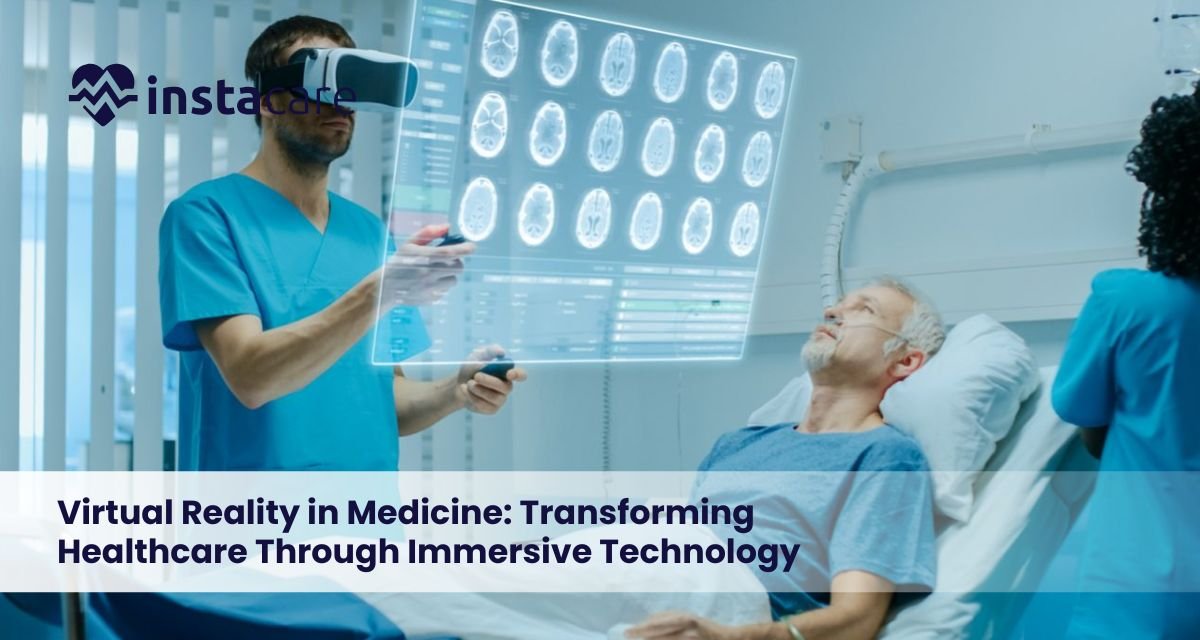
Virtual Reality in Medicine: Transforming Healthcare Through Immersive Technology The medical field is experiencing the digital revolution, and the idea of immersive technology in medicine is the focal point of the revolution. VR has not been restrained to entertainment anymore, but is currently being implemented in hospitals, medical schools, and therapy centers. VR is transforming healthcare delivery, whether it is creating more accurate surgery or making the procedure more comfortable. The use of modern medical virtual reality applications can provide healthcare workers with the opportunity to train in a safe manner, treat patients better, and increase clinical results thanks to real simulations. What Is Virtual Reality? Virtual reality refers to a three-dimensional environment and is a simulated environment created by computers and experienced by users through VR headsets and motion tracking devices. The major features of VR are: Complete involvement in an online world. Live communication with virtual objects. A great deal of visual and sensory stimulation. Augmented reality vs virtual reality in healthcare is a common comparison in healthcare-related discussions. Whereas AR is used to overlay digital objects on the physical one, VR is more preferable for training, therapy, and simulation-based care as it is fully immersive. How is Virtual Reality Used in Medicine? Virtual reality has clinical uses in many spheres of healthcare and has been used to benefit both the practitioners and the individuals receiving care. VR is commonly used for: VR in medical training and skill building. Treatment and therapy of patients. Virtual reality surgery simulation and planning. Physical recovery and rehabilitation. These applications indicate the way that VR for patient care enhances safety, accuracy, and involvement in the medical environment. VR in Medical Training and Education Medical training VR has altered the way medical workers understand complicated practices. Virtual reality medical education allows students to practice again and again without any risk in the real world. Perks to education include: Interactive 3D learning of anatomy. Simulation of emergency response. Procedural accuracy in a virtual reality simulation of surgery. Less use of cadavers and live patients. This simulative method enhances self-esteem, decision-making and technical ability. Virtual Reality in Patient Treatment The use of VR therapy in healthcare as a therapeutic tool is gaining more and more use. In the healthcare sector, VR therapy is used to control physical and mental health. Some typical uses of the therapy include: Virtual reality for pain management. Lessening anxiety and stress. Diversion therapy of chronic pain. Preoperative emotional preparation. The patients feel more comfortable, less dependent on medications, and their recovery is more successful. VR in Surgery and Clinical Practice VR promotes planning and execution in surgical settings. Virtual reality surgery simulation enables surgeons to practice complicated surgeries using patient-specific information. Clinical benefits include: Higher accuracy of surgery. Less risk of complications. Greater comprehension of the patients through graphic explanations. Improved cooperation between teams of medical workers. The developments enhance credibility and overall quality of care. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Virtual Reality in Medicine The benefits of virtual reality in the healthcare systems include: Increases learning experiences. Enhances the level of patient engagement and satisfaction. Embraces VR rehabilitation therapy. Reduces medical errors. Makes the process of treatment personalized. Increases medical education. VR is transforming the field of modern medicine through its ability to bring together innovation and empathy. Challenges and Limitations Although it has potential, VR adoption has a number of obstacles: Expensive initial costs of setup and maintenance. Training and technical complexity. Dizziness or eye strain to others. Data security and privacy issues. These limitations would have to be tackled in order to increase the use of medical virtual reality applications. Future of Virtual Reality in Healthcare The future of virtual reality in medicine is bright. VR will be combined with wearables, telemedicine platforms, and artificial intelligence with the advancement of technology. Possible future developments are: AI-based simulated personalized treatments. Remote VR-based medical training. High-level exposure to virtual reality therapy. More extensively used in mental and physical rehabilitation. Such innovations will turn VR into a commonplace feature of healthcare provision. Real-World Examples Virtual reality is already changing patient outcomes across the globe. Examples include: VR in PTSD and anxiety Phobia virtual reality exposure therapy. Stroke rehabilitation therapy using VR. Immersive distraction programs for pain management. These practical applications indicate the increased clinical effects of VR. When VR Is Most Effective in Medical Settings? VR would be best applied in a situation where simulation, visualization or emotional involvement is needed. It works best in: Healthcare education and training. Pain and anxiety management. Mental health therapy. Physical rehabilitation. Preoperative preparation and rehearsal. Immersive and controlled digital experiences are very useful in such environments. Conclusion VR is revolutionizing the medical field by contributing to better education, patient outcomes, and clinical efficiency. Immersive technology in medicine is transforming the medical field with VR in medicine training, therapy, and surgical uses. With an increasing number of issues addressed with virtual reality and increased accessibility, patient care, education, and clinical practice will remain redefined worldwide. FAQs What is the application of virtual reality in medicine? Medical training, surgery simulation, pain management, rehabilitation, and mental health treatment are some of the areas where medical virtual reality applications are applied. Does virtual reality work in the management of pain? Yes, virtual reality for pain management is useful in decreasing the perception of pain, which distracts the brain and decreases anxiety. What becomes of virtual reality in healthcare? The future of virtual reality in medicine involves AI-driven simulations, customized therapy, and broader application in everyday clinical use.
