What Is ERP? Understanding Enterprise Resource Planning Systems In the present-day day fast-paced, and data-driven business world, organizations are adopting integrated systems within their operations in order to be efficient in running business operations. With the growth of the business, there is no easy way to manage departments like finance, human resources, supply chain, sales, and inventory independently. Enterprise Resource Planning systems are also instrumental in this. ERP systems can assist the organization centralize data, automate their processes and make better decisions. An ERP system helps companies achieve a more efficient, cost-effective, and productive operation by allowing the adaptation of several business functions into one platform. What Is ERP? ERP is an acronym that refers to Enterprise Resource Planning, software, which is used to coordinate and administer fundamental business activities in an organization. ERP enables all functions to be run on a single database as opposed to separate systems used by different departments. With an ERP software system, data within various business regions is collected, stored and processed in real time. This will guarantee uniformity, precision and availability of information throughout the organization. ERP systems are popular among small, medium, and large enterprises to automate the processes and improve working together. ERP, at its simplest, is a way of utilizing organizational resources, be it people and processes, better to accomplish organizational objectives through the use of technology. Key Features of ERP Systems The contemporary ERP systems have broad features that cater to the functions of the business in various departments. These ERP software features are meant to enhance efficiency, transparency and control. Key features include: Database that is centralized to access real-time data. Routine business process automation. Unified financial management and accounting. Supply chain and inventory tracking. Payroll management and human resource. Reporting and analytics dashboards. ERP modules are ready to be customized by modular design to suit the demands of various industries and business scales. Types of ERP Systems Types of ERP systems come in various forms which are tailored to suit different business needs, financial constraints and preferences of deployment. On-Premise ERP On-premise ERP solutions get installed and supported on the own servers of a firm. They are very controllable and customizable but demand a large outlay and IT. Cloud-Based ERP Cloud ERP systems are stored on those of the vendor and are accessed through the internet. Such systems are affordable, expandable and less technical to maintain and have become popular with the current business world. Hybrid ERP Hybrid ERP integrates cloud and on-premise platform and enables businesses to store sensitive data in-house and enjoy the flexibility of cloud computing. Industry-Specific ERP Other ERP solutions are targeted at particular industries including manufacturing, healthcare, retail and education providing specialized ERP modules and workflow, such as Lab Management Software designed for diagnostic centers and medical laboratories. Benefits of Implementing ERP Adopting ERP system has many benefits that facilitate business development in the long term. The ERP benefits are not limited to the efficiency of operations but also to strategic planning and customer satisfaction. Major benefits include: Enhanced proper data quality and consistency. Improved interdepartmental cooperation. Automation leads to increased productivity. Decision-making and reporting in real time. Low operation and administrative expenses. Better compliance and risk management. ERP solutions for enterprises help organizations have more visibility of the operations and thus proactively make plans and responsive operations to changes in the market. Challenges of ERP Implementation Although ERP has benefits, it also has its own challenges. The ERP implementation process may give delays, overruns on budget and resistance to change by users in case the implementation process has not been laid out properly. Common challenges include: Expensive first-mover expenses. System complexities in customization. Opposition to change by employees. Data migration issues Training and skill gaps In a bid to address these challenges, organizations should invest in adequate planning, involvement of stakeholders, and continued support. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation How to Choose the Right ERP System? The choice of appropriate ERP solution is essential in attainment of desirable business results. Organizations ought to be keen in analysing their requirements then selecting an ERP platform. Using the following as the main factors to be considered: The size of the business and industry demands. Necessary ERP modules and scalability. Preference to deploy (cloud, on-premise or hybrid) Total cost of ownership and budget. Customer service and reputation of the vendor. Intuitiveness and integration. The right ERP software solution helps to match the business objectives and provides future expansion without the complexity that should not exist. Conclusion ERP systems have become a necessity for all organizations that aim to gain efficiency in their operations and strategic leveraging. ERP systems enhance accurate and transparent business operations and interdepartmental cooperation by removing business processes as isolated entities. Even though the ERP implementation process is complicated, the long-term advantages greatly exceed the obstacles, provided they are adequately implemented. ERP can change the way enterprises use resources, make decisions, and grow with the appropriate planning and solution. FAQs Why is an ERP system important? An ERP system is primarily aimed at unifying and automating the key business procedures to supply one location of precise information to enhance effectiveness and decision-making. Does ERP software apply to large organizations only? No, small and medium-sized businesses can also use modern ERP software, which has scalable solutions depending on the needs of organizations. What is the time the ERP implementation takes? Depending on the complexity of the systems, customization and the preparedness in the organization, ERP implementation may be completed in few months to more than one year. What are ERP modules? ERP modules are specific parts of an ERP system (finance, HR, inventory, or sales) that can be implemented in a business jointly or separately, depending on the business requirements.
