Information Management System: Definition, Types, Benefits & Uses In the digital environment we now live in, organizations receive and process large amounts of information every day. The management of such data is essential to decision-making, compliance and operational success. An Information Management System (IMS) is a framework of organizing of information collection, storage, processing, and use. Whether the information is on businesses, health facilities or government departments, a sound IMS makes sure that information is correct, readily available and safe. Modern solutions contribute to streamlined processes, enhanced productivity, as well as regulatory compliance of organizations, based on data governance frameworks as well as integrated information systems. What is an Information Management system? Information management system refers to tools, processes and technologies that resulted in the capture, management and dissemination of information within an organization. It enables orderly gathering, processing, storage, and retrieval of information, which will ensure that information, is available when required by the decision-makers. The information management software in use today usually incorporates the functionality of the document management systems, records management system and the content management systems (CMS) to provide a full service to the enterprises. The end vision is to make sure that the flow of information is effective between all organizational levels, in the support of strategic goals and operational activities. Key Components of an Information Management System An effective IMS has several important elements: Data Management System (DBMS): It will store and categorize structured information so that it is easily accessible. Document Management System: It is used to manage digital documents, which should be version-controlled and securely accessed. Content Management System (CMS): aids in content creation, publication, and cooperation. Records Management System: Archives and maintains records of the past within the regulations of the requirements. Information System Architecture: Determines the interaction of data, hardware, software, and processes. Information Security Management: Prevents sensitive information against unauthorized access and breach. Data Governance Framework: Signs the policies and sets of data quality, privacy, and compliance. These elements are used to aid in the lifecycle management of information, both creation and storage, retrieval and disposal, to guarantee data integrity and usability. Types of Information Management Systems In terms of data type and purposes to serve the organization, IMS may be divided into: Enterprise Information Management (EIM): A solution covering all the data in the organization, incorporating several digital information management systems. Database Management System (DBMS): It is dedicated to the structured storage and retrieval of data with the high level of query and reporting features. Document Management System: Manages Electronic documents, and is used to support version control, automation of workflows and secure access to the documents. Content Management System (CMS): Manages online material like web pages, web blogs, multimedia, and collaborative material. Records Management System: Provides the long term storing, compliance and retrieval of corporate records. Healthcare Information Management System: Hospital Management Systems or Hospital Information Management System are hospital- and clinic-specific platforms designed to manage patient records, laboratory reports, and core medical workflows efficiently. All of them respond to particular organizational needs, yet nowadays most IMS solutions are combined to provide more functionality and efficiency. How an Information Management System Works An IMS is executed in such a way that it simplifies the process of information flow: Data Collection: Data is recorded in different sources including sensors, databases or manually. Data Storage: It is stored in centralized repositories such as a data management system, making it easily accessible and secure. Data Processing: Data is arranged, processed, and classified into actionable information Data Distribution: Relevant Data is disseminated to stakeholders in form of reports, dashboards or notifications. Data Archiving and Disposal: Archiving or destroying data that is old or unnecessary is stipulated by information lifecycle management policies. By doing so, an IMS enhances decision-making, decreases redundancy, and promotes regulatory compliance. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of an Information Management System The benefits of adopting a strong IMS are many: Increased Productivity: Faster access to correct information helps to minimize the time in search of information. Informed Strategic Decisions: Real-time insights are used to make informed strategic decisions. Accuracy of Data: Centralization will minimize replications and mistakes. Regulatory Compliance: Aids in the compliance of legal and industry standard. Information Security: ensures sensitive data is secured by controlling access and encryption. Cost Efficiency: This means less operational cost through the improvement of operations and the elimination of paper-based operations. Teamwork: Supports teamwork by sharing digital information management tools. Applications of Information Management Systems The application of IMS solutions is in industries: Business Information Systems: Control corporate information, customers and financial data. Information Management System: Manages patient records, appointments, and treatment records. Educational Institutions: student records, research data, and administrative records. Government Agencies: Deal with public records and licensing, and interdepartmental communication. Corporate Enterprises: Deploy enterprise information management (EIM) solutions to harmonize the global operations. Organizations get efficiency, compliance, and competitive advantage through such applications. Challenges in Implementing an IMS Nevertheless, organizations have IMS adoption challenges: Expensive initial cost of implementation. Employee resistance due to a lack of knowledge of new technology. Connection to legacy systems. Assuring data quality and consistency. Using information security management procedures. Staying abreast with the fast-changing technologies. These challenges need special planning, training, and constant monitoring in order to address them. Best Practices for Effective Information Management Organizations ought to adhere to best practices in order to maximize IMS efficiency: Create a powerful data governance initiative. Establish clear roles and responsibilities for handling information Install digital information management tools with having scalable architecture. Audit and clean data regularly to keep it accurate. Employee training on compliance and usage of IMS. Check the performance of the monitor system and update the software. The practices will provide a secure, reliable, and productive information management software environment. Future Trends in Information Management Systems The IMS technology is also changing in accordance with new trends: AI/ML: To have predictive analytics and machine learning data processing. Cloud-based Systems: Allow accessibility and scalability. Blockchain to Data Security: Improve information