How AI Agents Are Transforming Modern Business Operations? Artificial intelligence is not an additional operation in business; it is emerging as the support of the future AI in business operations. Automation, decision-making support, and intelligent task execution are being adopted in organisations today as a way of minimizing human efforts and maximizing efficiency. AI Agent for Business are ushering in this change and they are programmed to act, learn and make autonomous decisions. By the year 2025, AI has ceased being an early experimentation tool to a business transformation tool where businesses can work smarter, faster and at reduced operational expenses. With the increase in the competitiveness of industries, AI-powered systems are setting new productivity and customer experience standards. What Are AI Agents and How Do They Work? AI Agents are smart computer systems which do the tasks independently by processing information, making a decision, and acting upon it with minimal human involvement. The AI agents are able to learn through experience, change as per current data context, and optimize performance on-the-fly unlike the traditional software programs which use coded instructions only. These are machine learning powered agents, natural language processing agents, deep learning network powered agents, and workflow logic powered agents that allow them to act independently. The behavior of the AI agents is generally composed of three essential steps: Input Interpretation – The agent gathers information through various channels which include CRM platforms, websites, emails, spreadsheets, or communication channels. Decision Processing- Algorithms consider and analyse the available data and compare patterns, predict and decide on the best course of action. Output Execution – The agent executes the necessary operation, responds to a query, transmits a reply, produces a document or initiates automated processes. Key Benefits of AI Agents for Businesses AI agents can provide quantifiable value by enhancing productivity, decreasing the operational expenses, and assisting the companies in their more efficient functioning. The major benefits include: Automated performance of tasks with reduced manual workload. More rapid decision-making on a real-time basis. More accurate data-dependent tasks. Scalability with no extra labour expense. 24/7 performance, which offers 24/7 operational performance. This is the reason why various organisations currently embrace AI agents on behalf of companies as a necessary addition to the workforce. Practical Use Cases Across Industries Artificial intelligence is reshaping various industries, including retail and healthcare, finance, logistics, etc. In real life, they can be used in: Retail & E-Commerce AI agents will study the behaviour of consumers, keep track of inventory, price optimisation, and product recommendations. They also automate processes of order processing and logistics Banking and Finance Agents identify fraud, automate loan checks, create financial reports and analyse credit scoring swiftly and accurately. Healthcare AI Agents help in diagnosing the patient, scheduling appointments, recording data, and predictive treatment planning. Supply Chain and Manufacturing. Agents control the production cycles, predict demand, minimize waste, and predictive maintenance of machinery. Hospitality & Travel The AIs are in charge of making a reservation, answering client requests, and personalising travel suggestions and simplifying the check-in procedures. These applications demonstrate the AI agent use cases in business when industries are shifting to smart automation. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation How AI Agents Improve Customer Experience? One of the fastest-growing fields of AI implementation is customer engagement and support. Smart systems can process high requests, respond immediately and present customised customer experiences. Chatbots and AI-based help desks steer the users towards queries, order tracking, payments and troubleshooting without human interruptions. Such improvements result in a higher level of satisfaction, faster resolution of cases and improved quality of communication. The AI agents are also used to study the emotions, preferences, and historic interactions of customers to personalize every service. It has rendered AI agent for customer support one of the most used types of enterprise AI implementation. Implementation: How Businesses Can Get Started The implementation of AI agents in business activities must be effectively planned and implemented in phases. The organisations need to identify areas of inefficiency, redundancy of processes and areas of operation where automation would bring the most value. Upon identification, the subsequent actions are involved: Mapping automatable business processes. Choosing the appropriate AI tools, platforms, and deployment structures. Training based on previous business information. Controlled experimental testing prior to full implementation. Slowly expanding implementation into departments. Several firms are currently embracing business automation with AI agents, which they are exploring to automate all the functions of the company starting with HR onboarding, accounting, and daily business communication. Businesses also use tools that are aimed at enhancing performance like AI productivity tools for business, which makes automation accessible and scalable. In the case of small firms just entering the arena of AI transformation, such solutions as small business AI solutions can provide inexpensive entry points to the world of AI transformation without extensive technical investment. Challenges and Considerations Although AI agent benefits for enterprises, there are also implementation issues that a company should consider. These include: Issues of data safety and confidentiality. First-level complexity of integration. Skill gaps and training needs of the workforce. Reliance on quality information in order to produce best outputs. Autonomous decision-making has an ethical implication. Those enterprises which are able to overcome these obstacles have the greatest returns- a key point being AI agent benefits as a long-term growth resource to an enterprise. The Future of AI Agents in Business Multi-stage tasks that are performed with a small amount of supervision are the future of artificial intelligence as it will be powered by independent reasoning systems. The next-generation agents of AI will handle end-to-end processes, i.e., data analysis and workflow triggers up to long-term forecasting and decision-making. The use of autonomous AI agents for business is also increasing, and they are meant to perform similarly to digital workers. These agents have the ability to learn, devise working processes, interact with software and generate strategic output. These developments are a transition between conventional
AIOps in Healthcare: Transforming IT Operations for Smarter, Safer Patient Care Healthcare organizations are facing mounting pressure to deliver high-quality patient care while dealing with cutting-edge technology. Hospitals and clinics rely on dozens of digital assets, from patient records to diagnostic equipment. The IT staff must keep the systems running, resulting in mammoth challenges. AIOps brings artificial intelligence into IT operations to make healthcare technology intelligent and reliable. The benefits of AIOps in healthcare extend beyond simple automation. These systems look ahead and predict problems before they happen, respond to troubles in real-time, and get smarter with every experience. AI operations in healthcare IT represent a radical shift in how hospitals organize their digital infrastructure. What is AIOps? AIOps combines IT operations management with artificial intelligence. The technology uses machine learning to monitor systems, recognize patterns, and automatically repair problems without the need for human interaction. In healthcare settings, that means computers monitoring medical equipment, software programs, and data networks constantly. AIOps machine learning in healthcare analyzes data to spot unusual patterns that might signal problems. When issues arise, the system can often fix them without human intervention. This approach reduces downtime and keeps critical medical services running smoothly. Healthcare IT automation with AIOps changes traditional IT management completely. The technology works around the clock, never gets tired, and processes information faster than any human team could manage. Challenges in Healthcare IT Operations Healthcare institutions have unique technology concerns that are fairly different from any other company. Patient lives hang in the balance with systems running smoothly every second of every minute. A