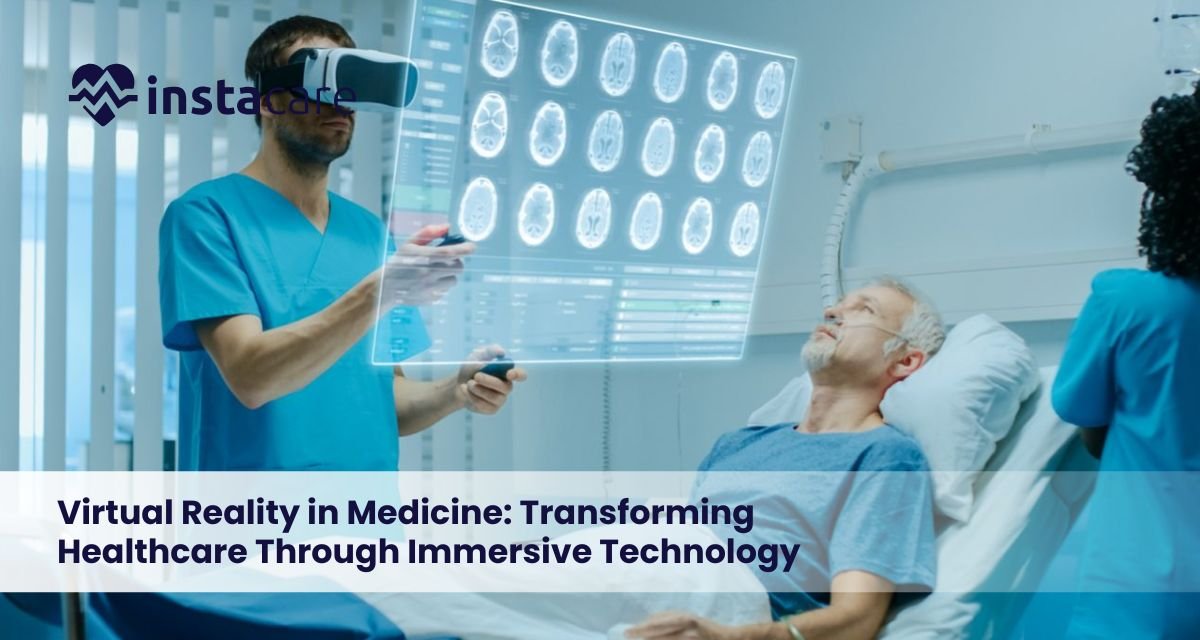
Virtual Reality in Medicine: Transforming Healthcare Through Immersive Technology The medical field is experiencing the digital revolution, and the idea of immersive technology in medicine is the focal point of the revolution. VR has not been restrained to entertainment anymore, but is currently being implemented in hospitals, medical schools, and therapy centers. VR is transforming healthcare delivery, whether it is creating more accurate surgery or making the procedure more comfortable. The use of modern medical virtual reality applications can provide healthcare workers with the opportunity to train in a safe manner, treat patients better, and increase clinical results thanks to real simulations. What Is Virtual Reality? Virtual reality refers to a three-dimensional environment and is a simulated environment created by computers and experienced by users through VR headsets and motion tracking devices. The major features of VR are: Complete involvement in an online world. Live communication with virtual objects. A great deal of visual and sensory stimulation. Augmented reality vs virtual reality in healthcare is a common comparison in healthcare-related discussions. Whereas AR is used to overlay digital objects on the physical one, VR is more preferable for training, therapy, and simulation-based care as it is fully immersive. How is Virtual Reality Used in Medicine? Virtual reality has clinical uses in many spheres of healthcare and has been used to benefit both the practitioners and the individuals receiving care. VR is commonly used for: VR in medical training and skill building. Treatment and therapy of patients. Virtual reality surgery simulation and planning. Physical recovery and rehabilitation. These applications indicate the way that VR for patient care enhances safety, accuracy, and involvement in the medical environment. VR in Medical Training and Education Medical training VR has altered the way medical workers understand complicated practices. Virtual reality medical education allows students to practice again and again without any risk in the real world. Perks to education include: Interactive 3D learning of anatomy. Simulation of emergency response. Procedural accuracy in a virtual reality simulation of surgery. Less use of cadavers and live patients. This simulative method enhances self-esteem, decision-making and technical ability. Virtual Reality in Patient Treatment The use of VR therapy in healthcare as a therapeutic tool is gaining more and more use. In the healthcare sector, VR therapy is used to control physical and mental health. Some typical uses of the therapy include: Virtual reality for pain management. Lessening anxiety and stress. Diversion therapy of chronic pain. Preoperative emotional preparation. The patients feel more comfortable, less dependent on medications, and their recovery is more successful. VR in Surgery and Clinical Practice VR promotes planning and execution in surgical settings. Virtual reality surgery simulation enables surgeons to practice complicated surgeries using patient-specific information. Clinical benefits include: Higher accuracy of surgery. Less risk of complications. Greater comprehension of the patients through graphic explanations. Improved cooperation between teams of medical workers. The developments enhance credibility and overall quality of care. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Virtual Reality in Medicine The benefits of virtual reality in the healthcare systems include: Increases learning experiences. Enhances the level of patient engagement and satisfaction. Embraces VR rehabilitation therapy. Reduces medical errors. Makes the process of treatment personalized. Increases medical education. VR is transforming the field of modern medicine through its ability to bring together innovation and empathy. Challenges and Limitations Although it has potential, VR adoption has a number of obstacles: Expensive initial costs of setup and maintenance. Training and technical complexity. Dizziness or eye strain to others. Data security and privacy issues. These limitations would have to be tackled in order to increase the use of medical virtual reality applications. Future of Virtual Reality in Healthcare The future of virtual reality in medicine is bright. VR will be combined with wearables, telemedicine platforms, and artificial intelligence with the advancement of technology. Possible future developments are: AI-based simulated personalized treatments. Remote VR-based medical training. High-level exposure to virtual reality therapy. More extensively used in mental and physical rehabilitation. Such innovations will turn VR into a commonplace feature of healthcare provision. Real-World Examples Virtual reality is already changing patient outcomes across the globe. Examples include: VR in PTSD and anxiety Phobia virtual reality exposure therapy. Stroke rehabilitation therapy using VR. Immersive distraction programs for pain management. These practical applications indicate the increased clinical effects of VR. When VR Is Most Effective in Medical Settings? VR would be best applied in a situation where simulation, visualization or emotional involvement is needed. It works best in: Healthcare education and training. Pain and anxiety management. Mental health therapy. Physical rehabilitation. Preoperative preparation and rehearsal. Immersive and controlled digital experiences are very useful in such environments. Conclusion VR is revolutionizing the medical field by contributing to better education, patient outcomes, and clinical efficiency. Immersive technology in medicine is transforming the medical field with VR in medicine training, therapy, and surgical uses. With an increasing number of issues addressed with virtual reality and increased accessibility, patient care, education, and clinical practice will remain redefined worldwide. FAQs What is the application of virtual reality in medicine? Medical training, surgery simulation, pain management, rehabilitation, and mental health treatment are some of the areas where medical virtual reality applications are applied. Does virtual reality work in the management of pain? Yes, virtual reality for pain management is useful in decreasing the perception of pain, which distracts the brain and decreases anxiety. What becomes of virtual reality in healthcare? The future of virtual reality in medicine involves AI-driven simulations, customized therapy, and broader application in everyday clinical use.
