reality in Mental Health The future of VRET is directly related to advancements in artificial intelligence, wearable sensors, and telehealth integration. Trends include personalized virtual environments and adaptive scenarios. With greater accessibility, virtual reality therapy in mental health is expected to expand beyond specialty clinics, reinforcing its role in modern psychiatric and psychological care systems. Conclusion Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy represents a significant advancement in mental health care, integrating psychological science with immersive technology. It enhances treatment precision and patient engagement through controlled exposure experiences. As evidence grows, VRET continues to strengthen its position within digital mental health care, offering scalable and personalized solutions. FAQs Is Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy safe? Yes, when delivered by trained professionals, VRET is considered safe and effective. What is the
Revolutionizing Healthcare: How Conversational AI is Transforming Patient Care Healthcare is undergoing a significant transformation due to the emergence of conversational AI. Hospitals, clinics and online health platforms are currently implementing AI-based tools that facilitate communication, symptom analysis and administration. The interaction between providers and patients is currently changing rapidly with the emergence of new technologies like AI chatbots for healthcare. This change is turning healthcare to be more accessible, efficient and personalized. What is Conversational AI in Healthcare? Conversational AI is a type of intelligent tool that can have a conversation with you, either in written or spoken form. This also covers virtual health assistants in the healthcare sector that can assist patients, provide responses to their questions, and even support medical personnel. Advanced algorithms, speech recognition, and NLP in healthcare in these systems to learn what the patient means and provide correct answers. These tools have promptly been embraced in healthcare organizations due to their capacity to handle large numbers of patients and also the elimination of administrative workload. Key Applications of Conversational AI Medical applications of conversational AI can be used in medical care in many ways, including as a clinical aid or as an administrative assistant. Among the most influential applications, there are: Automated Patient Support Hospitals are under a continuous stream of inquiries by patients. Conversational tools offer automated patient support, which enables the patients to receive responses 24/7. These systems deal with FAQs regarding hospital schedules, lab results, prescriptions and others as well- ease the burden of manual work, and take the strain off the staff when it comes to communication. AI-Powered Symptom Checkers and Triage The latest symptom checkers are AI-driven to assist patients in evaluating health issues at home. The tools gather the symptoms by natural discussion, interfere with medical databases, and propose symptoms on whether immediate attention should be applied. Smart AI triage systems also direct patients to the appropriate department, specialist, or emergency care, enhancing the response time and decreasing the number of visits. Enhancing Patient Engagement and Experience Patient engagement automation is one of the largest contributions conversational AI is making. Healthcare facilities can offer patients with automation that helps them with reminders, follow-ups, medication reminders, and wellness tips to keep them involved even after they have come out of the hospital. Administrative and Workflow Support Conversational tools facilitate communication, and organizational work in a busy setting. As an example, an AI-based solution applicable in a hospital helps nurses and doctors by retrieving patient information or updating their record or sending a message. Such tools minimize mistakes and speedy processes, which enhance the efficiency of hospital teams. Healthcare Chatbot Applications The emergence of healthcare chatbot applications is transforming digital patient experience. The chatbots assist in making appointments online, insurance, billing insights, and pre-admission. They are presenting a vital intermediary between the healthcare provider and patients in that they provide real-time, precise assistance without prolonged waits in the call center. Improving Digital Experiences Conversational applications are also improving the online patient experience by providing a smooth customer experience in mobile applications, telehealth, and hospital websites. Patients will feel free to communicate with a smart system that is fast to react, comprehends situations and offers explicit instructions. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Conversational AI in Healthcare Conversational AI is associated with numerous benefits that can be of benefit to both hospitals and clinicians and patients. 1. Improved Efficiency The AI makes the healthcare industry less burdened with routine tasks, and the health care provider is able to have time to attend to important cases. Thousands of interactions are handled in automated systems at a time reducing waiting time and speeding up the workflow in hospitals. 2. Enhanced Communication and Coordination Hospital-specific conversational AI for hospital communication in and out of the organization. Clinicians are able to get necessary updates quicker and the patients are notified timely and the healthcare teams are able to work together across the departments. 3. Cost Savings and Resource Optimization Conversational AI for hospitals reduces the expenses on labor since it decreases the necessity of manual operations, eliminates delays, and minimizes the use of hospital resources. 4. Better Clinical Support Assistants powered by AI offer medical professionals access to patient information and treatment plans and initial diagnostics in real-time. With these automation tools in healthcare, there is a great deal of human error minimization, and all decisions are made on the basis of appropriate information. 5. Improved Patient Outcomes AI-based care is beneficial to patients on a big scale. Improved adherence, reduced complications and increased satisfaction levels are achieved through better communication, on time reminders, and responsiveness. These improvements are indicative of the larger medical chatbot benefits that are currently being reaped by contemporary healthcare organizations. Challenges and Limitations Although conversational AI is positive, it is associated with a number of difficulties: Accuracy and Reliability AI technologies should be able to comprehend medical terms and patient-related information correctly. The wrong guidance may result in misinterpretation and that is why training and improvement are to be performed continuously particularly in case of using conversational interfaces in healthcare. Data Privacy Concerns Healthcare is a very sensitive matter. Before the adoption of conversational systems, it is essential to ensure the security of data, encryption, and adherence to the regulations, such as the HIPAA. Integration with Existing System Many hospitals have several systems of management. The incorporation of conversational AI into the EHRs, lab software, and billing systems may be complicated and involves technical skills and planning. Limited Human Touch Although AI is very efficient, there are still patients who like to be interacted with by a human being. The issue of striking the right balance between technology and individual care is one of the challenges facing most healthcare institutions. The Future of Conversational AI in Healthcare Conversational technology promises to have a promising future in the healthcare industry. The smarter the AI is, the more the hospitals will depend on the support systems that will act automatically.