crashed server or a lost network connection would potentially delay life-saving treatments or block access to essential medical information. AIOps for hospital IT operations must deal with phenomenal complexity. Hospitals run hundreds of different applications, ranging from scheduling software to imaging equipment. Each one must communicate with the others while maintaining strict security protocols. AIOps for healthcare cybersecurity must protect confidential patient information from rising cyber attacks. Cyber hackers target health organizations because health records contain valuable personal information. A data breach can expose personal medical histories and disrupt patient treatment. Primary Operational Challenges Systems must be available every hour without failure Different software systems must share information freely IT staff struggle with alert fatigue because of excessive false alarms Challenges of AIOps in healthcare are interoperability with legacy infrastructure Budget constraints limit technology spend with escalating requirements Staff shortages mean fewer individuals managing increasingly complex systems Book Your Free Marketing Consultation How AIOps Benefits Healthcare AIOps use cases in healthcare demonstrate concrete value across multiple areas. Medical imaging equipment generates huge quantities of data that must be stored securely and accessed quickly. AIOps in healthcare cloud systems manages this data competently, enabling doctors to see scans and reports directly when needed. AIOps for electronic health records (EHR) improves how facilities handle patient data. The system monitors database performance, prevents loss of data, and maintains quick access times. When problems happen, there are automatic measures in place before users ever notice a slowdown. Predictive analytics with AIOps in healthcare detects future problems before they occur. It identifies issues when server performance is beginning to dip or when storage space is low. Alerts are sent automatically to IT teams with sufficient time to resolve issues during planned maintenance windows. Key Benefits System downtime is minimized, keeping vital services up all the time Less time wasted on problem-solving results in decreased delays in patient care delivery AIOps and patient data management ensure data stays safe and accessible Decreasing IT operation costs through automation and optimization More precise resource allocation based on insight into when systems need to be upgraded Improved compliance with healthcare laws through improved monitoring Implementation Considerations Deploying AIOps takes planning and realistic expectations. Healthcare institutions will have to think through their current infrastructure prior to installing new systems. AIOps in telemedicine needs highly reliable network connectivity in addition to video platforms that are safe and secure. One of the key challenges is legacy system interoperability. Legacy systems are present in most hospitals, and they weren’t developed with any AI tool in mind. Healthcare IT automation with AIOps requires middleware solutions that integrate legacy and emerging technology. Staff training is also something to factor in. IT personnel need to understand how AIOps machine learning in healthcare works and when to trust automated decisions. Open communication prevents false expectations and gets everyone on the same page. Planning Steps Assess current IT infrastructure and identify areas of weakness Set well-defined goals for what AIOps must accomplish Initiate pilot projects in non-mission-critical areas before full deployment Plan for technology costs and necessary staff training Establish metrics to measure success and track progress Provision for routine maintenance and system refreshes The Future of AIOps in Healthcare The future of AIOps in healthcare is looking increasingly sophisticated. Advanced systems will predict equipment failures days or weeks in advance. AI operations in healthcare IT will automate maintenance, maximally available with minimal downtime. Integration between different healthcare systems will become much improved. AIOps in healthcare cloud systems will enable seamless data transfer between hospitals, clinics, and research centers. Patients will have their care coordinated as their complete medical history follows them from provider to provider. AIOps for healthcare cybersecurity will become more proactive. Systems will actively block attacks in real time, adaptively refining their defenses on the fly based on emerging threats. This security is increasingly needed as hospitals add more networked devices and telemedicine services. Emerging Trends Real-time monitoring of patients using networked medical equipment Autonomous allocation of resources based on forecasted patient flow Enhanced AIOps in telemedicine to support enhanced remote consultations Advanced predictive analytics with AIOps in healthcare for population health Better integration between clinical and operational systems Intelligent AIOps for electronic health records (EHR) with natural language processing Conclusion AIOps transforms healthcare IT operations from reactive firefighting to proactive management. The technology enables the essential challenges faced by medical facilities on a day-to-day basis. Increased system reliability, better security,
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): The Future of AI-Powered Knowledge Artificial intelligence is developing at an incredible speed, changing the manner in which we engage with information and knowledge bases. Retrieval-augmented generation is a groundbreaking strategy that merges the power of large language models with dynamic information retrieval. This technology surpasses the built-in constraints of conventional AI systems by giving users access to current, reliable information from the outside world. The arrival of the RAG model in AI has transformed the manner in which complex questions are responded to by artificial intelligence systems and responses are produced. In contrast to fixed language models existing based on training data, RAG systems can retrieve and gather up-to-date information from diverse databases and knowledge bases. This makes AI responses more precise, context-relevant, and authoritative for various users across various industries and uses. What is Retrieval-Augmented Generation? Retrieval-augmented generation meaning refers to a new wave that supercharges conventional language models with the ability to harness outside knowledge and retrieve related information. The technology fuses two different AI elements: a retrieval model that searches for relevant information and a generation side that produces human-sounding text as outputs based on retrieved information. The fundamental principle is to expand the knowledge base of the language models from what they were initially trained on. As users submit queries, the system draws the relevant information first from external sources and then uses this information to create precise and contextually relevant responses. This functionality allows AI systems to provide timely information and address issues that might not have been covered by their original training sets. Retrieval-augmented generation architecture generally includes three fundamental elements: an encoder that handles user queries, a retrieval unit that performs a search for knowledge bases, and a generator that generates final responses. All of these elements operate together to provide improved AI performance as well as strength. How RAG Works? The RAG pipeline starts when a user enters a query in the system. The query encoder translates the input into a vector representation that can be utilized for similarity matching. The encoded query is then applied in searching against indexed knowledge bases and external documents. When retrieved, the system extracts the best-fitting documents or information segments for the user search. The text passages that are retrieved are ranked according to relevance and chosen to be added at the generation time. Retrieval uses semantic search methods to extract information related on a conceptual level rather than keyword retrieval. The generation phase integrates the original user query with extracted information to create in-depth and precise answers. The language model uses the context established by extracted documents along with its learned knowledge to generate natural language suitable for the user’s particular requirements. RAG with vector databases also improves this process by storing document representations as high-dimensional vectors. Vector databases can accomplish fast similarity search and retrieval of useful information from large sets of documents efficiently. Benefits of RAG Benefits of retrieval-augmented generation go beyond what is achievable using standard language models. The biggest advantage is that it is exposed to up-to-date and correct information not available in the training data for the model. It makes responses timely and factually correct irrespective of the manner in which information evolves with time. RAG vs traditional language models shows significant improvements in terms of accuracy and reliability. Classical models can only access information during training time and hence provide stale or inaccurate replies. RAG systems always draw on new information and hence are more appropriate for tasks that require up-to-date knowledge. The technology is also more transparent and explainable. Users can trace information sources employed in response generation, which instills confidence and trust in AI content. Traceability is important in enterprise usage where authenticity and accountability are emphasized. Scalability of knowledge is yet another vital advantage. Companies can scale up their AI capabilities by incorporating new documents and information sources without training entire language models. It brings RAG systems increased cost-effectiveness and versatility to changing business circumstances. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Applications of RAG Retrieval-augmented generation applications have implementations across many sectors and uses. The most successful use may be customer service, where RAG for chatbots enables automatic systems to have the capability to give precise responses based on up-to-date product information, policies, and manuals. Retrieval-augmented generation for enterprise search shifts the manner organizational knowledge is searched and leveraged by employees. These systems are able to search corporate documents, databases, and knowledge bases and provide rich responses to sophisticated business questions. Retrieval-augmented generation use cases in the medical field are medical diagnosis support and treatment suggestion systems. Schools use RAG to develop smart tutoring systems, while banks use retrieval-augmented generation in NLP to support market analysis and regulatory reporting. Challenges of RAG Retrieval-augmented generation challenges pose various technical and practical issues. Information quality control is the biggest issue, since RAG systems rely on the validity and reliability of outside information sources. Low-quality source material can impact the generated output negatively. The complexity of RAG system integration is higher with the integration of RAG systems into installed enterprise applications and databases. Organizations need to recall data protection, access controls, and system compatibility when they install RAG solutions. Fine-tuning RAG models is based on experience with retrieval systems and language models. Organizations require technical staff with suitable skills to optimize performance and render the system effective in the long term. Future of RAG in AI The future of retrieval-augmented generation is towards more capable and intelligent AI. More advanced retrieval systems will enhance the accuracy and relevance of information selection. Machine learning methods will enable improvements in the ability to identify and prioritize the most beneficial sources of information. Multi-modal RAG models will include images, videos, and other content apart from text. The inclusion will enable more robust AI applications that can handle information of varied types and render improved user experiences. Integration with some of the newer technologies, such as quantum computing and new neural architectures, will also enhance the capabilities of RAG.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): What It Is, How It Works, and Use Cases The contemporary business environment runs at the pace of velocity, efficiency, and precision. The world is racing fast, so companies are continuously looking for the means to automate routine tasks and cut costs. One of the most innovative technologies to achieve the same is Robotic Process Automation (RPA). Automation has existed for decades in the past, but RPA is a fresh idea that operates very well with digital platforms without necessitating revolutionary IT reworks. This article describes what RPA is, how RPA works, robotic process automation workflow, RPA applications by industry, and the future of automation. What is Robotic Process Automation? Robotic Process Automation refers to the automation of structured and repetitive business processes by software robots. RPA is different from conventional automation, which demands much coding expertise. RPA can be applied with very minimal programming expertise. The software robots have the capability of performing any type of activity, from data extraction and processing of transactions to sending automated e-mails. RPA is applied by the majority of RPA in business companies to facilitate automation, enhance customer satisfaction, and assist employees in performing more meaningful work rather than repetitive ones. How RPA Works To appreciate its worth, one should understand how RPA works. In real life, RPA technology communicates with programs in the same manner as human beings clicking buttons, filling in forms with data, copying data, and dragging and dropping files but faster and more precisely. How it works is normally the following processes: Identify the Task – Identify the rule-based repeatable task that can be automated. Design the Workflow – Give the sequence of activities used to accomplish the task. Configure the Bot – Employ robotic process automation software to automate the bot to follow the workflow. Test the Automation – Test that the bot executes tasks flawlessly without bottlenecks. Deploy the Bot – Employ it in daily operations. Monitor and Maintain – Monitor performance and upgrade as processes evolve. Elements of an RPA Workflow A robotic process automation process is made up of a number of linked pieces: Input Triggers – Triggers to initiate automation, for example, receipt of email or file. Data Processing – Extraction and restructuring data based on predefined rules. System Interaction – Performing actions between multiple software tools such as CRMs, ERPs, or databases. Output Generation – Generating reports, notifications, or updating records. This work is developed by professionals who have domain knowledge, which in the context of RPA developer roles would be the people ensuring that the bots are running smoothly and securely. Benefits of Robotic Process Automation Robotic process automation benefits cross across lines of an industry as well as a business function. Some of the key benefits of robotic process automation are: Cost Savings – Automation negates labor expenses by handling high volumes of repetitive tasks. Accuracy – Robots remove human errors, and therefore there is consistency and precise output. Speed – Activities that would take hours to complete in the past can now be completed in minutes. Scale – Businesses can upgrade the number of bots for processing increased loads. Staff Satisfaction – Workers are relieved of redundant work to engage in strategic, value-critical work. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation RPA vs AI RPA vs AI are, at times, compared, but the two are not quite alike, even though both are automation tools. RPA runs under set rules and workflows, while AI involves learning, making decisions, and adapting to new situations. In real life, they seem to go hand in hand. AI can learn and decide what action to take, but RPA executes the resultant actions. ● RPA Use Cases in Different Industries There are a number of RPA use cases where automation provides real advantages. The most relevant examples are elaborated below. ● Banking and Finance In the banking sector, RPA in finance is implemented for fraud detection, compliance reporting, loan servicing, and onboarding customers. Bots can process massive transaction volumes without an error, provide regulatory compliance, and achieve operational effectiveness. ● Healthcare In medicine, RPA in healthcare automates medical record management, billing, claims processing, and patient scheduling. More time for patient care is available for clinics and hospitals since there is less administrative work. ● Retail and E-commerce Retail companies utilize bot control to control inventory, process orders, and accept returns. It helps minimize fulfillment time and improve customer satisfaction. HR departments leverage automation for the onboarding of employees, payroll processing, and hiring tracking that minimizes data input. Robotic Process Automation Examples To illustrate its application, the below realistic robotic process automation examples are presented: Invoice Processing – Invoices are automatically captured and uploaded into accounting systems. Customer Support – Chatbots can automatically respond to frequently asked questions via chat or email. Data Migration – Automated transfer of data from old systems to new application software with zero human intervention. Compliance Audits – Reporting in real-time compliance with regulatory authorities. RPA Implementation Strategy To RPA implementation effectively, there is a need for good planning and stakeholder engagement. Organizations need to: Identify High-Value Processes – Select processes with high volume, high frequency, and well-defined rules. Secure Executive Support – Executive sponsorship for funding and adoption. Select the Proper Tools – Select an extendable and secure RPA platform that can be integrated with the current systems. Pilot Test – Pilot small first, scale up. Train Employees – Make the employees comfortable working with bots. Watch and Refine – Continuous monitoring of performance and optimization. RPA success depends on mapping technology to business objectives and making it regular. Role of RPA Bots in Automation At the heart of automation are RPA bots computer codes that get work done just like they were instructed. The bots can operate 24/7, handle several workflows simultaneously, and operate on numerous