How Could Doctors Use AI? Transforming Modern Healthcare The adoption of AI in healthcare is literally changing the manner in which physicians make diagnoses, treat, and manage patients. Progress in information processing, robots, and predictive modelling can enable clinicians to process more complex medical data more quickly and effectively. Medical artificial intelligence in medicine is not a substitute of the physician; it enhances the clinical knowledge, decreases administration, and enhances patient outcomes. With the transition to data-driven healthcare systems, AI is becoming a key instrument to contemporary healthcare. AI in Medical Diagnosis Diagnostic medicine is one of the most effective AI applications for doctors. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems examine big data collected in the form of clinical records, laboratory results, and images in order to detect patterns that cannot always be apparent to human clinicians. AI in medical diagnosis can induce better diagnostic accuracy by: Pattern recognition of disease early signs. Eliminating cognitive bias-related diagnosis errors. Enhancing quicker triage in emergency and outpatient care. Machine learning algorithms have the potential to match patient data with millions of historical cases to allow early diagnosis of diseases like cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurological diseases. This evidence-based method improves the level of diagnostic confidence and can enable doctors to intervene at earlier phases of disease. AI for Personalized Treatment Plans AI is an important factor in personalized care using AI in treatment planning. The conventional treatment regimens tend to adhere to universal prescriptions, whereas AI allows custom-made approaches to be developed depending on a specific patient profile. Key benefits include: Genetic, clinical, and lifestyle data analysis. Treatment response and side effects prediction. Maximization of drug choice and dose. With machine learning in healthcare, artificial intelligence systems can constantly learn based on treatment results, improving their recommendations with time. This is an accurate methodology that facilitates more efficient interventions and minimizes unnecessary procedures. AI in Clinical Decision Support AI-driven clinical decision support systems are used to support physicians by making evidence-based recommendations at the point of care. The systems combine patient information and clinical regulations with the real-time research results. Decision support tools that are AI-based assist clinicians in: Identify high-risk patients Assess other types of treatment Minimize clinical practice variability Through data analysis of structured and unstructured data, AI improves the accuracy of decisions and does not limit physicians, who use all clinical control to make decisions. This integration enhances productivity without interfering with professional judgment. AI in Medical Documentation and Admin Tasks One of the greatest problems in healthcare is administrative workload. The solution to this problem lies in AI for administrative tasks in healthcare, which automates administrative operations and documentation. Key applications include: Speech recognition of medical records On-the-fly clinical note generation using automated medical documentation Billings automation and coding Record management and scheduling of appointments AI enables doctors to spend more time attending to patients because they are less involved in paperwork. Such efficiencies also reduce burnout and enhance operational productivity in healthcare systems. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation AI in Patient Monitoring and Remote Care The continuity of care, particularly with chronic and post-operative patients, is improved through AI-based monitoring technologies. AI for patient care can be used to collect data in real-time by use of wearables and remote sensors. Benefits include: Constant check of vital signs Preventive diagnosis of damage Practically no readmissions to the hospitals Predictive analytics in healthcare enables clinicians to foresee complications prior to their development. The AI systems are able to notify the health care provider of unusual trends so that they can take necessary action in time and enhance patient safety. AI in Surgery and Procedural Assistance AI helps in precision, planning, and safety in surgical settings. Technologies that are supported by AI improve accuracy in procedures and reduce the risk. Applications include: Premedical planning with the 3D model Surgical navigation in real-time AI-based robotic-assisted surgery supported by AI in medical imaging AI can also be useful in the interpretation of surgical results to enable surgeons to improve and perfect their methods. These inventions result in fewer complications and shortcomings. Ethical Considerations and Challenges In spite of the benefits, the implementation of AI is associated with ethical and operation challenges. The responsible use of AI in healthcare assumes paying attention to: Data privacy and security Fairness and algorithmic bias AI decision-making transparency Regulatory compliance Physicians need to learn about the limitations of AI and make sure that technology does not override clinical judgment and vice versa. Patient trust and safety rely on ethical systems of governance. The Future of AI for Doctors The future of artificial intelligence in medicine focuses on more integration and cooperation. The doctors will also be more and more dependent on AI systems as they become more sophisticated: Predictive diagnostics Preventive care planning Population health care AI will keep developing into a smart assistant, assisting doctors of various specialties. The emphasis will be made on data-driven, proactive care delivery and not on the reactive treatment. Conclusion The modern healthcare is being revolutionized through AI that gives physicians powerful tools to diagnose, plan treatment, and manage patients. AI improves clinical operational efficiency and decision making, which are achieved by AI in medical imaging and predictive analytics and in administrative automation. Although the issues of ethics and data control cannot be eliminated, responsible use of AI may make it even more powerful instead of taking medical expertise away. With the further development of technologies, AI will continue to be a part of innovative, patient-oriented healthcare. FAQs What are the benefits of AI in the everyday work of doctors? AI will help in diagnosis, treatment suggestions, documentation, and monitoring of patients. Is Artificial Intelligence a credible medical detector? Under the right conditions, AI can help to augment diagnostic accuracy. Can AI replace doctors? No, AI assists clinical decision-making, but cannot substitute human understanding and skills.