Database Management Software: Definition, Types, and Benefits In the present-day information-driven society, organizations produce, archive, and process large amounts of data on a daily basis. The efficacy, security, and precision of managing such data are essential in the functioning of a business, decision-making, and expansion. It is at this stage that the database management software comes in the picture. It offers an organized manner of storing information, the ability to retrieve it fast, consistency, and prevents information theft or destruction, making it a reliable data storage and management software solution. Database management software is the workhorse of the modern digital infrastructure, both in small businesses with the need to track customer information and large enterprises managing their systems with complex transactional aspects. The knowledge of its working, its types, and the advantages it has, assists organizations to select the appropriate solution to their needs, especially when choosing suitable database software for businesses. What Is Database Management Software? Database management software also referred to as a database management system (DBMS) is a computer program that enables a user to create, store, manage, retrieve and manipulate data in an organized way. It serves as a contact point in between the database and users or applications and makes sure that data is organized, accurate and safe. A DBMS gives a centralized storage of information rather than scattered files and as such it becomes easier to access as well as update and maintain information. It also dedicates regulations to verify data integrity and avoids completeness whereby there are many users of the database at once. Types of Database Management Software Database management software consists of a number of types that are created to serve various data needs and loads. Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) A relational database management system (RDBMS) stores information in structured tables, which are in form of rows and columns. Tables are related through keys thus making retrieval of data easy and predictable. It has the following key features: Access to structured query language (SQL). Good data integrity and data consistency. Applied in business and enterprise environments. SQL Database Software SQL database software is based on the Structured Query Language to define, manipulate and query data. It is best suited to complex queries, transactions as well as structured data models. Common use cases include: Financial systems Inventory management Customer relationship management (CRM) NoSQL Database Software NoSQL database software is not created to process unstructured data or semi-structured data. It is not based on predetermined table schemas as relational databases are. Key advantages: High scalability Flexible data models Big data and real-time applications Cloud Database Management Cloud database management enables databases to be managed and hosted on clouds. Such solutions provide scalability, flexibility and lower the infrastructure costs. Benefits include: On-demand resources Automatic updates and automatic backups Global accessibility Enterprise Database Software Enterprise database software is designed to serve large organizations that demand large volume of data, complex transactions and demand high level of security. Typical features: Advanced performance tuning Disaster recovery and high availability Well-developed access control and auditing Open Source Database Software Open source database software allows the source code to be free, customized and developed by the community. Startups and developers like it because it is relatively cheap and flexible. Key Features of Database Management Software The current database management software is featured with a broad spectrum of capabilities that aid effective data management. Core features include: Storage and management of structured and unstructured data Tools of data definition and manipulation Access control and authentication by users Backup and recovery systems Monitoring and maintenance using database administration tools Optimization of query and indexing Concurrent user support All these characteristics make databases reliable, secure, and performant while ensuring strong data security in databases. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation How Database Management Software Works? Database management software operates by arranging the data into rational arrangements and offers tools to work on the said data. The DBMS is used when a user or an application makes a request, where it processes the request, retrieves the necessary information and data integrity is maintained during the entire process. The basic workflow includes: Accepting user or application queries Converting queries into internal operations Efficiency in data accessibility Using rules of security and consistency Providing the results back to the user or the application On the backside of the scenes, the system handles memory allocation, indexing and transaction control and error handling to have a smooth running that supports effective database performance optimization. Benefits of Using Database Management Software The benefits of using database management software are quite many in any organization regardless of its size. Improved Data Organization Information is organized in a systematic and uniform way which minimizes repetition and mistakes. Enhanced Data Security Data in databases is secured by strong access controls, encryption, and authentication gaining protection of sensitive information. Better Performance Some features such as indexing and caching assist in optimizing performance of the database, which is fast in retrieving data. Scalability Existing systems offer scalable database solutions that are expandable to business requirements. Data Integration Data integration and management support enable the interaction with other applications and systems with ease. Reduced Operational Costs Centralized management and automation saves manual effort and maintenance money. Common Use Cases The software in database management is applied in many industries and applications. Common use cases include: ERP Software and business applications E-commerce platforms Banking and financial services Healthcare records management Educational institutions Reporting and analytics systems Business customer, sales and operations database Such systems provide the integrity of access to important data at any given time. How to Choose the Right Database Management Software? The choice of a suitable database management software will require a number of factors pertaining to the business needs and technical limitation. Key considerations include: Type and volume of data Scalability requirements and performance Budget and licensing model Compliance requirements and security Cloud deployment vs on-premise deployment Access to support and community services Organizations are expected to consider various opportunities
Hospital Information Management System (HIMS): A Complete Guide for Modern Healthcare The world’s healthcare systems are changing fast as a result of digital transformation and the necessity to provide efficient patient-centred care. Manual processes are currently virtually impossible and prone to errors in hospitals that deal with huge amounts of clinical, administrative and financial data. This is where a Hospital Information Management System is required. HIMS assists healthcare professionals in streamlining operations in hospitals by implementing technology in daily practices, decision support, and patient outcomes within a modern healthcare information system. What Is a Hospital Information Management System (HIMS)? A Hospital Information Management System (HIMS) is a complete online tool, which is meant to coordinate every side of hospital work. It integrates clinical, administrative, financial and operational operations into a single hospital information system. HIMS enables the hospitals to store, process and access patient information electronically as opposed to paper-based systems. It helps in registering patients, making appointments, diagnostics, billing, reporting, and compliance. Simply put, it can be described as the backbone of the digital world of the modern hospitals, functioning as advanced hospital management software that facilitates communication within the departments. Key Components of a Hospital Information Management System Strong hospital information system comprises a number of inter-linked modules, whose functions within the hospital activities are: Patient Registration and Admission Module: The module that handles the demographics of the patients, the details of their admission and their discharge, supporting a reliable patient information management system. EMR Stores: Holds clinical information including diagnoses, treatment plans, laboratory results and physician notes within an electronic hospital management system. Clinical Information System: Assists the doctors and the nurses with access to real-time data about the medical information, which enhances the clinical decision making as part of a structured clinical information system. Billing and Financial Management: Automates billing, insurance claims, payments and financial reporting. Pharmacy and Inventory Management: Tracks medications, stock levels, and usage to prevent shortages and wastage. Hospital ERP Software: Integrates into one system the human resources, procurement, payroll, and