AI in SaaS: Artificial Intelligence and Its Impacts on the Software Industry The marriage of artificial intelligence and Software as a Service (SaaS) is transforming how digital platforms run, expand, and build value. The dizzying technology landscape today does not just mean that AI is the evolution of back-burner SaaS-it is a revolution. From automated tasks to forecasting customer wants and delivering tailored experiences, AI use cases in saas solutions are changing the way businesses engage with software. From customer support to marketing, analytics, or product innovation, the SaaS application of artificial intelligence is tremendous and revolutionary. Here in this blog post, we are going to talk about the major benefits, real-world applications, and the future of AI for SaaS. What Is the Role of AI in SaaS? Effectively, AI in SaaS is intelligent software. A matter of connecting machine learning, natural language processing, and predictive analytics in saas into cloud application software. Why? To automate, learn, and personalize user interactions. Role of AI in saas industry is being increasingly integrated into SaaS apps to: Learn from user behavior and trends Automate routine tasks such as onboarding or support Offer real-time decision-making abilities Offer predictive business strategy insights AI adoption in SaaS businesses has come an incredibly long way from being an experimental feature to being one among the primary pillars of scalability and innovation. Benefits of AI in SaaS Benefits of AI in SaaS are all phenomenal, not just cost and automation, but even customer satisfaction, product fine-tuning, and strategic decision-making. 1. Smart Customer Support One of the most prominent applications of AI is customer care. AI-driven customer support in saas applications employs intelligent chatbots to assist customers in real time, address issues, and route difficult problems to human agents. This reduces response time and provides support 24/7. 2. Augmented Decision-Making With SaaS predictive analytics, businesses are able to predict churn, identify upsell opportunities, and track customer satisfaction levels precisely. AI technology sifts through mountains of data in seconds to identify patterns and behavior that might otherwise go unnoticed. 3. Operational Efficiency AI automation in saas allows business enterprises to automate back-end activities such as data entry, invoices, and reports. Automations provide teams the chance to shift focus towards strategic work instead of drudge work. 4. Tailored User Experience AI allows SaaS solutions to tailor dashboards, recommendations, and content rendering based on individual user activity. It enhances engagement, retention, and happiness. 5. Scaling Without Incremental Burden With AI, SaaS products scale without the expense of operation doubling. From onboarding large numbers of new clients using AI operations to monitoring performance in real-time, scalability is done beautifully and effortlessly. Machine Learning in SaaS: Real-Time Learning & Adaptation Machine learning (ML) is one of the four pillars of artificial intelligence in SaaS. Machine learning in saas allows apps to learn from the way individuals interact with them, get better with time, and change dynamically as needs evolve. Examples: A sales platform can use ML to offer recommendations for best prices based on historical purchase behavior. A project management tool can forecast deadlines or risk based on historical trends. A content recommendation platform can be enhanced to recommend more in line with user interaction with articles or media. SaaS machine learning does not automate but enhance-smartly, optimizing platforms and maintaining competition intact in a live environment. AI in SaaS Marketing Riding the personalization wave, AI in SaaS marketing is a success story. AI enables the marketing team to: Segregate audiences based on behavior and engagement Automate lead nurture campaigns Measuring campaign performance in real-time AI-powered prediction of the most likely to pursue leads AI-powered marketing applications like chatbots, content engines, and A/B testing have become the secret sauce of the growth-stage SaaS company. AI-powered customer journeys provide more contextually relevant interactions and improved conversion. AI Chatbots for SaaS: Transforming Customer Engagement Chatbots are the most visible and most widespread application of AI tools for saas companies. From a CRM tool to helpdesk software to an HR tool, AI chatbots for saas are transforming communication. The chatbots: Process run-of-the-mill questions automatically Enable onboarding and simplify product use Collect past feedback and escalate when needed What distinguishes SaaS AI chatbots from the conventional bots is that they are learnable through conversation, context-sensitive, and get smarter every day. They offer smooth, almost-natural conversation experience without any human delay or limitation. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation AI in SaaS Product Development AI has revolutionized product development. AI is involved in the entire life cycle of a product from ideation and testing to updates and support in the SaaS era these days. The development in this field is astounding: Autotesting: AI technologies are able to find bugs and usability problems to speed up quality assurance. Feature prioritization: AI takes into account user activity and feedback to identify what’s the top-priority feature. Code generation and optimization: AI power at scale makes developers code, test, and optimize code better. AI and SaaS product development go hand in hand when it comes to releasing enhanced, faster, and more reliable updates driven by data and centered on users. How AI Is Transforming SaaS Models Apart from functionality and features, AI is also transforming the business and growth model of SaaS businesses. Some of the prominent how AI is transforming saas are: Usage-based billing: AI tracks usage patterns to design equitable and scalable pricing. Customer success predictions: Platforms can now anticipate probable-to-churn customers in advance. Smart integrations: AI APIs are now a part of SaaS platforms, and third-party solutions can blend