Healthcare Analytics Software: How Data Is Transforming Modern Patient Care In modern healthcare, results depend more on how data is used. Because of this, clinics and hospitals now apply analysis tools to support choices in treatment, cut delays, reduce waste, also lift service quality. These systems give live updates on patient patterns, staff workloads, and equipment needs, while forecasting risks before they grow serious. They turn unorganized information into practical steps for care teams. What Is Healthcare Analytics Software? Healthcare analytics tools gather patient and system information to support better choices. These systems analyze medical records, use forecasts, show reports, plus display insights through interactive screens. Data flows in from EMRs, labs, or wearables, enabling clinics to track treatment progress while spotting dangers early. Providers gain clearer oversight, helping them act ahead of time to improve results. Key capabilities: Data aggregation across multiple sources Display of client data alongside system performance measures Predicting how illnesses develop plus sorting patient risks Linking EMR or EHR platforms to support smooth daily operations Why Healthcare Analytics Matters Today Today’s medical system deals with more patients, widespread long-term illnesses, plus higher running expenses. Using data tools matters greatly because it helps manage these challenges effectively through better insights and planning over time Improving patient results by using data-driven choices instead of assumptions Lowering hospital readmission rates while cutting mistakes in treatment Improving how workers are assigned, alongside better handling of supplies Using shared data to help public health efforts through combined analysis Groups that apply data tools in healthcare see higher satisfaction from patients, fewer workflow issues, also stronger adherence to rules. Key Features of Healthcare Analytics Software Healthcare medical analytics platforms offer a range of specialized features tailored for clinical and operational needs: Live health data tracking: instant updates on vital signs, test outcomes, triggering faster care actions when needed. Healthcare Dashboard Software: healthcare dashboard software tools let users adjust views to show key data, patterns, or patient details, helping leaders and care teams check info fast through tailored layouts that improve clarity and decision speed by organizing inputs clearly. Predictive Analytics for Healthcare: predictive analytics for healthcare uses machine learning to forecast illness trends, estimate needed resources, while also sorting patient risks by likelihood. Population Health Analytics Tools: Population health analytics tools assess community patterns, helping spot vulnerable patients, so clinics can act early. These systems track outcomes while guiding prevention strategies through data use instead of guesswork. AI-Based Healthcare Capabilities: Use AI-based healthcare to spot issues automatically. Or streamline daily operations efficiently. Also assist doctors with smart tools for better choices. EMR/EHR Analytics Integration: EMR/EHR analytics integration combines patient records with lab outcomes through a single analytical platform, also linking imaging details efficiently. Types of Healthcare Analytics Healthcare clinical data analysis falls into four main kinds Descriptive Analytics: gives an overview of past information to notice trends in patient entries, recovery results, or how equipment is used, using insights from earlier records while focusing on practical observations rather than complex theories. Diagnostic analytics: looks into causes of results, like why readmissions are frequent or treatments don’t work well, by examining patterns from past data using logical review methods. Predictive Analytics: Leverages math-based tools to estimate health risks, track illness development, or anticipate workload needs. Prescriptive Analytics: Recommends actionable strategies, including optimized treatment plans, staffing schedules, or resource allocation. Every kind supports different goals, some help hospitals track data, while others improve community well-being. Benefits of Healthcare Analytics Software Implementing robust analytics software provides tangible benefits: Data-Driven Decision Making: Data-driven decision boost clinical choices by using actual patient information to guide actions, through this, accuracy increases while assumptions fade. Operational Efficiency: Streamlined operations improve bed use, staffing plans, or supply tracking, cutting down on excess. Each part works better when linked through clear processes instead of isolated fixes. Enhanced Patient Outcomes: Patient results improve when forecasts and risk checks support timely actions or prevention steps. Regulatory Compliance: Simplifies documentation for HIPAA alongside ICD-10, meeting key healthcare requirements efficiently. Cost Reduction: Pinpoints key expenses, cuts redundant steps, while improving how resources are used. Essential Integrations & Technologies To work best, healthcare hospital analytics solutions tools need to connect with current systems through seamless compatibility. EMR/EHR Systems: EMR or EHR Software are essential; they enable ongoing patient information access. Lab Information Systems (LIS): Lab Information Systems deliver test outcomes, enabling timely medical decisions through immediate data access. Imaging Systems (PACS): Combines radiology info with visual records to support full patient review. IoT & Wearable Devices: IoT and wearable tools track health signs nonstop, sending instant warnings when needed. Business Intelligence & Visualization Tools: Business intelligence tools help create reports for hospital leaders. These systems turn data into clear visuals. They assist decision-makers with up-to-date insights. Information is shared through dashboards tailored to management needs. Good integration allows smooth operations, correct reports, or shared data access. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Challenges in Implementing Healthcare Analytics Even though the benefits are obvious, hospitals struggle with putting things into practice because of various obstacles. Data Quality & Standardization: Data quality varies between EMRs, lab results, or imaging records, which impacts analysis accuracy. Different formats from sources like clinics plus hospitals create mismatches that slow down processing. Uniform standards help align entries yet gaps remain common in practice. Expense to set up: Requires big initial spending on tools, equipment, or learning. Costs rise due to technology purchase, setup needs, also employee education. Compatibility problems: Challenges linking various platforms between teams or locations, due to mismatched standards. Systems often fail to communicate properly, creating delays, especially when software versions differ widely. Data Privacy & Security: Using secure systems that follow HIPAA rules, access is limited, sharing happens under strict checks, while storage stays protected through monitored protocols. Resistance to Change: Some clinicians resist shifting to data-based methods instead of familiar approaches. To tackle these issues, a careful strategy is needed along with a step-by-step rollout while preparing those involved. Future Trends in Healthcare Analytics The future of