asset management through hospital ERP software. The Hospital Workflow Management System: Organizes work in different departments to ensure efficiency and minimization of delays using a comprehensive hospital workflow management system. These elements combined form an all inclusive electronic hospital management system supported by a centralized hospital data management system. How HIMS Works in a Hospital Environment? HIMS is a digital ecosystem that is centralized. Every time a patient comes, he or she is keyed into the system and immediately available in all departments. In real time, doctors can access medical histories, nurses can update on the progress of treatment, the labs can post test findings, and the billing departments can create the bill. This continuous flow of data enhances coordination and gets rid of duplication. The hospital data management system will guarantee accuracy and consistency in information and secure access to information, allowing staff to dedicate more time to the patient, as opposed to the administrative aspect, through integrated hospital IT systems. Benefits of Implementing HIMS Implementation of a hospital management software has many benefits: Better Efficiency: Automated processes save on paper work and administration overheads. Improved Data Accuracy: Digital records reduce mistakes that come about due to recording by hand. Enhanced Clinical Decision-Making: Real-time patient access helps in proper diagnoses and treatment plan. Cost Reduction: Improved operations and rationalized resource use reduced the cost of operation. Regulatory Compliance: Ensures that there is proper documentation and reporting in line with the healthcare regulations. Centralized Hospital IT: Systems forms a single point of all operations of the hospital. In general, HIMS enhances productivity at the same time with high care standards using a secure medical information management system. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Role of HIMS in Improving Patient Experience One of the healthcare performance indicators is patient satisfaction. HIMS is essential in improving the patient experience through the reduction of wait time, enhancement of communication and continuity of care. Having a stable patient information management system, patients can be registered faster, have timely test results, correct billing, and easier follow-ups. Digital documentation also facilitates tailored care, since the medical history is available to the health practitioners. Moreover, billing and treatment plans promote transparency that fosters trust between the patient and health care provider. Challenges in Implementing HIMS Notwithstanding its positive side, HIMS has challenges: The cost of High Initial Investment: Infrastructure, software licensing, as well as training, may be expensive. Resistance to Change: The staff might be hard to adjust to the digital systems replacing the manual systems. Data Safety and Privacy Implications: Assure confidentiality of medical records. System Integration: Problematic with existing system may be complicated. Training Requirements: On-going employee training is also necessary to make good use of it. Nevertheless, these challenges could be managed with the help of appropriate planning and support of vendors. HIMS vs Other Healthcare Information Systems HIMS is not to be confused with other systems, however, it is broader in its scope: Electronic Medical Records (EMR): Only clinical information. Laboratory Information Systems (LIS): Laboratory operations. Radiology Information Systems (RIS): Processes imaging information. HIMS is more comprehensive and involves all these functions in a single medical information management system as compared to standalone solutions. Future of Hospital Information Management Systems The future of HIMS is strongly related to new technologies. The operations in hospitals are being changed by artificial intelligence, machine learning, cloud computing, and big data analytics. The future systems will be predictive, diagnostics based on automation, integration of telemedicine, and interoperability. The postmodern hospitals will be based on the enhanced hospital workflow management systems that will enable hospitals to provide quicker, safer, and more individualised care. HIMS will also be more innovative, safer, and patient-centred and yet again, healthcare will be becoming more digital. Conclusion A Hospital Information Management System is more than a luxury, nowadays, it is a necessity in healthcare institutions. HIMS is also an efficient approach that helps to improve patient care, promote long-term sustainability, and integrate clinical, administrative, and
Product Information Management (PIM): What It Is and Why Your Business Needs It? The modern-day digital-first business world has led to the sale of products in a variety of platforms such as websites, market places, mobile applications, social commerce and physical stores. The control of the correct, consistent, and timely product information in all these channels has become more complicated. Product Information Management (PIM) is an essential part in this. Properly deployed PIM system assist business to place product data in a centralized and managed and enriched and distributed location to enhance better customer experiences, time-to-market and operational control, especially when supported by advanced PIM software solutions. What Is Product Information Management (PIM)? Product Information Management A systematic process and software-based methodology of collecting, storing, managing and distributing product-related information on a single point of truth. This contains product descriptions, specifications, pictures, videos, pricing attributes, technical information and localization information using modern PIM tools. A product data management system would provide the same validated and updated information to all teams and channels, unlike spreadsheets or disconnected databases, which would help reduce errors and inconsistencies while maintaining centralized product information. Why Product Information Management Is Important? With the increasing product catalogs and number of sales channels, manual management of product information will be inefficient and prone to errors. PIM guarantees consistency, accuracy and scalability. It helps companies to react better to the changes in the market, build stronger brand reputation, and make expensive errors due to out-of-date or incomplete product information, highlighting the overall benefits of product information management. PIM for ecommerce is particularly imperative to businesses that operate over the Internet since product information is a direct factor in determining the rate of conversion, search popularity, and consumer confidence. Key Components of a PIM System A sound PIM system can consist of the following: Store of all product characteristics. Enrichment and validation processes of data. There are version control and approval processes. Image and video media asset management. Support to localization and translation. Formatting of channel specific data. These elements, combined collectively, produce centralized product information that will not be duplicated on several platforms. How PIM Works? PIM operates by serving as a distribution center in between internal and external sales channels. External data on products are imported through ERP systems, suppliers or internal databases. This information is then augmented with marketing content, technical details and compliance details. Upon the approval, this information is automatically disseminated to ecommerce sites, marketplaces, print catalogs, and mobile applications. Prominent systems are used to enable PIM integration with ERP to synchronize pricing, inventory and SKU data in real time. Benefits of Using Product Information Management Product information management has more advantages than operational efficiency. Key advantages include: Quick channel product launches. Data accuracy and consistency are improved. Less manual labour and fewer errors. Greater customer experience and confidence. More powerful brand image. Better search and findability. Enterprise PIM solutions also allow governance, scalability, and role-based access control to large organizations. PIM vs Other Systems PIM tends to be mixed with other systems of business. It is imperative to know the differences. ERP emphasises on the business transactions, inventory, and finance. DAM is concerned with digital content or images and videos. CMS manages website content PIM is not a replacement system, but a complement to these systems. The product data management vs PI debate has frequently pointed out that PIM is specifically involved in enriching as well as distributing product data. In contrast, traditional product data management is more involved with internal product life-cycle data. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Who Needs a PIM System? A PIM system can be useful to any business with a large or complicated product catalog, such as: Ecommerce retailers Distributors and manufacturers B2B wholesalers Brands that are sold in various markets Omni-channel retailers PIM for omnichannel retail makes sure that the customers are provided with the same product data no matter where they plan to shop online, in-store, or via third-party channels. Common Challenges Without PIM Some of the recurrent problems facing businesses, which do not have a PIM system, include: Different channel descriptions of products. Delayed product launches Overdependence on spreadsheets. Recurring data malfunctions and replications. Inadequate team cooperation. Limited scalability Thousands of SKUs cannot be managed efficiently and cost-effectively in the long term without digital product catalog management. How to Choose the Right PIM Solution? The identification of the appropriate PIM relies on the size of the business, complexity and growth strategies. Some of the major considerations to make are: User friendliness and personalization. Scalability of the future expansion. Ability to integrate with the existing systems. PIM integration with CM integration. Security and governance of the data. Vendor support and roadmap The latest PIM tools are more cloud based and they are able to be deployed quickly and at lower cost of infrastructure. Future of Product Information Management Automation, AI, and personalization are the aspects that are closely related to the future of PIM. Emerging trends include: AI-based enhancement and classification of data. Personalization of real-time content. Greater integrations at the marketplace. Intelligent analytics and data quality management. More integration with customer experience platforms. With the development of digital commerce, a PIM software solution will be an inseparable part of the enterprises that use data. Conclusion Product Information Management is no longer an option to businesses that exist in competitive, multi-channel markets. PIM enhances efficiency, accuracy and the customer experience by centralizing and streamlining the product data. Scaling an ecommerce business or dealing with complex product catalogs, a properly selected PIM system is the backbone of sustainable growth of a digital economy. FAQs What are the most effective businesses of PIM? Companies that have voluminous product lists, more than one channel to sell products, or that change products often are the biggest benefactors of a PIM system. Is PIM limited to ecommerce firms? No. PIM is also utilized by manufacturers, distributors and B2B organizations to control and transmit correct product information effectively. Is PIM compatible with
Human Resource Management Software: Streamlining Workforce Management for Modern Businesses Human Resource Management Software (HRMS) is now a critical enterprise level technology, which organizations are looking to best automate, optimize and centralize their workforce related functions. Manual HR methods that are used as companies grow lead to inefficiencies like duplication of data, compliance risk, slow approvals, and false insights into the workforce. HRMS solutions address these problems by offering end-to-end digital ecosystems of employee lifecycle functions, real-time analytics, and policy-based automation. Today, companies need a system that can accommodate distributed teams, high volume data processing and compliance with strict regulation. HRMS solutions are able to offer this and at the same time maintain cost-effectiveness, data integrity, and operational efficiency. What Is Human Resource Management Software? An integrated digital platform that provides management of the entire employee lifecycle including recruitment and onboarding, payroll, attendance, and performance analytics. An HRMS is a central human resource system that consolidates data on the employees, automates the processes, and allows HR teams to work more precisely and with less manual intervention. Typical modules of comprehensive HRMS architecture are modules covering personnel management, document management, compliance management, time management, calculation of payroll, and benefits management. There are also cloud-native formations of remote accessibility, multi-location operation, and continuous scaling. Key Features of HRMS An effective HRM software has integrated several levels of functionality to facilitate the operations of the workforce. Key features include: Single-point Employee Information Management The company keeps employee records, contracts, digital documents and organizational structures in a safe database instead of paper methods of storage. Automation of Talent Acquisition and Onboarding of HR Companies automate formalities related to joining, documents submission, role allocation, and induction processes with the help of HR onboarding software, which saves time, and increases compliance accuracy. Biometric Integration and attendance HRMSs tend to incorporate HR attendance management that has time clocks, geofencing of field workers, and automated shift assignments. Payroll Generation and Compliance Since it has inbuilt HR payroll software, monthly payroll calculation encompasses overtime, deductions, insurance, EOS benefits, tax compliance and allowances. Performance Monitoring Structures HR performance management modules are the modules through which organizations monitor KPIs, OKRs, competencies, and appraisal cycles based on analytics and organized evaluation templates. Cloud Infrastructure Contemporary systems are implemented in the form of cloud-based HR software that guarantees their availability, portability, and low scalability. Personnel Management Analytics and Dashboards HRMS systems create real-time attrition, absenteeism, performance, training requirements, and workforce cost projection dashboard like. Benefits of Using HRMS Improved Operational Effectiveness In this way, the HR departments automate repetitive processes in employee management like attendance validation, leave approvals, contract renewals, and payroll by use of employee management software. Minimization of Compliance Risk and Red errors Digitized workflows guarantee that the rules of labor law, policy limits and organizational SLAs are followed in an uninterrupted manner. Data-Driven Decision Making HR software solutions provide embedded analytics that allow leaders to evaluate the performance of the workforce, staffing requirements, trends in overtime, skills gaps, and inefficiency by department. Better Employee Engagement Workforce management software has self-service portals through which employees request leave, upload documents, receive payslips, monitor performance scores and file grievances. Lean Recruitment and Retention The automation saves time to hire, enhances the hiring experience, and offers HR an insight into attrition trends. Growth Business Scaleability Cloud-based architecture will guarantee easy growth to a new location and department without limitations on the infrastructure. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Choosing the Right HRMS When choosing an HRMS, it is necessary to consider the operational requirement as well as the long-term organizational strategy. Key Criteria: Functional Coverage See to it that the core services like payroll, attendance, performance and onboarding are not third-party add-ons. Integration Capabilities Systems will have to integrate with ERP, financial platforms, access control devices, biometric devices and external identity systems. Adaptability Flexibility Role-based workflows Approval matrices, leave policies, pay structures should be able to be customized to complex organizations. Compliance Alignment The HRMS should facilitate the regional labor laws, the visa renewal process, labor working hours, and insurance policies. Data Security Architecture Find ISO-certified hosting, password encryption, MFA, and role-based access controls. Automation & AI Layer Solutions This provides HR automation tools solutions that would greatly cut down the HR overhead through predictive alerts, automated onboarding and anomaly detection. Implementation Tips for Businesses A successful implementation must have an organized implementation roadmap: Conduct a Process Audit Mapping the existing HR functions to determine manual bottlenecks, redundant processes, and compliance lapses. Data Migration Strategy Clean up and harmony employee data formats and integrity checks completed prior to uploading the HRMS. Configure Custom Workflows Consistent and align the policies of leaves, wage structure, overtime arrangements, and approval lines with the HR governance model of the organization. Integration Phase Integrate the HRMS and the ERP systems, biometric systems, email systems, and document management systems. This is necessary to have a smooth environment for the HR management system. User Training Train HRs, heads, and employees to make sure that the employees know how to use the systems. Pilot Testing Practice soft-launch rollouts to discern the issues with the system, delays in the workflow, and challenges at the user level. Full Deployment & Monitoring Implement organization-wide go-live and observe the system regarding compliance obedience and processes efficiency. Future of HR Management Software HRMS systems will keep on developing with highly automatized systems, analytics and cognitive computers: Anticipatory Workforce Analytics The high-tech models to predict attrition, drops in productivity, and staffing needs will be based on advanced forecasting methods of predictive analytics applied to healthcare but with an HR twist. AI-Driven Recruitment The AI-based engines will filter the resumes, detect skill deficiencies, schedule interviews and rank shortlisted applicants with AI-based healthcare-like reasoning but adapted to the HR. Real-Time Decision Engines The systems in the future will incorporate the enhanced algorithms of real time scheduling, dynamic workload balancing, and the proactive performance interventions. Improved EHR-style Employee Profiles Similarly to the medical systems that have clinical profiles, the HRMS will