How AI Helps in Detecting Medical Errors? Healthcare life is racing at light speed, and even tiny errors can be costly. From misdiagnosis to incorrect prescriptions, medical errors are a danger to patient safety. Luckily, technology has come to the rescue. Artificial intelligence in medicine, for example, is increasingly assisting with risk reduction and outcome optimization. With the ability to sort through massive amounts of information and learn from trends, AI is changing the way hospitals identify and respond to errors. From identifying the incorrect dose of medication to notifying an off-reader lab test result, AI for patient safety is becoming a higher priority in modern practice. Identifying Medical Errors Medical mistakes are preventable events that can lead to or result from inappropriate outcomes in healthcare. Some examples include: Diagnostic Mistakes: Missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis Medication Mistakes: Patient is incorrect, drug is incorrect, or dose is incorrect Treatment Mistakes: Departure from clinical practice guidelines or faulty procedures Communication Breakdowns: Inadequate handoff of physicians Documentation Mistakes: Incomplete or inaccurate health records These mistakes are not necessarily negligent. In most cases, they happen because of overburdened systems, exhaustion, and complex procedures. This is where Medical error prevention using AI fits in, to relieve medical practitioners and bring about uniformity in decision-making. How AI Detects Medical Mistakes? AI works by searching for patterns in big collections of data from patient records, images, lab work, and medical literature. Through Machine learning in medicine, AI systems detect anomalies, variations from professional norms, and dangerous conditions. AI recognizes some of its methods of detecting mistakes as below: Flagging Drug Interactions: AI quickly cross-references current medications with patient allergies and medical histories to alert physicians to potential issues. Scanning Imaging Outcomes: AI detects abnormalities on imaging scans that might be missed by the human eye. Vital Signs Monitoring: Predictive analytics in healthcare-driven monitoring systems detect early signs of complications in real-time. Verify Documentation: AI in electronic health records (EHRs) verifies correct or complete data fields in documents. All these capabilities turn AI into a productive team player in real-time detection of medical mistakes in a hospital setting. Principal Applications of AI in Error Identification 1. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) They offer evidence-based guidance to doctors and nurses. When patient data is merged with clinical guidelines, Clinical decision support systems (CDSS) is capable of suggesting a diagnosis, treatment regimen, or warning about possible medical mistakes. 2. AI in Diagnostic Accuracy AI in diagnostic accuracy learns from millions of cases to aid in disease detection at high accuracy levels. In pathology, radiology, and dermatology, AI will equal or exceed human specialists, and aid in reducing misdiagnosis with AI. 3. AI for Identifying Medication Mistakes Drug mistakes are among the most common in hospitals. AI scans medicine for dosage mistakes, allergic reactions, or toxic drug combinations with existing medicines. 4. Predictive Healthcare Analytics Patient history and live monitoring allow predictive algorithms to notify caregivers about potential future complications, enabling early intervention and risk avoidance. 5. AI for Medical Documentation AI in medical documentation is used widely. Natural language processing (NLP) technology can review physician notes and transcripts to identify inconsistencies, missed diagnoses, or conflicting entries in patient histories. 6. AI for Clinical Workflow Optimization AI streamlines business, automates mundane labor, and ensures that nothing crucial is missed; hence, AI in clinical workflow improvement. Hospital environments become more secure and efficient. Book Free Demo Benefits of AI-Based Fault Finding 1. Reduced Human Error AI systems do not get fatigued or distracted. Their tenacity reduces human Real-time error detection in hospitals, especially under pressure. 2. Faster Diagnosis and Treatment With real-time information processing, AI shortens the diagnostic period or the identification of a possible issue, which increases patient outcomes. 3. Enhanced Risk Management Hospitals and clinics benefit from healthcare risk management AI, making them proactive at avoiding issues rather than reactive. 4. Enhanced Document Quality Medical documentation is rendered accurate, complete, and consistent using automated review and transcription technology. 5. Cost Savings Avoiding unnecessary procedures and hospitalization due to errors translates to cost savings while improving the quality of care through AI. Limitations and Challenges Although promising, AI is not problem-free: Data Quality: AI requires full, clean data. Incomplete or erroneous records may yield flawed results. Bias and Fairness: AI will amplify biases in training data, resulting in unfair treatment of different patient groups. Integration Challenges: Merging AI into existing hospital systems is complex and costly. Over-reliance: Physicians need to remember AI is a tool, not a substitute physician. Privacy Concerns: AI use of sensitive health information is creating concerns regarding safeguarding the information and confidentiality of the patients. In bridging these gaps, planning with caution, continuous monitoring, and a liaison between clinicians and technology vendors are required. The Future of AI in Patient Safety The future looks good. The better and more AI learns, the more it will be able to avoid medical mistakes with AI. Soon enough, we may have AI systems offering real-time second opinions, detecting risk even before signs appear, and creating extremely personalized treatment plans based on genes, lifestyle, and history. In addition, Artificial Intelligence in healthcare and healthcare automation will become increasingly powerful, allowing even more repetitive and mundane tasks to be cost-effectively processed, especially within systems like Clinic Management Software, freeing more clinicians to focus on what they do best: caring for patients. AI usage within electronic health records and clinical workflows will also be further optimized, with safety checks included in every patient’s journey. Conclusion Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming how the medical field addresses patient safety. Leveraging real-time data analysis, predictive modeling, and clinical decision support, AI detects and averts previously unseen medical mistakes. From
AI in Telehealth: Transforming Virtual Care with Smart Technology With digital health taking off around the globe, Artificial intelligence in healthcare is introducing a new paradigm of customized, effective, and affordable virtual care. Telehealth, once a novelty relegated to rural or underserved locations, has now transformed into a mainstream healthcare practice, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic era. AI has driven this growth much faster through automating workflows, improving decision-making, and supporting more preventative models of care. From Telemedicine AI tools that support physicians with diagnoses to AI-based healthcare apps empowering patients to manage chronic illnesses, artificial intelligence is transforming how care is delivered remotely. With the promise of cost savings, scalability, and better patient outcomes, AI is no longer something out of the future it is the future and present of telehealth. The Evolution of Telehealth Telehealth has existed for decades, with initial simple audio and video interactions between patients and physicians. As technology evolved with better internet connectivity, wearable devices, and cloud computing, the reach and availability of virtual medical services improved. However, a complete shift only occurred with the injection of AI technologies. The incorporation of Machine learning in telehealth enables systems to learn from patient information and get better with time, which helps providers deliver more accurate and effective care. The transition towards telehealth automation is also minimizing administrative weight, simplifying workflows for patients, and enabling healthcare professionals to concentrate more on important tasks Telehealth is not just video calls anymore. It now involves remote patient monitoring with AI, mobile health apps, and even AI-driven robots that engage patients. The convergence of telehealth and AI provides a more complete, interactive, and data-based solution for healthcare. Key Applications of AI in Telehealth AI-Based Diagnostics: One of the most compelling uses of AI in telemedicine is in AI-based healthcare apps diagnostics. Through patient history, lab tests, and image analysis, AI can assist clinicians in achieving faster and more accurate diagnoses. This reduces diagnostic error and reduces treatment time both essential in managing health outcomes. AI for Virtual Consultations: Virtual consultation AI leverages natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to allow real-time doctor-patient interaction. Conversational speech may be transcribed by AI systems, provide possible diagnoses, or even alert providers to inconsistencies or left-out information within a patient’s clinical history. AI for Patient Triage: In crises or peak-demand cases, AI patient triage prioritizes cases according to severity. AI programs examine symptoms and medical histories to direct patients to the right level of care, self-care, virtual consultation, or emergency care. Remote Patient Monitoring: With the advent of wearables and IoT devices, remote patient monitoring using AI has also picked up much steam. Data from heart rate monitors, glucose meters, and other sensors is interpreted by AI algorithms to identify abnormalities and alert doctors in real time. Predictive Analytics in Telemedicine: Predictive analytics for telemedicine helps healthcare professionals anticipate complications even before they occur. AI can recognize trends and patterns in patient information to predict hospital readmissions, medication non-adherence, or impending disease outbreaks. Chronic Disease Management: For patients suffering from chronic diseases, AI chronic disease management offers sustained, individualized care. AI algorithms can observe vitals, modify treatment suggestions, and warn healthcare professionals about deteriorating conditions, allowing for more proactive intervention. Benefits of AI-Enhanced Telehealth Enhanced Accuracy and Efficiency: AI technologies automate processes involving the execution of routine tasks and enable informed decisions. Healthcare providers are given tools that learn and improve continuously in AI-based diagnostics and machine learning, which in turn leads to higher clinical accuracy. Increased Accessibility: By triaging and consultative services using AI, healthcare services are made more available through rural or underserved areas. 