Virtual Reality in Healthcare: Transforming Diagnosis, Treatment, and Medical Training Virtual Reality (VR) is currently one of the most effective technologies that transform contemporary healthcare. It is no more gaming approach or entertainment tool, as currently hospitals, medical universities, and clinics implement VR systems to provide better patient care, better diagnosis, and support the making of clinical decisions and improve the level of medical training. Due to the development of simulation hardware, motion sensors and haptic feedback, medical VR technology is increasing the transition towards an immersive and data-driven delivery of healthcare. VR provides a simulated digital setting, in which clinicians, trainees, and patients can communicate with realistic situations without any real-life hazards. Consequently, it is still being embraced in the fields of surgery, mental health, physical rehabilitation and patient education. In this blog you will know How VR is used in healthcare. What Is Virtual Reality in Healthcare? In healthcare, Virtual Reality is the application of real-like computer-controlled environments, which create a virtual replica of a medical environment or simulate a clinical scenario. These systems enable the users to visualize anatomy in 3D, practice surgery, simulate patient cases, and undertake complex procedures without taking risks. Its central goal is the improvement of VR-based medical learning, greater accuracy, and better patient outcomes. VR is used more and more in hospitals to facilitate diagnostic imaging, pre-operative planning, and the individualization of treatment. Since clinicians start investigating the way VR can be applied in healthcare, it becomes evident that VR is helping to bridge the gap between theory and practice. Key Applications of VR in Healthcare VR in healthcare applications is also developing with each passing year, some of the most notable applications being: Surgery Simulation and Planning VR changes surgical practice as it allows organ, tumor, and vascular structure 3D modeling. Virtual reality for surgery simulation where the surgeons practice the complicated procedures before they enter the operating room. This minimizes errors, decreases the length of surgery and maximizes patient safety. VR-Based Medical Training VR medical training that simulates real clinical environments is used in medical schools and hospitals to engage students in medical practice and training. Students will be able to develop emergency response, visualization of anatomy and handling of patients, without compromising on the safety of the real patients. VR also has the benefit of repeatability, consistency, and fine-grained performance metrics, something that is not available in the traditional training. Pain Management VR for pain management has become a non-pharmacological intervention used by clinicians as part of the process in non-acute setting during procedures, childbirth, dressing changes, and chronic illness treatment. Immersive surroundings focus the brain, which decreases the perceived pain and the anxiety. Mental Health and Psychological Therapy Virtual reality is experiencing growing use in mental health treatment in the treatment of anxiety disorders, PTSD, phobia, and depression. VR-based exposure therapy enables clinicians to administer stimuli in a controlled and gradual manner, which provides safe and effective treatment directions. Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy VR rehabilitation in healthcare provides guided, interactive recovery channels. VR rehab systems in the medical field are used to aid recovery after a stroke, mobility training, balance and neuro-rehabilitation. The motivation and adherence of patients increases. Patient Education The immersive modules of Virtual reality in patient education that are utilized in clinics in patient education aid patients in comprehending the processes of surgery, treatment, medical procedures, and post-surgical care. Decision-making and fear of treatment before treatment are enhanced with visual learning. Physical Therapy Enhancement The advanced systems designed to be used in VR for physical therapy apply real-time motion tracking to allow patients to rehearse the movements patterns and restore their strength. The therapists can vary the level of difficulty, track progress and create individual routines. Hospital Operations and Workflow VR is often incorporated in modern facilities to train staff in hospitals on emergency protocols, infection control as well as equipment usage and high risk activities. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Using VR in Healthcare The Benefits of virtual reality in medicine are numerous and can be measured, and those will become especially significant in the 2025s and further: Improved Accuracy and Precision Clinicians and surgeons are able to study anatomy, practice and simulate complications beforehand. This increases the levels of clinical confidence and minimizes the chances of errors. Controlled, Risk-Free Training There are no consequences of practicing on a particular case of trauma or a rare disease so that trainees can practice as many of them as possible. Medical educational VR is more effective in developing competence more quickly than conventional training. Enhanced Patient Comfort Virtual reality for anxiety treatment decreases the levels of anxiety among patients undergoing painful procedures. It also assists the pediatric patients as well as geriatric patients in keeping calm during the MRI scans, injections and treatments which are time-consuming. Personalized Recovery VR is used to provide customized exercises and therapeutic spaces in rehabilitation and mental health and make the treatment more interactive and successful. Higher Efficiency and Lower Long-Term Cost VR decreases surgical errors, shortens recovery time, accelerates training, and improves patient satisfaction, which results in reduced operational costs in the long term despite high initial set-up costs. Challenges and Limitations Along with its benefits, various issues affect the implementation of VR: High Initial Cost The investment in VR systems, haptic devices, sensors, and simulation that are medical-grade and high quality is very high. It demands significant resources to be invested, particularly in large hospitals. Technical Complexity Some platforms are delicate to calibrate and maintain. Healthcare workers do not necessarily feel comfortable using new technologies at once. Weak Clinical validation Although VR has potential, numerous applications are yet to undergo extensive clinical trials to be approved and evidenced. Motion sickness and Discomfort A very high percentage of the users might develop dizziness, fatigue or nausea in the immersive sessions. Data Privacy Concerns Medical VR is a sensitive type of data covering patient information, which needs a high level of cybersecurity and meets the requirements of HIPAA/GDPR.