How Digital Health is Shaping the Future of Medicine? The medical industry is experiencing a radical change, which is brought about by the Telemedicine advancements. Digital tools are transforming the experience and delivery of medicine, whether it is in patient care or hospital management. Knowing the trends in digital health is important to the providers, policymakers, and patients to move through this changing environment. Digital health is a combination of technologies, data analysis, and communication systems aimed at enhancing access, quality, and efficiency of healthcare. The future of healthcare technology will ensure that hospitals and clinics provide quicker diagnoses, treatments tailored to each person, and constant checkups to build a patient-centred healthcare system. What is Digital Health? Digital health is defined as the application of the use of digital technology to improve health care delivery and administration. It includes an extensive set of tools, starting with the telemedicine platforms and wearable devices and ending with AI-based diagnostics and electronic health records (EHR). Digital health has the primary aim of enhancing patient outcomes in addition to streamlining clinical operations. In comparison to traditional healthcare which has been largely based on the traditional face-to-face communication, digital health incorporates virtual health models, remote patient care, and mobile apps to ensure patients and providers remain constantly in touch. Key Components of Digital Health The most important elements of the digital health ecosystem are a combination that promotes efficiency, innovation, and patient-centered care. Evolution of Telemedicine: Remote visits enable patients to meet providers at any time and save them time on the road and enhance access to care. AI in Healthcare: Artificial intelligence assists with diagnostics, predictive analytics, treatment planning, and automation of administration. Remote Patient Monitoring: Sensors and devices that monitor patient health in real time allow preventive actions and chronic disease treatment. Electronic Health Records (EHR): Centralized records of patients enhance sharing and coordination of information and accuracy in the health care systems. Digital Therapeutics: Evidence-based computer applications control disease prevention, management, and rehabilitation. Health Data Analytics: Aggregation and analysis of patient data gives information on improved clinical and operational decisions. Combining these parts, a full-fledged patient-oriented digital care model will be created that enhances efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility. Key Stakeholders in Digital Health The healthcare innovation ecosystem is a diverse group of stakeholders that help to introduce and achieve success of digital health initiatives. Patients: The primary beneficiaries of digital health by having wearable technology, apps, and virtual care. Healthcare Providers: Hospitals, clinics, and individual practitioners who utilize technology in order to enhance service delivery. Technology Developers: Firms developing AI algorithms, computer programs, applications in mobile devices and medical devices. Pharmaceutical and Biotech Firms: Incorporating digital therapeutics into treatment and assessing drug effectiveness. Insurance Companies: Use Data to streamline the claims, risk management and enable telemedicine reimbursements. The idea of successful cooperation between these stakeholders will guarantee a successful digital transformation in healthcare that will produce tangible benefits to both patients and providers. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation The Flow of Value in Digital Health With the introduction of digital tools, the value flow in the healthcare sector has changed considerably. The providers can now predict the needs of the patient and act early instead of responding to them. Wearable, remote patient monitoring, and health data analytics data is processed through EHR systems and can be used to make predictive insights and customized care. The diagnostics and healthcare automation with the help of AI are used in hospitals to optimize the workflow, minimize errors, and increase patient satisfaction. Challenges in Digital Health Regardless of the potential, digital health has a number of challenges to overcome to be embraced by many: Privacy and security: Sensitive patient information mustn’t fall into the hands of hackers. Interoperability Problems: A large number of the systems are unable to interact with each other and impede the flow of data. Digital Literacy: Knowledge on how to use digital tools in a manner that is effective should be trained to both the patient and the providers. Regulatory barricades: Adherence to changing health technology regulations may hamper it. Cost Constraints: Costs of early technology adoption by hospitals and clinics may be high. These challenges need to be addressed in order to achieve the full potential of future of healthcare technology and secure sustainable use of digital health. The Role of Technology and Digital Transformation Digital transformation in healthcare exploits the use of advanced technology to improve the care of patients and operational effectiveness. AI algorithms can help to diagnose diseases with great precision, whereas digital therapeutics offer remote treatment. Telemedicine services lessen geographic boundaries and mobile health (mHealth) applications involve the patients when it comes to health management. Also, wearable health devices offer sustained monitoring, producing real-time data, which