24/7 access to health care is offered by the Chatbots in telehealth and the AI-based virtual consultations, especially to people who have a limited mobility or no access to traditional clinics. Personalized Patient Care: AI analyzes overwhelming volumes of patient information in order to produce highly individualized recommendations. Healthcare apps based on AI can be adjusted to the peculiarities of each patient, making fitness, nutrition, and medication plans tailored to meet specific needs; this will increase engagement and outcomes. Cost Savings: AI automation lessens the necessity for in-office visits and eliminates excessive tests or procedures. Telehealth automation slashes administrative and operational expenses considerably, rendering healthcare more affordable. Early Detection and Prevention: With predictive analytics in telemedicine, possible health threats can be identified early. AI algorithms evaluate past and present data to raise warning flags about chronic conditions or acute illnesses, often before symptoms become apparent. Less Burnout for Clinicians: By handling routine questions, bureaucratic paperwork, and data entry, AI lets clinicians off bureaucratic duties. This enables them to focus on more relevant cases, therefore improving their job satisfaction and preventing burnout. Book Free Demo The Future of AI in Virtual Healthcare The prospects for AI in telehealth are huge. Advances in healthcare, Natural language processing in healthcare will make patients’ interactions with AI systems less formal and more sensible. NLP can not only be utilized to record consultations but also to monitor patient sentiment, mood, and mental health status. Another critical growth space is AI-powered healthcare applications, which will become smarter and more user-focused. Such applications will harness behavioral information and feedback to improve and evolve continuously, making health plans seamless. Telemedicine AI systems will continue to develop, whereby they will be multi-modal systems for diagnostics, treatment planning, and follow-up management. Interoperability will improve as AI systems will be able to draw and work with data from various e-health records, lab systems, and patient-generated sources. Conclusion The rollout of artificial intelligence throughout healthcare is revolutionizing the telehealth by facilitating more intelligent, faster, and personalized virtual care. From remote patient monitoring with help of AI to predictive analytics for telemedicine, AI is changing all patient touchpoints. Looking forward, the collaboration between clinicians, technologists, and policymakers will be important in actualising the full potential of AI in telehealth. Smart
Future of Chatbots in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Engagement and Medical Services Healthcare industry is undergoing a shift towards digitalization where AI chatbots in healthcare are being established as a revolutionary solution to healthcare delivery. These is how these high end tools, driven by natural language processing in healthcare, are changing the ways patients interact with medical providers. Virtual health assistants are at the forefront of using care by making it easier for appointments to be scheduled, among other things. As the Healthcare technology trends continue to evolve, chatbots will most likely be part of the modern medical systems and assist in getting better outcomes, become more efficient, and enhance patient satisfaction. What are Chatbots? Chatbots are applications that pretend to imitate a human conversation with the use of AI and machine learning. They are able to interpret and answer user queries in real time using text or voice. In healthcare, conversational AI in healthcare is a term used for these intelligent bots intended to communicate with the patients, medical staff, and healthcare systems. These chatbots learn from huge medical datasets and are capable of doing anything from answering simple health questions to triaging patients. With AI in patient support, chatbots are no longer restricted to roles of Q&A interactions but are emerging as active players in the delivery of healthcare. Applications of Chatbots in Healthcare It has as a result of medical chatbot applications, it has been into various use cases in the medical field. These are some of the most exemplary cases for healthcare chatbot use: Appointment Scheduling and Reminders: Patients’ engagement tools such as chatbots may schedule, reschedule or cancel appointments automatically without involving human beings. They also send reminders thus reducing no-show rates and increasing efficiency of the clinic. Triage and Symptom Assessment: Chatbots for medical diagnosis can analyse symptoms based on structured questions and provide an adequate solution as a next step. These bots employ AI algorithms in directing the patients to emergency care, at-home remedies, or follow-ups. Mental Health Support: Chatbots for mental health provide round the clock support for those with anxiety, depression, or stress. These bots are used to give coping strategies, monitor the mood of users, and link users to mental health professionals whenever necessary. Telemedicine Integration: Telemedicine chatbots facilitate distance consultations by acquiring patient history, recommending specialists, and instructing users to establish video calls. They make telehealth services easier to be accessed and less scary. Medication Reminders and Management: By connecting with pharmacy systems, chatbots can prompt patients to use medications, warn them of the probability of side effects, and arrange the refill of the prescriptions. It enhances better compliance and health outcomes. Health Education: Virtual health assistants are very good at delivering evidence-based information about diseases and preventative measure as well as betterment of ways of living. They are trained to offer accurate and comprehensible health education. Administrative Assistance: Chatbots can be useful to Insurance companies and hospital billing departments because they can be used to answer FAQs and facilitate the processing of claims and insurance verification. It is a key catalyst of healthcare automation. Benefits of Chatbots in Medical Services The advantages of application of the AI Chatbots in healthcare are far-reaching as they extend to the patients, healthcare deliverers as well as the health care administrators. Some of the most potent Benefits of AI chatbots include the following: Enhanced Patient Engagement: The patients of today demand instant answers and smooth communication. Patient engagement tools such as chatbots provide real-time interaction and as such enhance satisfaction, promote proactive health management, and yield trust. Round-the-Clock Accessibility: Unlike human staff, chatbots work 24/7. This availability at all times will help patients to obtain care information and/or support whenever they need to, which is essential for chronic conditions or mental health cases. Reduced Operational Cost: Automation through chatbots ensures that their tasks in the healthcare field include automating repetitive duties such as answering questions, making appointments, or simply processing paperwork, thereby minimizing administrative costs and the loads borne by the staff. Improved Accuracy and Consistency: Virtual health assistants, unlike human agents, do not tire and get distracted. They provide reliable information each time hence eliminating the chances of miscommunicating or human error on each patient encounter. Scalability and Flexibility: Hospitals can implement chatbots to facilitate high volumes of queries without straining in human resource. Whether in the flu seasons or pandemics, bots can scale themselves without compromising their quality. Data