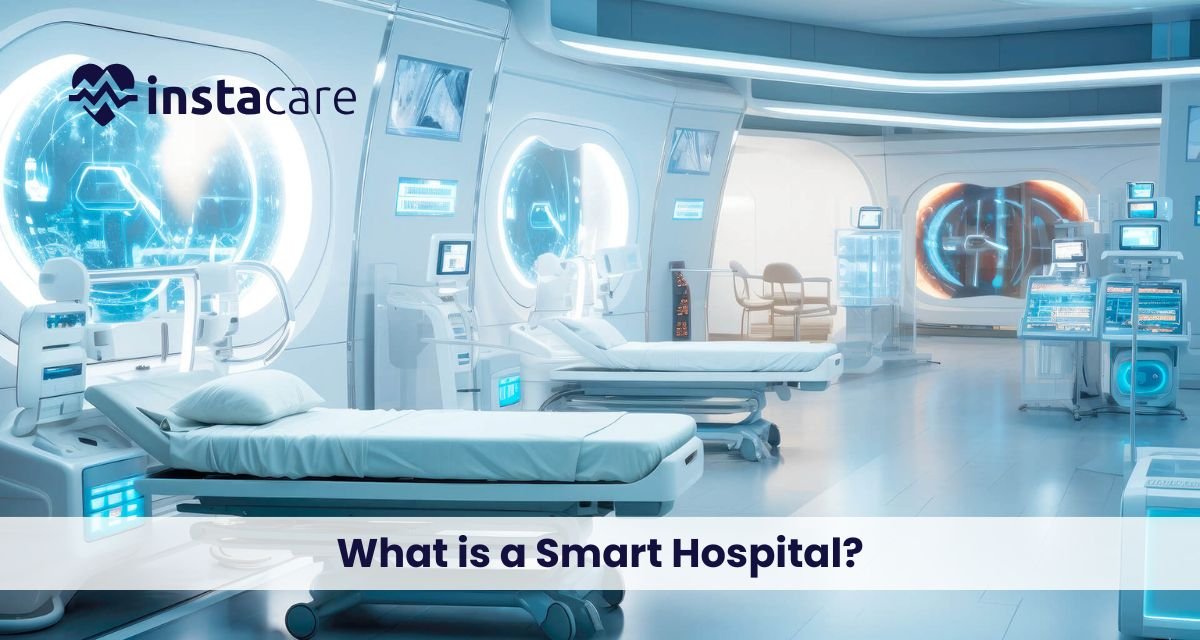
Smart Hospitals: The Future of Healthcare Driven by Technology The healthcare systems of the world are experiencing a significant change and the development of smart hospitals is one of the most radical changes. The merging of digital solutions, automation, artificial intelligence, and high-end connectivity is transforming the delivery of medical services. Hospitals today are ceasing to simply utilize the old mechanisms of operations but are integrating intelligent hospital solutions in order to maximize accuracy, improve patient experience and lessen the workload. What is a Smart Hospital? A smart hospital is a medical center that targets the use of sophisticated digital systems, automated procedures, artificial intelligence, and interconnected equipment to streamline the patient care process, promote medical processes, and overall efficiency. The vision of these hospitals is to become a complete digital hospitals in which technology will assist in all the steps of the patient journey, admission, treatment, and discharge. AI in hospitals, which are going to be smart and enable quicker diagnostics, auto-documentation, customized treatment, and predictive analytics. They also rely on interconnected devices and sensors that run on IoT in healthcare, which forms real-time data streams that enhance the decision-making of healthcare personnel. Core Components of a Smart Hospital ● Advanced Connectivity and IoT Devices Smart hospitals rely heavily on connectedness with the help of sensors, medical equipment, and automation software. Connected healthcare systems are based on these interconnected systems that make it possible to monitor patients in real-time, track their location, issue automatic notifications, and share medical information. ● Hospital Automation and Robotics To enhance the accuracy and decrease the human workload, automation is necessary. Robots are employed in the transportation of medication, room disinfection, or even surgeries. These systems are included in hospital automation systems that facilitate the flows of operations and decongest the staff to attend to patients. ● Digital Infrastructure and Data Systems Smart hospitals are based on the robust digital framework that is able to store, process, and analyze enormous volumes of medical information. The high-tech platforms can contribute to the healthcare digital transformation, as they allow centralizing electronic records, diagnostics, imaging, and workflow management into a single system. ● Integrated Smart Solutions The interconnected solutions used in smart hospitals include AI-based diagnostic solutions, automated pharmacies and telemedicine portals, and virtual reality therapy. These systems are classified as smart hospital solutions, which can assist physicians and personnel to provide more precise medical services at a higher speed. ● Enhanced Monitoring and Wearables Smart hospitals include real-time monitoring of patients. Devices and sensors will deliver constant information that facilitates early complications identification. This is referred to as smart patient monitoring and this is relevant in minimizing hospital readmissions and avoiding medical emergencies. ● Strong Technological Foundation Smart hospitals require a sound digital base called smart healthcare infrastructure to provide continuous services, and it consists of networks, cybersecurity, cloud, and digital storage. ● Automated Hospital Management Not only digital appointments, but also automated billing, modern hospitals are dependent on the automation of hospital management to minimize the number of manual errors and increase administrative efficiency. These systems facilitate the internal operations and the internal departmental orderly operations. ● Virtual Healthcare and Telemedicine One of the greatest strengths of the modern hospitals is their capability to provide care past physical walls. They promote virtual healthcare systems that enhance accessibility and convenience to the patients across the globe through virtual consultations, remote diagnostics, and follow-ups. ● Innovations in Health Technology The emergence of health tech innovations (AI diagnostics, robotics and digital wearables) will ensure the smart hospital of tomorrow will be more developed and patient-centred. ● Paperless Operations Innovative hospitals are determined to get rid of the old paper trails and move entirely to the electronic system. This idea is called paperless hospitals and contributes to the minimization of administrative delays, enhancement of the quality of data, and environmental sustainability. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Benefits of Smart Hospitals ● Improved Patient Care Smart hospitals guarantee more precise diagnoses, quicker treatment and customized care plans. It is also possible to provide doctors with a rapid response to the needs of patients with the help of continuous monitoring and data-driven insights. ● Reduced Human Error Having automated processes that cover the routine operations, the hospitals could minimize the risks of human errors in the documentation process, medication, or diagnostics. ● Enhanced Efficiency Workflow enhancement across departments is enhanced through automation. The processes of admission, discharge, medical imaging, lab reporting and the process of pharmacy become quicker and more structured. ● Cost Savings Smart hospitals minimize unnecessary tests, decrease hospitalization, and enhance resource utilization, which lead to financial savings in the long term both to patients and hospitals. ● Better Patient Experience Patients get to get quicker services, more convenient appointments, and more individualized care. Smart environments make the environment comfortable, transparent, and well communicated. Challenges and Considerations of Smart Hospitals ● High Initial Investment The development of a smart hospital will consume a lot of financial resources in digital products, cloud computing, hardware, software, and training solutions. ● Cybersecurity Risks Hospitals are at risk due to cyberattacks with increased dependence on digital systems. Good security systems are required to safeguard patient information. ● Staff Training There is a need to embrace new smart hospital technologies by doctors, nurses, and administrators. Training requires time and could cause a disruption in the normal work process in the first place. ● Integration Issues Various software platforms are used in healthcare systems. The process of seamless integration of devices, applications and departments can be complicated. The Future of Smart Hospitals Hospitals will become fully automated, their diagnostics will be supported by artificial intelligence, and remote