can be used to make clinically-related decisions. The combination of EHR and analytics will facilitate a smooth flow of information among providers and minimize errors and redundancies. It is a technology-based solution that changes the concept of healthcare delivery to a proactive, information-driven, patient-centered digital care system, with clinical decisions based on the information obtained through live data analysis. Opportunities for Optimization Digital health is associated with many opportunities to streamline healthcare delivery: Diagnosis with AI: Diagnosis will be quicker and more precise. Expansion of Telemedicine: The expansion of care to remote and underserved groups. Predictive Health Analytics: The early detection of risk factors to preventive actions. Integrated Digital Platforms: Connecting EHR, wearable to patient apps to enable data flow. Remote Care Solutions: Virtual care models and post-discharge follow-ups: chronic disease management. Automation of Administrative Processes: Release of clinicians to work on patient care with healthcare automation. These measures would lead to efficiency, cost reduction, and patient satisfaction, as well as create a continuous advancement in healthcare. The Future of Digital Health Medicine of the future is becoming more digital, patient-centric, and connected. New technologies such as AI,
HealthTech vs Biotech: What’s the Difference and Why It Matters The difference between HealthTech and Biotech remains the key to balancing biology with technology in advancing human health. The two industries have transformed the delivery of healthcare, biomedical science research, and patient outcomes, but differently. HealthTech is the use of information technology and computer technology to enhance healthcare accessibility and efficiency, while Biotech is the use of microbe processes and biological functions to create new medicines, treatments, and diagnostic equipment. Both created the unimaginable health and well-being world a decade or two decades ago. What Is HealthTech? HealthTech is the utilisation of computerised technologies such as wearables, telemedicine, and artificial intelligence to attempt to introduce more effective and improved methods of providing care and managing it. HealthTech industry trends are a sum of numerous innovations where digitalisation is attempting to find its place to sweep through the healthcare systems of the world. From AI-powered diagnostic devices to app wearables in mobile phones to monitor chronic disease, HealthTech patient zones the med, and even democratises it. A few of the prime HealthTech examples include Teladoc, Fitbit, and Babylon Health, providing telemedicine solutions, fitness tracking solutions, and AI-based diagnostic solutions, respectively. Apart from that, many HealthTech startups are in the process of going live worldwide and developing solutions to bridge the knowledge gap with healthcare information, make the patients more robust, and automate hospital procedures. What Is Biotech? What Is Biotech? Biotech is only one of the applications of living material, biological processes, and cell function for the manufacture of medicine products and solutions. Biotechnology is one of the areas of concentration in vaccine manufacturing, gene therapy, and targeted medicines. It is only one of the applications of biological material manipulation for medical, agricultural, and environmental problems. Some of the biotech examples include genetic engineering in insulin production, CRISPR gene editing technology, and monoclonal antibodies against cancer. Some of the biotech giants of history are Amgen, Genentech, and Moderna, which have pioneered life-saving drugs that save billions of lives worldwide. Biotech innovations like stem cell therapy, regenerative medicine, and organ-cultured organs are some of the biotech innovations in ushering a new age of science. Differences between HealthTech and Biotech While the two sectors have one aim, which is to make health outcomes a reality, the drivers function in operationally different manners: Type of Innovation: HealthTech is innovation led by digital platforms, software, and analytics, while Biotech is led by molecular biology, genetics, and biochemistry. Chief Focus: HealthTech concentrates on healthcare platforms, patient activation, and process improvement. Biotech concentrates on biological drugs and drug discovery. End Users: Biotech is primarily serving researchers, pharma, and physicians constructing biological products, while HealthTech is serving clinicians and patients requiring improved management tools. Regulation and Risk: Biotech is tougher in clinical trials and regulatory approvals, while HealthTech technologies are able to whizz through with little to no safety trials. Briefly, compared to digital health vs biotechnology, HealthTech is all about digital transformation and Biotech is all about biological innovation. How HealthTech Is Revolutionising Healthcare? HealthTech industry trends in the sector are exposing enormous investments in AI, IoT, and big data analysis that redefine the operational mode of health systems. From smartwatches tracking heart rate to electronic health records stored on the cloud, HealthTech is making care intelligent and personalised. Among the most exciting new emerging technologies in healthcare are predictive disease outbreak software, chatbots as 24/7 patient companions, and virtual reality simulation-based medicine training. HealthTech is also more accessible, particularly in rural areas, as it is web consultation- and telemedicine-compliant. Apart from that, there are