Collection and Analytics: Chatbots collect well-defined information about the behavior, preferences and feedback of the patient. This data is priceless in enhancing service delivery, patients’ needs and health care plans reorientation. Empowerment of Healthcare Staff: Taking over the redundant, non-critical tasks, the chatbots release doctors, nurses and the admin staff to engage in high-value patient-centered activities. This leads to improved care quality and staff satisfaction. Book Free Demo Chatbots vs. Traditional Healthcare Communication Conventional healthcare communication is based on human contact, whereby phone calls, physical visits, and emails are used extensively. Although personal, this method is time-consuming and only available during business hours and is subject to delays. Patients have to wait for a long period, face inconsistent information, and experience administrative bottlenecks. Unlike AI chatbots in healthcare that are instant, 24/7, they offer answers, appointments scheduling, symptom assessment, and even mental health support. Empowered by natural language processing for healthcare, chatbots guarantee consistent and correct responses and can process thousands of queries at the same time – something that traditional systems are unable to do. Besides, chatbots enhance patient engagement tools as they provide individual attention and tips while relieving the staff members. They also gather and analyze data to improve decision-making and services. Although not a substitute for human feeling, virtual health assistants enhance medical teams as they simplify communication and access. When it comes to the Future of digital health, efficient and accessible, it is clear that chatbots are shaping it as healthcare automation
AI-Driven Pharmacovigilance: Revolutionizing Drug Safety Monitoring Pharmacovigilance is the study of the monitoring and evaluation of all adverse effects related to pharmaceutical products, and all of this has undergone a drastic transformation owing to the impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) on this field. Traditional systems are important, but rather reactive and limited in scope. The rise of AI innovations in healthcare is changing the way the world manages drug safety with real-time, data-driven insights. Even countries like Pakistan tend to see Pharmacovigilance System Implementation that need to be implemented for a stronger AI in the Public Health infrastructure and improved patient safety. Understanding Pharmacovigilance By identifying, monitoring, and preventing ADRs, pharmacovigilance can maintain safety to the patient and public trust in medicines, especially upon the introduction of new drugs. A process through which adverse drug reaction notification can greatly increase public safety and trust in medicines. Pharmacovigilance in Pakistan is still developing in countries like Pakistan. It is evident in the growing interest by many health institutions in building better drug safety systems that conform to international standards. Traditional methods, however, seem to fall short on several challenges relating to speed, accuracy, and scope. Limitations of Traditional Pharmacovigilance Methods Conventional pharmacovigilance primarily relies on manual reporting, case analysis, and passive databases for recording adverse reactions to drugs. These enable underreporting, delays, and inconsistencies in the detection of adverse reactions to drugs. Certain incidents may not be reported by healthcare providers, whether owing to time constraints or due to sheer lack of awareness, thereby compromising the efficacy of the entire monitoring system. To add to that, these systems cannot withstand any further scaling with the current volume of healthcare data that continue to be generated from hospitals, pharmacies, and digital health platforms such as telemedicine and drug safety consultations. This becomes a bottleneck for real-time detection of emerging safety signals or effortless management of complex datasets. How AI is Transforming Pharmacovigilance? Artificial intelligence is throwing its weight on drug safety to mitigate various limitations in the above situations by automating the data collection, processing, and analysis processes. Machine learning in pharmacovigilance enables the identification of patterns from large datasets that facilitate the early detection of ADRs that may evade traditional reviews. Natural language processing (NLP) extracts relevant safety information from unstructured data sources, such as clinical notes, social media posts, and electronic health records. AI can merge different information sources to enhance real-time drug safety monitoring and predictive model building. Such AI systems in healthcare are capable of analyzing the patient’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and medical history for predicting Drug Reactions that would otherwise occur. This approach shifts pharmacovigilance from a reactive system to a proactive one regarding its intervention for improving patient outcomes. Book Free Demo Benefits of AI-Driven Pharmacovigilance ● Detection of ADRs at an Early Stage Millions of health records and reports on incidents may be rapidly analyzed by AI for untoward drug reactions. This will enable safety regulators or pharmaceutical companies to react promptly by sending safety announcements or amending drug dosage, etc. ● Enhanced Scalability and Efficiency Automation shortens the time we need to analyze extensive sets of data on pharmacovigilance, thus alleviating the pressure on human resources. This is particularly a huge blessing in nations like Pakistan, where there is hardly any resource for carrying out manual assessment. ● Enhanced Decision-Making With a modular form of AI, decision-making is aided by real-time dashboards and actionable insights to healthcare professionals and regulators. This enhances decision-making to combat safety threats at an early stage of their development. ● Increased Patient Safety By using artificial intelligence, hospitals can enhance Patient Safety through AI with pharmacy data and telemedicine platforms. Artificial intelligence highlights high-risk drugs or interactions, thereby decreasing patient harm. ● Support for Health Initiatives Public AI plays an important role in identifying trends in the public health sector, whether drug misuse or areas of regional side effects, which, when monitored and predicted better, can be useful in designing more effective health policy interventions. ● Convergence with Wearable and Mobile Health Data AI systems typically aggregate and analyze data received from wearable devices and integrated health applications for tracking Adverse Drug Reaction Detection incidents outside clinical settings. Thus, the entire health picture becomes better visible for a patient. It allows real-time, continuous monitoring of drug safety. ● Predictive Assessment of Patients on an Individual Level By better individualizing risk profiles, including genetic evaluation, age, gender, comorbidities, and drug history, artificial intelligence through machine learning in the field of pharmacovigilance can provide risk assessments at the individual level. Hence, personal drug safety improvements in intervention, along with better treatment efficacy and reduced side effects. ● Compliance Support from Regulatory Agencies AI technologies make the financial house easier to recognize to fulfill local and international regulatory requirements through a much more reliable reporting and documentation system created for the pharmaceutical industry and healthcare providers. Automation reduces human error and provides reliability, making pharmacovigilance reporting consistent. ● Strong Clinical Trial Monitoring Automatic processing of participant data leads to a quicker detection of ADRs using AI in the course of clinical trials. This advances safety when conducting trials and facilitates quicker approvals of promising treatments. ● Improve Communication Healthcare Provider AIs can provide notifications and alerts for doctors and pharmacists at the time real-time events when there is an incident likely to warrant a follow-up. Thereby improving communication, the readiness for quick clinical decisions will significantly minimize the possibility of complications. Challenges and Ethical Considerations These AI healthcare innovations are promising in nature, but they have their challenges and some points of ethical concern. ● Data Privacy and Security About the need for AI to enhance pharmacovigilance, a huge volume of sensitive health data is paramount. Privacy and security become a major issue in bringing Healthcare Data Integration with AI under the wings of AI because mishandling of the data can dent public trust. ● Bias in Algorithms “The
- 1
- 2