Telehealth Training 101: A Beginner’s Guide for Medical Students The growth of online healthcare has turned telehealth into a key piece of today’s medicine. Because of it, doctors can treat patients from a distance through video chats or smartphone apps. As a result, medical students must now learn telehealth training for medical students, which is central to their training in digital health. As telemedicine grows globally, learners require organized instruction to develop basic telehealth abilities, such as online consultations, using digital tools, while managing clinical processes efficiently through guided practice. What is Telehealth Training 101? Telehealth Training 101 is never a single standardized course. Still, it is often used as the generic name under which numerous organizations (including the California Telehealth Resource Center (CTRC) and the Northwest Regional Telehealth Resource Center (NRTRC)) provide introductory training resources that outline the basics and best practices of providing medical care remotely through the use of technology. These orientation programs are generally supposed to prepare health practitioners with the background information they need to utilize and apply telehealth in their practice properly. Understanding telemedicine workflow Getting used to doing medical checks online Familiarity with basic telehealth tools Building abilities in online health talks Training modules usually feature web-based skill practice, scenario exercises, or live instructor feedback. Such courses help learners handle actual situations without compromising care standards or conduct. Key objectives of the introduction to telemedicine for students include: Improving how doctors talk to patients online Guaranteeing precise information gathering from a distance Understanding rules plus morals in online medical talks Finding out how telemedicine systems work, also exploring useful software options Various Telehealth Technologies Telehealth technology basics use various digital tools along with online systems. To deliver proper care, students need to adapt to such technology Video Conferencing Tools – Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and dedicated telemedicine tools and platforms Electronic Health Records (EHRs) – Systems for storing and accessing patient data remotely Remote Monitoring Devices – Wearable devices, home diagnostic kits, and patient portals Mobile Health Apps – For appointment scheduling, messaging, and patient engagement AI & Decision Support Systems – Assist in diagnosis, triage, and patient education Familiarity with these tools forms a core element of telemedicine learning, also vital for today’s healthcare delivery. Key Skills for Telehealth Consultations Future doctors need certain abilities to do well in online appointments: different tools help them connect clearly with patients using tech platforms designed for remote care Telehealth communication skills mean explaining things clearly. Also, paying attention when others speak matters a lot. At the same time, understanding how people feel helps build trust Clinical Reasoning Remotely – Interpreting patient symptoms without physical examination Skilled in managing video meetings, programs, or troubleshooting systems without hesitation Documentation Skills – Accurate recording in EHRs during virtual visits Managing time well, handling visits smoothly while covering every health question Learning these abilities allows learners to manage online clinical skills training well, also boosting care recipient approval. Telehealth Etiquette and Best Practices Being professional matters a lot when doing telehealth. Students should follow telehealth etiquette and professionalism rules for proper behavior during virtual care sessions. This includes acting appropriately on camera while representing themselves as future healthcare providers Dress suitably; keep your backdrop neat during video meetings Keep patient details private while using secure methods in online meetings Express ideas plainly; skip complex terms Verify who the patient is before beginning the session Adhere to the organized telemedicine workflow training phases Reply quickly to questions or notes Such methods support reliability while maintaining secure, fair, plus functional distant treatment. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Challenges and Limitations Although telehealth provides several advantages, it brings certain difficulties Limited Physical Examination – Some conditions require an in-person assessment Connectivity Issues – Poor internet can affect consultation quality Patient Technology Literacy – Not all patients are comfortable with digital tools Data Security Concerns – Maintaining confidentiality is crucial Regulatory Barriers – Different countries have varying telemedicine laws Knowing these limits matters so learners can deliver proper care in distant areas, which means being aware, prepared, yet cautious at each step. While telehealth skills for beginners are key, judgment plays a bigger role when help isn’t nearby. Telehealth in Medical Education Telehealth is becoming more common in medical training. While some schools add it through digital health education for medical students, others include live virtual sessions; both methods teach students how to conduct virtual clinical exams. Curriculum updates now reflect this shift, preparing future doctors for digital care settings Getting started with remote healthcare for learners: Telehealth learning modules Interactive online medical assessments Simulated teleconsultations Online case discussions Digital health ethics and compliance These units let learners apply telemedicine best practices for students effectively, preparing them for real-world placements as well as evolving online health settings. Future of Telehealth Telehealth could change how care is given. Coming shifts involve: AI-assisted Consultations – Helping in triage and diagnostics Wearable Devices – Continuous monitoring of vital signs and chronic conditions Global Telemedicine Access – Connecting patients in remote areas with specialists Enhanced Training Platforms – Virtual reality simulations for clinical skills Integration with Traditional Care – Combining in-person and remote care seamlessly Future doctors who learn telemedicine can adapt easily to new tech, also deliver strong care online. Conclusion Telehealth education has become essential for future healthcare workers. Gaining basic telehealth competencies gives learners technical know-how, digital confidence, plus effective interaction techniques suited to today’s care environments. Through virtual patient consultations training, learners gain confidence in digital health tools. Because they train with simulated patients, they adapt more easily to real-world demands. While working through virtual cases, their decision-making improves under pressure. As workflows are practiced repeatedly, efficiency grows naturally. Since technology changes fast, this preparation matters more than ever. When guidance is clear, students perform better across settings. FAQs 1. What is telehealth training for medical students? Telehealth training for med students means learning to run online visits through organized courses. These classes show learners how to work with tech platforms while