even medical healthtech startups spearheading this transformation in technology. They’re transforming the conventional model of care and substituting it with network models to ensure real-time monitoring of the patient and dynamic intervention. How Biotech Is Changing Medicine? Pharmaceuticals are nowadays altered in genetic therapy, drug discovery, and regenerative Biotechnology in medicine. Due to enhanced research on DNA sequencing and bioengineering, Biotech has helped us eliminate diseases that were previously incurable. How biotech impacts healthcare medicine can be seen in how mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, gene therapy for disease cure of genetic diseases, and bioengineered cells for sensing and targeting cancer cells are made possible. Beyond disease cure, early diagnosis with biomarkers and genomically screening is what biotech promises. These biotech innovations are moving towards more specific, targeted therapy so that doctors can create personalized therapy in line with the lineage of a patient. This predict-to-react medication is, perhaps, the biggest hype of the past decades. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Points of Convergence between HealthTech and Biotech They differ but overlap. Where life science and data science interact has also given birth to a new hybrid healthcare innovation trend. For example, HealthTech’s artificial intelligence technology is now helping Biotech scientists to recognize drugs and genomics data analysis. This intermingling is creating smart laboratories where biological data are being computed with the assistance of advanced algorithms to guide the creation of new medicines. Wearables are monitoring physiological data used to execute clinical trials and biotech research. This intermingling of HealthTech and Biotech is thus creating a synergistic platform for therapy and diagnosis discovery. Challenges and Ethical Considerations Even though both of these industries have a huge potential, there are some negatives associated with them as well. HealthTech has issues of data privacy issues, cyber weapons attacks, and system compatibility. Biotech has issues of gene tampering, ethical scandals, cloning, and clinical trials. Secondly, regulatory overcomplexity is an innovation de-killer. HealthTech vs Medtech vs Biotech is also counterproductive to differentiate compliances on the basis of variation in degree of risk and ethics concern within respective sectors. Equal access to technology is also a necessary issue; both sectors must maintain affordance and accessibility at par so they would not augment the global healthcare gap. Future Outlook: Technology-Biology Convergence The future of HealthTech and Biotech is a wild amalgamation of digital and biological intelligence. Consider this AI to predict genetic disease or medicine by nanorobotics at
What is Chronic Care Management? Millions of patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, and asthma require continuous coordinated medical treatment. Their care does not consist of episodic visits to health care providers but is continuous observation, behavior modification, and preventive health. That is where the CCM services are needed. Chronic Care Management (CCM) provides managed care for chronically ill patients in a bid to enable them to have consistent, evidence-based care to improve outcomes, reduce hospitalization, and improve quality of life. What is Chronic Care Management? Chronic Care Management is the planned process of providing ongoing care and coordination to patients who have two or more Care coordination for chronic conditions that will probably persist for at least 12 months. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) created chronic care management CPT codes so that clinicians can get reimbursed for these priceless services. CCM patients are provided with coordinated care planning to target the personalized needs of each. The treatment is most often conducted outside the standard office visit and includes remote communication, personalized treatment modifications, and follow-up. Providers can use Medicare chronic care management programs to improve the health of patients and get compensated for time devoted to treating patients outside of the standard appointment. Key Components of Chronic Care Management In order to offer quality care, the providers must adhere to CCM program requirements that describe the step-by-step manner in which services are provided. The most important characteristics are: Comprehensive Care Planning: Creating a patient-centered, individualized care plan. 24/7 Access to Care: Permitting patients to call health professionals with questions at any time they arise. Medication Management: Continuous monitoring of medications and compliance to prevent complications. Care Coordination: Care coordination with specialists, primary care physicians, and support organizations. Follow-up: Ongoing contact, preferably by telephone or electronically, to track progress. Payment policy for Chronic care management reimbursement also compensates the healthcare provider financially to enable them to accept CCM practice so that the patient receives the appropriate care. Benefits of Chronic Care Management The benefits of CCM are to the patient, the clinician, and the healthcare system. The patients are positively benefited with routine monitoring, fewer complications, better compliance with medications, and better control of the disease. The clinicians are positively benefited with improved patient trust and better use of time. Macro-level, CCM reduces hospital readmission, emergency room utilization, and overall healthcare expenditure. Evidence suggests that CCM-enrolled patients would be at risk for adopting healthier habits, following care plans, and achieving improved quality of life. Practices are also provided with chronic care management software, which allows for automated billing, tracking, and documentation of patients thus, the process becomes much less time-consuming. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Who is Eligible for CCM? Patient enrollment into Chronic disease management programs is on the premise that the patient has two or more conditions endangering the health, functioning, or quality of life of the patient. Some of them include hypertension, diabetes, COPD, and arthritis. The patient should consent to being enrolled in a CCM program and sign an agreement consenting that one provider bills for CCM services for one month only. Patient eligibility for chronic care management also encompasses the fact that patients stand to gain from the intensity of monitoring and coordination, as opposed to episodic or acute care interventions. The Role of Technology in CCM Technology is at the center of providing quality CCM. Practitioners use remote chronic care management technology like smartphone applications, wearable tech, and telemedicine clinics daily to remain abreast of patients readings of their health readings and converse between visits. The technologies optimize patient participation by simplifying symptom entry, monitoring vital signs, and medication or lifestyle reminders. Higher computer technologies in chronic care management also assist providers with time documentation, reporting, and billing integrity for compliance. Technologies like Clinic Management Software, EHR Software, Patient Management Software, etc, advance not only to streamline operations but also enhance access to chronic care for residents in medically disadvantaged and rural communities. Challenges in Implementing CCM Though it has numerous positive features, CCM does have a downside. Perhaps the largest obstacle is searching for and keeping track of chronic care management billing guidelines, which are time-consuming and convoluted. More seriously, not all providers will be able to have staff or resources to provide twenty-four-hour care. Patients also present with barriers like restricted access to locations on the internet, insufficient knowledge about CCM programs, or inadequate adherence to care plans. Financial difficulties being in a position of can also make the process complicated, especially if the insurance benefits are not well understood. Also, having seamless coordination of care for serious chronic ailments by various experts is all a matter of proper communication and standard practices, which are not necessarily easy to adhere to. Future of Chronic Care Management CCM has a bright future with more emphasis on prevention, treatment and chronic disease management solutions. As soon as the healthcare delivery model is transformed into value-based care, the use of Chronic condition management versus value-based care will rise. CCM allows the providers to have access to improved health outcomes at reasonable costs, which is exactly the future in store for the advantage of value-based models. Further, with increasingly advanced digital health technology, CCM will now incorporate artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and personalized medicine. It will enable providers to be better able to know what to expect through pre-empting complications prior to the fact and to deliver even more anticipatory care. With evolving policies and growing utilization of digital health, comparison between chronic care management and master care management will be all the more needed as the providers would have to determine which model they could use for their patients. CCM will increasingly become more sophisticated as a standard of care for chronically ill patients. Conclusion Chronic Care Management is a holistic model of healthcare that gives patients with chronic disease integrated, continuous, and coordinated care. Organized CCM service programs improve the patient
What is Remote Therapeutic Monitoring? The health care industry is undergoing the process of digitalization as technology is revolutionizing the way care is being traditionally delivered. Telecare cannot be an indulgence anymore; it’s increasingly becoming a necessity, chiefly for chronic disease management, musculoskeletal diseases, and post-surgical recovery. Among the more recent innovations brought by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) is Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM), a care service to uphold the provider-patient relationship beyond the clinic. RTM allows health care professionals to track the status of a therapy patient in real time, maintain therapy sessions intact, and adjust them as needed. RTM bridges gaps between office visits with an illusion of uninterrupted care that speeds healing, promotes patient independence, and enables outcomes. What is Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM)? Remote Therapeutic Monitoring is the use of networked devices and computerized equipment to monitor non-physiological patient information such as musculoskeletal function, pain, medication, or functional ability. RTM differs from more traditional care plans in that clinicians can obtain reliable information without having to have patients visit the clinic on multiple occasions. For example, Remote therapeutic monitoring in physical therapy may involve monitoring patients’ adherence to their exercise as