Healthcare Analytics Software: How Data Is Transforming Modern Patient Care In modern healthcare, results depend more on how data is used. Because of this, clinics and hospitals now apply analysis tools to support choices in treatment, cut delays, reduce waste, also lift service quality. These systems give live updates on patient patterns, staff workloads, and equipment needs, while forecasting risks before they grow serious. They turn unorganized information into practical steps for care teams. What Is Healthcare Analytics Software? Healthcare analytics tools gather patient and system information to support better choices. These systems analyze medical records, use forecasts, show reports, plus display insights through interactive screens. Data flows in from EMRs, labs, or wearables, enabling clinics to track treatment progress while spotting dangers early. Providers gain clearer oversight, helping them act ahead of time to improve results. Key capabilities: Data aggregation across multiple sources Display of client data alongside system performance measures Predicting how illnesses develop plus sorting patient risks Linking EMR or EHR platforms to support smooth daily operations Why Healthcare Analytics Matters Today Today’s medical system deals with more patients, widespread long-term illnesses, plus higher running expenses. Using data tools matters greatly because it helps manage these challenges effectively through better insights and planning over time Improving patient results by using data-driven choices instead of assumptions Lowering hospital readmission rates while cutting mistakes in treatment Improving how workers are assigned, alongside better handling of supplies Using shared data to help public health efforts through combined analysis Groups that apply data tools in healthcare see higher satisfaction from patients, fewer workflow issues, also stronger adherence to rules. Key Features of Healthcare Analytics Software Healthcare medical analytics platforms offer a range of specialized features tailored for clinical and operational needs: Live health data tracking: instant updates on vital signs, test outcomes, triggering faster care actions when needed. Healthcare Dashboard Software: healthcare dashboard software tools let users adjust views to show key data, patterns, or patient details, helping leaders and care teams check info fast through tailored layouts that improve clarity and decision speed by organizing inputs clearly. Predictive Analytics for Healthcare: predictive analytics for healthcare uses machine learning to forecast illness trends, estimate needed resources, while also sorting patient risks by likelihood. Population Health Analytics Tools: Population health analytics tools assess community patterns, helping spot vulnerable patients, so clinics can act early. These systems track outcomes while guiding prevention strategies through data use instead of guesswork. AI-Based Healthcare Capabilities: Use AI-based healthcare to spot issues automatically. Or streamline daily operations efficiently. Also assist doctors with smart tools for better choices. EMR/EHR Analytics Integration: EMR/EHR analytics integration combines patient records with lab outcomes through a single analytical platform, also linking imaging details efficiently. Types of Healthcare Analytics Healthcare clinical data analysis falls into four main kinds Descriptive Analytics: gives an overview of past information to notice trends in patient entries, recovery results, or how equipment is used, using insights from earlier records while focusing on practical observations rather than complex theories. Diagnostic analytics: looks into causes of results, like why readmissions are frequent or treatments don’t work well, by examining patterns from past data using logical review methods. Predictive Analytics: Leverages math-based tools to estimate health risks, track illness development, or anticipate workload needs. Prescriptive Analytics: Recommends actionable strategies, including optimized treatment plans, staffing schedules, or resource allocation. Every kind supports different goals, some help hospitals track data, while others improve community well-being. Benefits of Healthcare Analytics Software Implementing robust analytics software provides tangible benefits: Data-Driven Decision Making: Data-driven decision boost clinical choices by using actual patient information to guide actions, through this, accuracy increases while assumptions fade. Operational Efficiency: Streamlined operations improve bed use, staffing plans, or supply tracking, cutting down on excess. Each part works better when linked through clear processes instead of isolated fixes. Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Patient results improve when forecasts and risk checks support timely actions or prevention steps. Regulatory Compliance: Simplifies documentation for HIPAA alongside ICD-10, meeting key healthcare requirements efficiently. Cost Reduction: Pinpoints key expenses, cuts redundant steps, while improving how resources are used. Essential Integrations & Technologies To work best, healthcare hospital analytics solutions tools need to connect with current systems through seamless compatibility. EMR/EHR Systems: EMR or EHR Software are essential; they enable ongoing patient information access. Lab Information Systems (LIS): Lab Information Systems deliver test outcomes, enabling timely medical decisions through immediate data access. Imaging Systems (PACS): Combines radiology info with visual records to support full patient review. IoT & Wearable Devices: IoT and wearable tools track health signs nonstop, sending instant warnings when needed. Business Intelligence & Visualization Tools: Business intelligence tools help create reports for hospital leaders. These systems turn data into clear visuals. They assist decision-makers with up-to-date insights. Information is shared through dashboards tailored to management needs. Good integration allows smooth operations, correct reports, or shared data access. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Challenges in Implementing Healthcare Analytics Even though the benefits are obvious, hospitals struggle with putting things into practice because of various obstacles. Data Quality & Standardization: Data quality varies between EMRs, lab results, or imaging records, which impacts analysis accuracy. Different formats from sources like clinics plus hospitals create mismatches that slow down processing. Uniform standards help align entries yet gaps remain common in practice. Expense to set up: Requires big initial spending on tools, equipment, or learning. Costs rise due to technology purchase, setup needs, also employee education. Compatibility problems: Challenges linking various platforms between teams or locations, due to mismatched standards. Systems often fail to communicate properly, creating delays, especially when software versions differ widely. Data Privacy & Security: Using secure systems that follow HIPAA rules, access is limited, sharing happens under strict checks, while storage stays protected through monitored protocols. Resistance to Change: Some clinicians resist shifting to data-based methods instead of familiar approaches. To tackle these issues, a careful strategy is needed along with a step-by-step rollout while preparing those involved. Future Trends in Healthcare Analytics The future of
Virtual Reality in Healthcare: Transforming Diagnosis, Treatment, and Medical Training Virtual Reality (VR) is currently one of the most effective technologies that transform contemporary healthcare. It is no more gaming approach or entertainment tool, as currently hospitals, medical universities, and clinics implement VR systems to provide better patient care, better diagnosis, and support the making of clinical decisions and improve the level of medical training. Due to the development of simulation hardware, motion sensors and haptic feedback, medical VR technology is increasing the transition towards an immersive and data-driven delivery of healthcare. VR provides a simulated digital setting, in which clinicians, trainees, and patients can communicate with realistic situations without any real-life hazards. Consequently, it is still being embraced in the fields of surgery, mental health, physical rehabilitation and patient education. In this blog you will know How VR is used in healthcare. What Is Virtual Reality in Healthcare? In healthcare, Virtual Reality is the application of real-like computer-controlled environments, which create a virtual replica of a medical environment or simulate a clinical scenario. These systems enable the users to visualize anatomy in 3D, practice surgery, simulate patient cases, and undertake complex procedures without taking risks. Its central goal is the improvement of VR-based medical learning, greater accuracy, and better patient outcomes. VR is used more and more in hospitals to facilitate diagnostic imaging, pre-operative planning, and the individualization of treatment. Since clinicians start investigating the way VR can be applied in healthcare, it becomes evident that VR is helping to bridge the gap between theory and practice. Key Applications of VR in Healthcare VR in healthcare applications is also developing with each passing year, some of the most notable applications being: Surgery Simulation and Planning VR changes surgical practice as it allows organ, tumor, and vascular structure 3D modeling. Virtual reality for surgery simulation where the surgeons practice the complicated procedures before they enter the operating room. This minimizes errors, decreases the length of surgery and maximizes patient safety. VR-Based Medical Training VR medical training that simulates real clinical environments is used in medical schools and hospitals to engage students in medical practice and training. Students will be able to develop emergency response, visualization of anatomy and handling of patients, without compromising on the safety of the real patients. VR also has the benefit of repeatability, consistency, and fine-grained performance metrics, something that is not available in the traditional training. Pain Management VR for pain management has become a non-pharmacological intervention used by clinicians as part of the process in non-acute setting during procedures, childbirth, dressing changes, and chronic illness treatment. Immersive surroundings focus the brain, which decreases the perceived pain and the anxiety. Mental Health and Psychological Therapy Virtual reality is experiencing growing use in mental health treatment in the treatment of anxiety disorders, PTSD, phobia, and depression. VR-based exposure therapy enables clinicians to administer stimuli in a controlled and gradual manner, which provides safe and effective treatment directions. Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy VR rehabilitation in healthcare provides guided, interactive recovery channels. VR rehab systems in the medical field are used to aid recovery after a stroke, mobility training, balance and neuro-rehabilitation. The motivation and adherence of patients increases. Patient Education The immersive modules of Virtual reality in patient education that are utilized in clinics in patient education aid patients in comprehending the processes of surgery, treatment, medical procedures, and post-surgical care. Decision-making and fear of treatment before treatment are enhanced with visual learning. Physical Therapy Enhancement The advanced systems designed to be used in VR for physical therapy apply real-time motion tracking to allow patients to rehearse the movements patterns and restore their strength. The therapists can vary the level of difficulty, track progress and create individual routines. Hospital Operations and Workflow VR is often incorporated in modern facilities to train staff in hospitals on emergency protocols, infection control as well as equipment usage and high risk activities. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Using VR in Healthcare The Benefits of virtual reality in medicine are numerous and can be measured, and those will become especially significant in the 2025s and further: Improved Accuracy and Precision Clinicians and surgeons are able to study anatomy, practice and simulate complications beforehand. This increases the levels of clinical confidence and minimizes the chances of errors. Controlled, Risk-Free Training There are no consequences of practicing on a particular case of trauma or a rare disease so that trainees can practice as many of them as possible. Medical educational VR is more effective in developing competence more quickly than conventional training. Enhanced Patient Comfort Virtual reality for anxiety treatment decreases the levels of anxiety among patients undergoing painful procedures. It also assists the pediatric patients as well as geriatric patients in keeping calm during the MRI scans, injections and treatments which are time-consuming. Personalized Recovery VR is used to provide customized exercises and therapeutic spaces in rehabilitation and mental health and make the treatment more interactive and successful. Higher Efficiency and Lower Long-Term Cost VR decreases surgical errors, shortens recovery time, accelerates training, and improves patient satisfaction, which results in reduced operational costs in the long term despite high initial set-up costs. Challenges and Limitations Along with its benefits, various issues affect the implementation of VR: High Initial Cost The investment in VR systems, haptic devices, sensors, and simulation that are medical-grade and high quality is very high. It demands significant resources to be invested, particularly in large hospitals. Technical Complexity Some platforms are delicate to calibrate and maintain. Healthcare workers do not necessarily feel comfortable using new technologies at once. Weak Clinical validation Although VR has potential, numerous applications are yet to undergo extensive clinical trials to be approved and evidenced. Motion sickness and Discomfort A very high percentage of the users might develop dizziness, fatigue or nausea in the immersive sessions. Data Privacy Concerns Medical VR is a sensitive type of data covering patient information, which needs a high level of cybersecurity and meets the requirements of HIPAA/GDPR.
Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care with Data Healthcare is gradually moving into a new phase where medical decisions are becoming more of an active planning process as opposed to a reactionary one. The modern-day hospitals, clinics, and health systems contain colossal quantities of patient data, diagnostics reports and treatment histories to lifestyle trends. With smart healthcare data analysis, such information can be a potent tool that aids in forecasting diseases, the results of treatment, hospitalization, and preventive measures. This technology is called predictive analytics – a technology-based strategy that is revolutionizing patient outcomes, cost reduction, and enhancing efficiency in the operations of healthcare networks. What Is Predictive Analytics in Healthcare? Predictive analytics is the application of statistical modeling, data mining, and artificial intelligence to predict the future health of given the current data. The option is applied in the healthcare setting to discover trends and patterns in patient data to predict medical events as disease progression, response to treatment, readmission likelihood, or emergency risk. The main idea is basic, it is possible to use past and present information to create healthier possibilities in the future Medical prediction models help healthcare organizations to justify decisions, diagnose more accurately, and become less uncertain in medical planning. These systems neither substitute clinicians but empower them with scientifically supported evidence. How Predictive Analytics Works? The predictive analytics system starts by getting a considerable amount of patient data in the form of electronic medical records, diagnostic equipment, wearable health devices, clinical notes, and even genomic data. After collection, the information is cleaned and organized in order to make it true and useful. The data are then analyzed through advanced algorithms to identify the patterns that cannot be seen by the human eye. These algorithms are expected to take into account various factors, including age, lifestyle, previous history, vitals, and lab outcomes, to determine who is possibly at risk of particular health events. The results are presented in dashboards or clinical systems, which allow healthcare personnel to act in time – even prior to the manifestations of symptoms. Major Applications of Predictive Analytics in Healthcare Predictive analytics has become embedded in most spheres of medicine. Here are some key predictive analytics use cases in healthcare: 1. Early Detection of Chronic Diseases Such diseases as diabetes, hypertension and heart diseases are most likely to be forecasted months or even years ahead of complete development. Lifestyle changes and intervention care are more effective when the warning signs are detected early to minimize complications. 2. Prediction of Patient Readmissions Patients are usually readmission cases in hospitals. Predictive analytics can recognize those that have the greatest probability of returning to help doctors with the added monitoring, follow-up, or discharge planning. 3. Treatment Personalization Predictive devices develop personalized treatment regimens by analyzing the reaction of various patients to drugs and treatment. This has a tremendous effect in enhancing success rates and minimizing side effects. 4. Demand Forecasting Resource Management Forecast models enable healthcare systems to plan how they staff, availability of ICU, medicine stock in the system, and equipment placement with more precision, resulting in increased operational efficiency. 5. Public and Population Health Planning Predictive analytics provides an important contribution to the management of outbreaks, seasonal behavior, and health policy at the community level. All these are potent predictive analytics applications in healthcare, where information and technology drive more intelligent decisions. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Predictive Analytics in Healthcare The benefits of predictive healthcare are far reaching and ever-widening. Some core benefits include: Less hospitalization due to timely intervention. Quickly identified and precise clinical decisions. Improved patient satisfaction and care quality. Reduced spending on healthcare and efficient use of resources. Guaranteeing organization of future disease trends. Individualized therapy and response to drugs. Powerful evidence-based treatment of doctors and experts. All of these strengths reflect the increasing worth of predictive analytics benefits in healthcare, which is a change that can improve patient health and medical outcomes. Key Technologies Behind Predictive Analytics Predictive healthcare is driven by a number of digital solutions that are important in interpreting and forecasting data. These include: Neural networks and artificial intelligence. Pattern recognition software and data mining. EHRS integration systems. Real-time tracking and wearable data gathering. Clinician visualization dashboards. Cloud storage of data security. Automation and machine-guided processing assist healthcare teams in large datasets analysis in a short amount of time and to a high degree of accuracy. Such methods as healthcare predictive modeling, machine learning in healthcare, and big data analytics in healthcare collaborate and provide profound understanding of patient trends. Challenges and Limitations In spite of its impressive growth, predictive analytics has such difficulties as: Data Privacy & Security Concerns The data about patients is very confidential. There must be good cybersecurity and regulatory compliance. Technical Complexity Medical institutions do not necessarily have sophisticated digital infrastructure and qualified staff. Model Accuracy & Bias Algorithms also demand constant optimisation so that they would be precise, equitable, and impartial in a broad population. Integration Issues Linking various data resources, old systems, and clinical processes can be time and resources-consuming. Despite the challenges, adoption is still on the rise worldwide as hospitals appreciate the importance of using ai for medical prediction, clinical decision-making through predictive analytics for hospitals, as well as accurate healthcare forecasting models. Future of Predictive Analytics in Healthcare In the coming ten years, predictive analytics is going to be a fundamental support of modern medicine. The systems will evolve out of mere risk predictions into full automated decision support eliminating human error and increasing the speed of diagnosis. Hospitals across the globe will be dependent on cloud-based monitoring systems, wearable devices, and automated warning systems. There will be easier remote management of patients particularly in chronic cases. Early disease detection using analytics will lower the number of mortalities, and hospital predictive analytics will optimise workflow, ambulance routes, the availability of ICUs, and resource allocation. At a
What Is Teleconsultation? A Complete Guide to Modern Virtual Healthcare Teleconsultation, which was in the past an innovative idea, has now become a normal way of attending to patients by millions of people across the globe. It allows patients to contact the doctor at home, office, or during traveling, through smart phones, tablets, and computers. Teleconsultation helps save time, minimize expenses, and enhance patient satisfaction regardless of whether the medical consultations are urgent, covering long-term conditions, or regular follow-ups. Telehealth tools are becoming more and more popular in healthcare systems, hospitals, and clinics to manage the growing patient demand and provide ongoing professional assistance. With the current trend of the drive to digital healthcare, teleconsultation will have an even more significant role to play in influencing the way medical care would be in the future. What Is Teleconsultation? Teleconsultation is a health care provision service in which the patients are able to interact with the medical workers digitally through the use of communication devices rather than physically going to the clinic. It is an inseparable aspect of Virtual healthcare where doctors are able to assess symptoms, make a diagnosis, recommend treatment and prescribe medications without the need to see the patient physically. It does not match the usually available online medical content as teleconsultation is done with licensed doctors or specialists in real-time. It facilitates live video/audio consultation as well as asynchronous communication (text-based or recorded messages). Teleconsultation is very much associated with Telemedicine services, which involve diagnostics, remote monitoring, and medical advice using technology. How Teleconsultation Works Teleconsultation is generally organized and secure: Patient Registration or Logging in Patients use telehealth platforms or mobile health apps to build accounts, identify themselves, and enter basic medical data. Appointment Scheduling Customers choose a physician, specialty, or time of appointment. There are also numerous services with the instant Online video doctor appointments in case of an urgent situation. Medical Submission of Information Patients complete questions, submit past reports or present the symptoms. This move helps the doctors to be ready in advance of the consultation. Live Consultation Consultations may occur via: Video call Audio cal Chat messaging In the session, physicians evaluate symptoms, test results and discuss treatment. This is what Remote patient consultation is all about. Electronic Prescriptions and Recommendations Hospital physicians discuss the prescriptions, lab tests orders, and follow-up details electronically. Aftercare and Internet-based medical support The patients are provided with constant attention by messaging, check-ins, and reminders of medications or tests. Online medical support is where the long-term outcomes are enhanced. Key Benefits of Teleconsultation Teleconsultation is becoming one of the most desired nowadays since it introduces hitherto unknown convenience and effectiveness to the medical experience. Comfort and Saving of time No commuting, no time wastage, and no time constraints. Teleconsultation is convenient and suitable to hectic schedules and enables instant healthcare. Increased Availability of Experts Patients in rural and remote areas will have access to the best specialists regardless of their location in the world. Reduced Healthcare Costs The Benefits of teleconsultation include the expense reduced. Patients save in transportation, clinic cost and sick leave. Services will become cheaper as providers will be able to lower the operational expenses. Improved Chronic Disease Management Teleconsultation enables regular check-ups with the help of digital devices, which are more effective in controlling the status of diabetes, hypertension, asthma, and heart disease. Improved Privacy and comfort Virtual channels may help patients to feel more relaxed when talking about sensitive matters. After-Hours Care Teleconsultation offers the possibility to get medical advice during the time when a clinic is closed, and it allows the patient to obtain the help on time. Lower Risk of Infection Virtual consultations enable the safety of both the patients and the medical practitioners because physical contacts are minimized. Common Services Offered via Teleconsultation Teleconsultation helps in a large scope of medical requirements. Common services include: Consultations with general physicians. Mental health counseling Dermatology assessments Pediatric consultations Nutrition and diet guidance Chronic care follow-ups Second opinions Medication reviews Post-surgery monitoring Interpretation of laboratory tests. Most of the sites also feature Online doctor consultation of urgent but non-emergency cases like cold, fever, allergies, infections, stomach-related problems etc. Who Should Use Teleconsultation? Tele Consultation is appropriate in: Busy Professionals Patients that have busy schedules and cannot easily access clinics. Parents with Young Children The virtual care minimizes the burden of taking ill children. Elderly Patients Less effort to get regular follow-ups without having to drive far. People in Remote Areas Teleconsultation fills the unmet needs gap that exists between medical facilities. Patients who demand Long- term care. Virtual check-in is simpler to monitor. Travelers Staff access to licensed medical practitioners, 24/7. People Who Are Frightened by Exposure to Infection Virtual care decreases the exposure to congested health facilities. Teleconsultation should not be used in an emergency and there is an urgent need of care like bleeding, big injuries, a heart attack, or a problem breathing. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Limitations of Teleconsultation Despite this, teleconsultation has some weaknesses: Absence of Physiological Analysis. Diagnosis of some of them needs physical examination like palpation, detailed auscultation, or imaging. Technology Dependency Needs consistent internet, compatible devices and digital literacy. Not Ideal for All Conditions Complex processes or emergencies cannot be addressed remotely. Data Privacy Concerns Patient information needs to be secured through secure platforms. Service Quality Fluctuation. The quality of care is based on the knowledge of the doctor, the reliability in the platform, and communication tools. The knowledge of such limitations enables patients to make an informed choice of when to use teleconsultation. Teleconsultation Trends & Future Digital innovation and expanding demand by patients keep the field of teleconsultation developing. Future trends include: AI-Powered Diagnostics Artificial intelligence will help in symptom analysis, providing potential diagnosis proposals, as well as determining the level of risk. Remote Monitoring Devices Smart medical sensors and wearable will enable real-time tracking of heart rate, glucose, oxygen, and blood pressure, etc. In-depth Digital Health Ecosystems There will be