Patient Consumerism: Empowering Patients in the Age of Value-Based Care Healthcare is undergoing a big change. Patients are no longer content to sit silently while physicians tell them what to do. Patients now wish to have a say in what happens to them. They want to know the costs, comparison shop, and make selections for themselves. This is called patient empowerment – making healthcare decisions as if shopping for anything else. All the while, value-based healthcare is growing fast. That is a model in which physicians and hospitals are paid for how well they keep patients healthy instead of just for how many procedures they do. The healthcare digital transformation enabled it by enabling patients to look up treatments on the internet and talk to doctors in new ways. What is Patient Consumerism? Patient consumerism is when patients act like smart consumers when deciding on their healthcare. This consumer-driven healthcare type of thinking in healthcare involves: Purchasing symptoms and treatment online Hospital and doctor price comparison Reading patient comments Asking many questions about treatment plans Healthcare consumerism trends of today show that patients want clear prices, easy access to their medical records, and personalized healthcare that suits how they live. This puts the patient in the driving seat of their own healthcare. The Rise of Value-Based Healthcare Value-based healthcare is a different way of compensating for healthcare. Instead of being compensated for every procedure or test, physicians get compensated for taking patients well and happy. This strategy is focused on: Good care instead of excessive care Patient satisfaction metrics that show concrete results Better health at reduced expense Preventing illness before it happens This is excellent with patient consumerism as both want the best patient outcomes. New rules on healthcare price transparency mandate that hospitals display their prices for everyone to see. This allows patients to make wise choices and puts pressure on hospitals to compete with each other. How Patient Consumerism Empowers Patients? Patient empowerment takes place in several important ways: Better Access to Information Contemporary technology offers patients immense access to medical information. Healthcare cost comparison tools show prices at different sites, and patient feedback helps others select physicians based on other people’s experiences. Decision-Making Patient decision-making gets simpler for patients when people have simple, understandable information. Second opinions get simpler through telehealth and patient consumerism, and patients receive information about costs prior to receiving the treatment. More Control Over Care Health care today delivers patient-centered care that puts patients’ needs first. Physicians use patient engagement strategies that engage patients and enable patients to communicate with their doctors in whatever way feels most comfortable for them – phone, text, or online. Benefits of Patient Consumerism in Healthcare Patient consumerism is a win-win for all: For Patients Patients are given a much better patient experience in healthcare with more convenience and individualized attention. They save money through smart shopping and gain better health outcomes through engagement in their care. This makes patients more satisfied with their healthcare choices. For Healthcare Providers Physicians and hospitals get better patient satisfaction metrics and better ratings from satisfied patients. Patient loyalty in healthcare increases because patients feel heard and valued. Work is easier due to technology, and more patients are attracted. For the Healthcare System The healthcare revolution has less paperwork and shorter waiting times for everyone. Telehealth and patient consumerism allow rural people to experience quality care. When hospitals compete with each other, quality improves and prices stay affordable. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Challenges and Issues of Consumerism in Healthcare While patient consumerism is good, it has some challenges: Information Issues There’s too much health information on the internet, and it becomes confusing to patients. Not all health websites are truthful or provide accurate information. Patients do not understand what medical jargon means. Social media can circulate false health falsehoods that hurt people. Fairness Issues Not everyone has the money to shop for the finest care. Individuals who did not finish school might have difficulty making patient decisions. Non-English speakers can’t make decisions. Individuals who live in small towns don’t have many doctors to select from. Quality Problems Patients opt for cheaper care that is actually not so good for them. Individuals wait to receive treatment because they would prefer to save some money. Healthcare decisions are hard and occasionally you have to have a doctor help you out. Emergency treatment does not give you time to shop around. Strategies to Strengthen Patient Empowerment Some things healthcare organizations can do will make patient empowerment work better: Technology Solutions Organizations need to create uncomplicated healthcare cost comparison tools available to everyone. Developing phone apps for appointment scheduling is good for patients. Giving patients online access to their medical records with safety empowers them. Adding telehealth and patient consumerism options makes care to get easier. Education Programs Healthcare systems are required to teach patients how to understand medical information in their own language. Offering personalized healthcare teaching based on what is wrong with each individual allows them to make more knowledgeable choices about getting better. Improved Services Health care should always be patient-centered care in all encounters with patients. Organizations should have patient engagement strategies that work for patients regardless of their ages and backgrounds. They should measure patient satisfaction metrics and respond to it when patients complain. Better Communication Doctors must explain treatment in plain terms that patients can comprehend. Giving patients cost estimates before procedures enables them to budget their finances. Balancing consumer-driven healthcare decision-making and safeguarding patients from damage necessitates intelligent training and equilibrium. Conclusion Patient consumerism is bettering care for everyone. Patients get healthier and happier with their care when they have better information, choices, and decision-making power with respect to their treatment. Value-based healthcare makes it possible for this to happen by reimbursing physicians for good results rather than just for doing lots of procedures. The healthcare digital transformation makes it possible for patients to get information and talk to doctors in completely new, more convenient, and