prescribed, monitoring improved mobility, or even pain flare reported through a mobile app. RTM in occupational therapy can also be activity of daily living-specific, like fine motor, grip strength, or functional independence. To simplify adoption, has developed several Remote therapeutic monitoring CPT codes for remote therapeutic monitoring to allow providers to be paid to review, message, and monitor patients. Coding is a giant leap in the direction of encouraging providers to incorporate RTM into routine care. How Does RTM Work? RTM operates through an amazing but coercive process: Data Collection – Progress is tracked by patients with applications, wearables, or associated sensors. For example, remote therapeutic monitoring devices might track gait, posture, or completion of exercises. Transmission to Providers – Data is securely transmitted with remote therapeutic monitoring software, which is linked to the provider’s clinical dashboard or EHR system. Analysis & Review – Providers assess information to ascertain whether or not the patient is adhering to the treatment plan and the efficacy of the treatment that has been followed. Communication & Engagement – Therapists provide feedback, encouragement, or adjust according to patient performance. A step-by-step in-home therapeutic monitoring process removes any phase from being omitted, from setting patient goals to data collection and altering treatment plans. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Remote Therapeutic Monitoring Benefits of Remote Therapeutic Monitoring to patients and medical professionals: Greater Patient Engagement – The patient is engaged directly in the treatment as they are monitoring progress and receiving immediate feedback. Better RTM and patient engagement heighten compliance with therapy. Reduced Recovery Time – Real-time data enables immediate intervention adjustments, which lead to better results of treatment. Convenience to the Patients – For rural or mobility-impaired patients, RTM spares them the inconvenience of making regular trips to clinics. Opportunities for Reimbursement – Remote therapeutic monitoring reimbursement opens opportunities for reimbursement for healthcare practitioners, thereby promoting digital health adoption with no additional cost. Musculoskeletal Specialized Care – Post-operative recovery, back injury, or arthritis are perfect conditions for RTM. Remote therapeutic monitoring for musculoskeletal conditions is one of the most rapidly changing uses. Case Example: Patient undergoing knee surgery has a wearable device with a sensor to monitor range of motion exercise. Automatically, the information is transmitted to the therapist, and the therapist is alerted that the regimen of rehabilitation treatment of the patient is off track. The therapist makes changes to the exercise regimen before the next visit, thereby preventing complications. Remote Therapeutic Monitoring vs. Remote Patient Monitoring All except the most sophisticated players are getting used to the Difference between RTM and RPM. While they’re similar, they address different objectives: Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is after physiological data like heart rate, glucose, or oxygen saturation. Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) is after therapeutic and behavioral metrics like exercise compliance, functional status, and patient-reported outcomes. From the compliance perspective, CMS guidelines for remote therapeutic monitoring suggest that RTM can be self-reported, while RPM needs to include device-derived physiological data. Having that data provides payers the opportunity to bill correctly, remain compliant, and choose the right service model for patients. Who Can Benefit from RTM? RTM is so versatile that it is worth it for so many practitioners and patients: Rehabilitation Patients – For trauma or surgical, or disease patients, frequent feedback and monitoring by therapists is worth it. Physical & Occupational Therapy Clients – from ADLs to gait, patient therapy outcome is improved when patients are maintained in balance with electronic monitoring. Musculoskeletal Patients – RTM’s ability to monitor functional attainment, posture, and activity is particularly well-suited to orthopedic rehab. Chronic Disease Patients – RTM vs chronic care management, both used in combination, can lead to an integrated care plan tracking therapy progress as well as long-term condition management. The Future of Remote Therapeutic Monitoring The RTM potential is boundless. Machine learning and artificial intelligence are driving the trends at historic velocities, and Virtual Care solutions enable providers to predict patient relapses more effectively. The algorithms, for instance, can identify treatment nonadherence signals in time, prompting providers to take swift and proactive action. There will be increased usability and accuracy with increased use of wearables and mobile apps. Voice-activated digital assistants can even provide instructions to patients for the performance of exercises in their home environment and provide data for clinicians. On the billing front, there is going to be a learning experience for billing remote therapeutic monitoring. There is documentation, appropriate coding, and Remote therapeutic monitoring workflow coordination that will pay back providers at the moment. Professional associations also publish remote therapeutic monitoring best practice guidelines such that care will be effective and trustworthy across health systems. RTM’s future is patient-centric models of care, as well. Merging RTM with virtual visits, digital