Telehealth Therapy vs In-Person Therapy: Benefits, Effectiveness, and Key Differences Mental health therapy has completely transformed over the last few decades. Nowadays, people can either get to have their own private therapists or chat with them via telehealth therapy. Both are in good practice, but are made up of some plus and minus points each. This handbook will get you into difference-oriented mode in an extremely easy manner so that you can opt for what is best for you. What is Telehealth Therapy? Telehealth mental health counseling is when you conduct your counseling session through video call, phone call, or messaging. You can talk to your counselor wherever you have internet, at home, at the office, or even while on the go. It is also referred to as online counseling, teletherapy, or virtual counseling. Most teletherapy is conducted via video calls on an application such as Zoom or a specific therapy software. Some long-term clients prefer it over speaking on the phone, but others like message therapy when they exchange messages with their therapist. What is In-Person Therapy? Face-to-face therapy is the old-fashioned method of obtaining mental health counseling. You simply sit in the same room as your counselor in his or her office. The sit-down face-to-face interview has been the norm for receiving therapy for many decades. With in-person sessions, you and your therapist can make use of nonverbal communication, share a gaze, and share a room. Certain therapists utilize specialized equipment or drills that function more effectively in person. Benefits of Telehealth Therapy Convenience and Accessibility The biggest benefit of telehealth therapy is how accessible it is. You will not have to drive, park, and wait in waiting rooms. This is wonderful for people who don’t have a therapist where they are or who live busy lives. The accessibility of telehealth therapy makes it particularly valuable for those in remote areas. The convenience of telehealth therapy extends beyond just location, offering flexible scheduling and eliminating travel time. Understanding the benefits of telehealth therapy helps many people overcome barriers to seeking mental health support. Telehealth counseling costs less than session-by-session counseling. You also don’t spend money on gas and parking, or on missed workdays. Even some insurance organizations pay back telehealth counseling more than regular counseling. The cost of telehealth therapy vs in-person often favors the virtual option for many clients. Comfort of Your Own Space Most people wish to be more relaxed when handling personal matters in their own sphere. Having the right to relax where you are does away with tension and relaxes you so that you can lower your guard and no longer worry so much about therapy. Better Privacy With telehealth therapy, you never have to be concerned with catching a glimpse of someone familiar sitting in a therapist’s waiting room. You can receive your therapy entirely in private. Less Inconvenient Scheduling A lot of web therapy is also less inconvenient with scheduling. Some therapists can work with you in the evenings or weekends when regular offices aren’t open. If you are relocating to a new town or take frequent flights on an airplane, you can still access the same therapist with telehealth. Then, you remain on track without having to begin anew with another one. Benefits of In-Person Therapy Greater Personal Connection Face-to-face sessions are in a better position to get you and your therapist closer. Eye contact, sitting at the same position as the other individual, and sitting in the same room as the individual can bring the closeness closer and more frequent. The in person therapy advantages include this enhanced personal connection. Better Communication In-person therapy allows therapists to observe your body language and notice small things that get lost behind the camera. This allows them to know you better and react to you better. Less Interruptions A therapist’s office is where a therapist can create a quiet, secluded area. In your home, you can be interrupted by the people who reside with you, pets, or background noise. Specialized Treatment Options Some modalities are optimally done face-to-face. Those who are dependent upon art, music, or body movement, and certain trauma or severe mental illness-specific interventions. Total Confidentiality Online counseling is done inside a soundproof room professional enough that no one can overhear your discussion or unintentionally view your session. Improved Crisis Care If you are in crisis, your therapist is able to provide you with a quicker solution and send you on to local services once you see them in person. Effectiveness: Telehealth vs In-Person Research indicates that telehealth therapy is as effective as going to see a therapist in person for the majority of psychiatric conditions. The effectiveness of telehealth therapy has been demonstrated through several studies that have reported both treatments decrease symptoms of depression, anxiety, and other prevalent mental illnesses. The recipients of telehealth therapy are equally satisfied and show the same amount of progress in their mental health as individuals who see therapists in person. Patient satisfaction telehealth vs in-person surveys show comparable results. Most importantly, make sure you have a good therapist that you enjoy, whether one whom you get to meet in person or one you see online. When asking is telehealth therapy effective, research consistently shows positive outcomes. But then certain conditions would be better suited to a face-to-face setting. They are severe mental illnesses, eating disorders, and in the case of an individual who may hurt himself or other individuals. Book Your Free Marketing Consultation Key Differences Between Telehealth and In-Person Therapy Technology Needs Telehealth therapy requires the use of a sufficient internet connection, a computer or cell phone with a camera function, and a quiet, private area. Technical issues occasionally interrupt sessions. Therapist Availability You can connect with more therapists via telehealth since location is no longer a factor. Therapists must still be licensed where they live to provide telehealth, however. The online therapy vs in-person therapy options differ significantly in terms of provider access. Session Environment Face-to-face therapy occurs within a
- 1
- 2